Magnesium Deficiency May Be Worsening Your Eye Floaters
For years, I thought the random squiggly lines and dots drifting across my vision were just a part of getting older—or maybe the result of staring at my screen too long. Turns out, they had a name: eye floaters. And when I started digging deeper, I was floored by the number of things that could be behind them. One unexpected culprit that really caught my attention? Magnesium deficiency. Yep, that seemingly simple mineral we often overlook could be messing with our vision more than we think.
How Magnesium Impacts Eye Health
Magnesium is often praised for helping with muscle relaxation, blood sugar regulation, and sleep quality. But few people realize it also plays a critical role in maintaining healthy eyes. It supports retinal function, regulates blood flow to ocular tissues, and aids in managing oxidative stress in the eye.
When magnesium levels are low, a cascade of issues can occur:
- Reduced retinal blood flow
- Increased oxidative stress
- Disrupted nerve signals
- Inflammation in ocular tissues
All of which can contribute to floaters—those translucent shapes that seem to float across your vision.
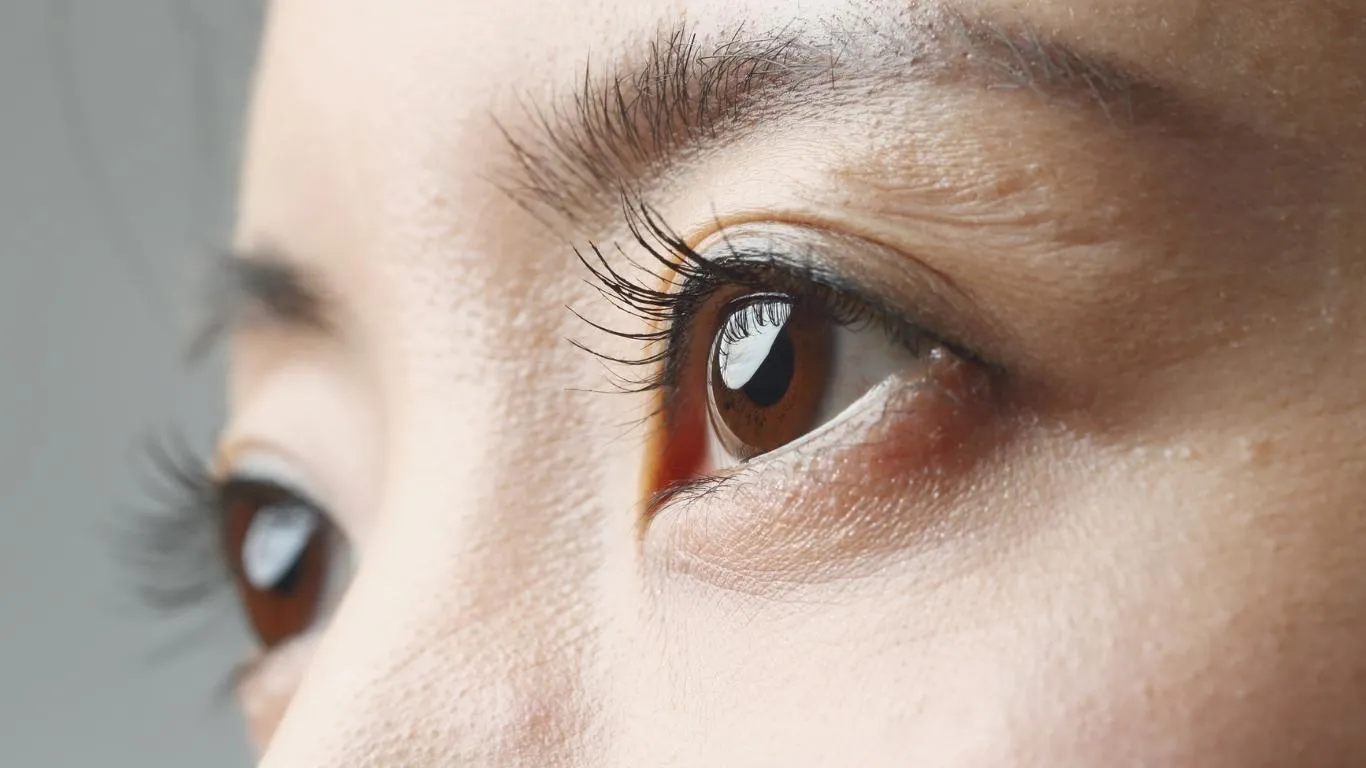
What Are Eye Floaters, Really?

