GERD Chest Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Understand GERD chest pain, its symptoms, and effective management strategies. Learn how to alleviate this common digestive health issue with practical tips and treatments.
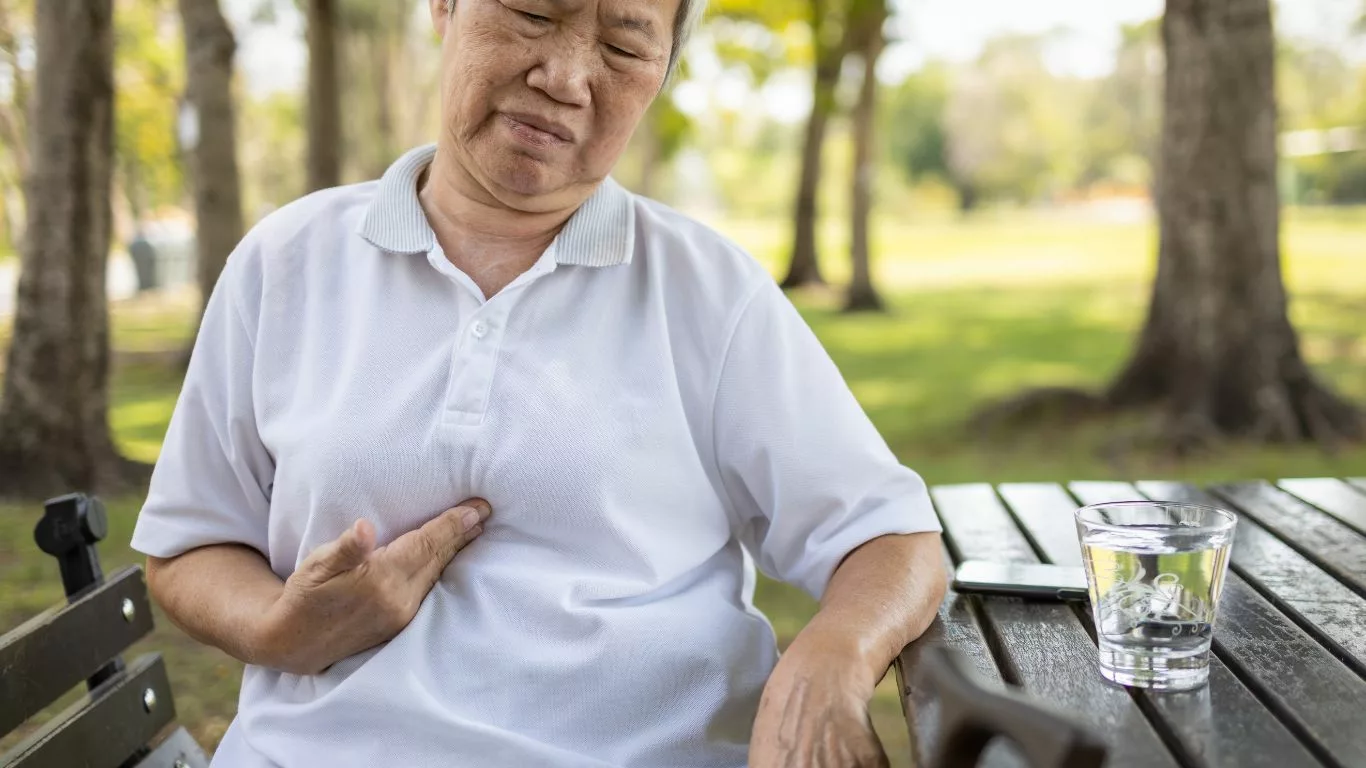
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic digestive condition that affects millions worldwide. Among its most concerning symptoms is chest pain, often mistaken for heart-related issues. GERD chest pain can significantly impact quality of life, making it crucial to understand its causes, symptoms, and management strategies. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the link between GERD and chest pain, its underlying mechanisms, and practical ways to manage it effectively.
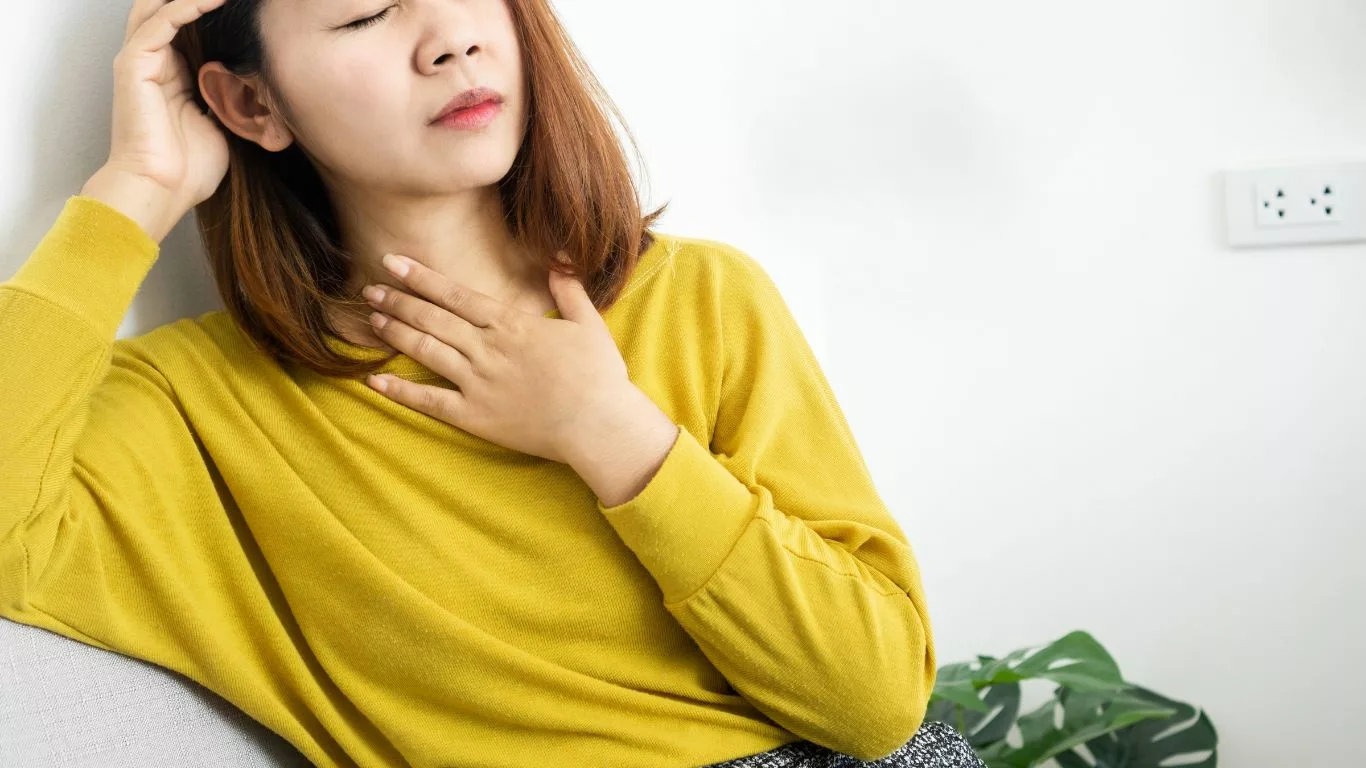