Eye floaters are tiny clumps of collagen that float inside the vitreous humor of your eye. They cast shadows on the retina and show up as dots, cobwebs, or squiggles. Most are harmless, but they can be annoying—especially when they suddenly increase in number.
Magnesium’s connection to floaters might not be obvious at first, but when you consider its role in the body, it starts making sense. Low levels of magnesium can affect the eye’s ability to deal with oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which are potential triggers for vitreous degeneration.
Could Your Floaters Be Telling You Something Bigger?

If your floaters appeared suddenly, seem to be increasing rapidly, or come with flashes of light, it’s essential to seek medical help. In some cases, floaters are an early sign of posterior vitreous detachment—a common condition that can lead to serious complications if ignored.
Other conditions that may link back to magnesium deficiency and floaters include:
- Diabetes – low magnesium is common in diabetics, increasing floaters risk
- Hypertension – poor magnesium intake affects blood pressure and eye vessels
- Thyroid conditions – linked with hormonal imbalances and magnesium issues
For more insight into the broad causes of eye floaters, check out our guide on common causes.
How I Realized My Magnesium Levels Were Low

I never connected my constant leg cramps, fatigue, and floaters—until a friend suggested getting my magnesium levels tested. Turns out, I was well below the normal range. After adjusting my diet and adding a quality magnesium supplement, the frequency and intensity of my floaters began to improve. No, they didn’t vanish completely, but they were definitely less noticeable.
There are subtle signs of deficiency you might be missing:
- Frequent muscle twitches or cramps
- Trouble sleeping or feeling “wired but tired”
- Headaches or migraines
- Low stress tolerance
- Unexplained eye floaters or vision disturbances
Best Dietary Sources of Magnesium to Support Eye Health
You don’t always need supplements to correct a deficiency. A magnesium-rich diet can go a long way:
- Leafy greens (spinach, Swiss chard)
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, pumpkin seeds)
- Whole grains (brown rice, oats)
- Dark chocolate (yes, a little indulgence with benefits!)
- Avocados and bananas
More than once, I swapped out my usual breakfast cereal for overnight oats with pumpkin seeds, and not only did I feel more energized, but I noticed fewer floaters by the third week. Coincidence? Possibly. But it worked for me.
To understand more about floater treatments—from lifestyle tweaks to surgical options—this comprehensive treatment guide is worth a read. And for a deeper dive into what floaters are and how they form, don’t miss our main pillar article: Eye Floaters: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment.
It’s amazing how something as small as a mineral deficiency can affect such a vital part of our lives—our vision. And if you’re like me and never gave magnesium a second thought, maybe it’s time you did.
How Magnesium Deficiency Can Worsen Floaters Over Time
When I ignored my magnesium intake, I didn’t realize I was setting myself up for more than just muscle cramps. Over time, my floaters went from occasional annoyances to a daily frustration. This isn’t just anecdotal—there’s growing recognition that long-term magnesium deficiency may accelerate vitreous degeneration, making floaters more prominent and persistent.
Here’s how it can compound:
- Chronic oxidative stress – A lack of magnesium weakens the eye’s defenses
- Calcium imbalance – Too little magnesium means too much unregulated calcium, which can lead to calcification in ocular tissues
- Weaker collagen repair – Magnesium supports collagen maintenance, vital for healthy vitreous structure
Left unchecked, this may even increase your risk for more serious issues like retinal tears or vitreous hemorrhage.
Who’s Most at Risk for Magnesium-Linked Floaters?
Not everyone with low magnesium will experience floaters—but if you’re in one of these groups, you might be more vulnerable:
- People over 40 – Magnesium absorption decreases with age. So does vitreous hydration. Bad combo.
- Heavy coffee or alcohol drinkers – Both deplete magnesium levels quickly
- Those with chronic stress – Stress increases magnesium loss through urine
- People with digestive disorders – IBS, Crohn’s, or GERD can interfere with absorption
Oh, and if you’re taking proton pump inhibitors or diuretics regularly? You may be at even greater risk for nutrient-related floater issues.
What Kind of Magnesium Works Best?

Once I figured out my magnesium levels were in the red, I went supplement shopping—and immediately got overwhelmed. Magnesium oxide, citrate, glycinate, malate… what even are all these?
Turns out, not all forms are equal when it comes to absorption and tolerability. Based on both research and personal trial-and-error, here’s what I found helpful:
- Magnesium Glycinate – Great for sleep and doesn’t upset the stomach
- Magnesium Malate – Helpful if fatigue and floaters both bug you
- Magnesium Citrate – More bioavailable but can have a laxative effect
For me, a combo of glycinate at night and malate in the morning kept things steady. And yep, over a few weeks, I noticed a drop in floater activity—less swarming black dots when I looked at a bright sky.
Can You Reverse Floaters by Fixing Magnesium Deficiency?

Let’s be real: once you’ve got floaters, there’s no magical pill that zaps them away. But based on my experience—and stories from others—correcting a magnesium deficiency can reduce their intensity, frequency, and impact.
This is especially true if the floaters are due to systemic stress, poor nutrition, or blood flow issues—all of which magnesium can help regulate. It’s also a low-risk option to try before jumping to invasive treatments.
Of course, it’s not a substitute for a medical diagnosis. If floaters are affecting your vision significantly, or if they appeared suddenly, don’t self-diagnose. You’ll want to rule out conditions like eye infections or autoimmune triggers.
Smart Habits to Pair With Magnesium for Better Eye Health
Magnesium isn’t a magic bullet—but it can be powerful when combined with smart habits. Here’s what I’ve found works best to keep floaters from becoming overwhelming:
- Stay hydrated – Dehydration worsens floaters dramatically
- Get regular eye exams – Especially if you’re over 40 or diabetic
- Reduce screen glare – Helps prevent unnecessary strain
- Wear UV-blocking sunglasses – Protects against long-term retinal damage
- Cut down on sugar and processed foods – Keeps inflammation in check
And don’t underestimate sleep. Inconsistent rest throws off magnesium balance, blood sugar regulation, and stress hormones—all of which affect floater severity. It’s one of the reasons I dug deeper into how sleep and floaters are more connected than I thought.
If you’re curious whether your floaters are part of a larger health picture, or just tired of seeing specs dance across your vision, consider checking in with a specialist. Sometimes the root cause is simple, like a magnesium shortfall. Other times, it’s a sign of something more serious—this guide covers what to watch for.
Floaters don’t have to take over your day. And sometimes, the first step to clarity is as simple as looking at what’s missing from your plate.

Camellia Wulansari is a dedicated Medical Assistant at a local clinic and a passionate health writer at Healthusias.com. With years of hands-on experience in patient care and a deep interest in preventive medicine, she bridges the gap between clinical knowledge and accessible health information. Camellia specializes in writing about digestive health, chronic conditions like GERD and hypertension, respiratory issues, and autoimmune diseases, aiming to empower readers with practical, easy-to-understand insights. When she’s not assisting patients or writing, you’ll find her enjoying quiet mornings with coffee and a medical journal in hand—or jamming to her favorite metal band, Lamb of God.