What is GERD Chest Pain?
GERD chest pain occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and discomfort. This pain is often described as a burning sensation in the chest (heartburn) but can sometimes mimic the sharp or pressure-like pain associated with heart conditions. Understanding the nature of GERD chest pain is essential for distinguishing it from other potential causes of chest discomfort.
Causes of GERD Chest Pain
The primary cause of GERD chest pain is the malfunction of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a muscle that acts as a valve between the esophagus and stomach. When the LES weakens or relaxes inappropriately, stomach acid can escape into the esophagus, leading to pain and irritation. Factors contributing to GERD chest pain include:
Dietary Triggers
- Spicy foods
- Acidic fruits and vegetables
- Fatty or fried foods
- Caffeinated or carbonated beverages
- Alcohol
Lifestyle Factors
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Overeating
- Eating close to bedtime
- Stress
Medical Conditions
- Hiatal hernia
- Delayed stomach emptying
- Pregnancy (due to hormonal changes and pressure on the stomach)

Symptoms of GERD Chest Pain
While chest pain is a hallmark symptom, GERD often presents with additional signs that help differentiate it from cardiac-related pain. Common symptoms include:
- A burning sensation in the chest, especially after eating or lying down
- Regurgitation of food or sour liquid
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Chronic cough or throat irritation
- Hoarseness or a sensation of a lump in the throat
- Worsening pain when bending over or lying flat
Diagnosing GERD Chest Pain
If you experience persistent chest pain, it’s crucial to seek medical evaluation to rule out cardiac causes. Diagnosis of GERD typically involves:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Discussing symptoms and risk factors with a healthcare provider.
- Endoscopy: Visual inspection of the esophagus for signs of inflammation or damage.
- pH Monitoring: Measuring acid levels in the esophagus over 24 hours.
- Manometry: Assessing the functionality of the esophageal muscles.
Managing GERD Chest Pain
Effective management of GERD chest pain requires a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, and medical treatments. Here are key strategies:
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Avoid smoking and alcohol consumption
- Elevate the head of your bed to reduce nighttime reflux
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals
- Avoid lying down immediately after eating
Dietary Changes
- Eliminate trigger foods
- Incorporate high-fiber foods to aid digestion
- Stay hydrated and opt for non-acidic beverages
Medications
Over-the-counter and prescription medications can provide relief by reducing stomach acid production or neutralizing acid. Common options include:
- Antacids
- H2-receptor antagonists
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
- Prokinetics

When to Seek Medical Attention
Although GERD chest pain is often manageable, certain symptoms require immediate medical attention, as they may indicate a heart attack or other serious conditions:
- Severe or sudden chest pain
- Radiating pain to the arm, neck, or jaw
- Shortness of breath
- Cold sweats or nausea
Conclusion
GERD chest pain, while uncomfortable, is a manageable condition with the right approach. By identifying triggers, adopting healthy habits, and utilizing appropriate treatments, you can significantly reduce symptoms and improve your quality of life. If symptoms persist or worsen, consult a healthcare professional for personalized care.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare provider for concerns about GERD or chest pain.

Camellia Wulansari is a dedicated health writer specializing in digestive disorders, contributing valuable insights and information to the health and wellness community. With a passion for promoting well-being through knowledge, Camellia serves as a reliable source of expert content on healthusias.com.