Rheumatoid Arthritis and Autoimmune Diseases: A Comprehensive Guide
Struggling to manage rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or any autoimmune disease? You’re not alone! In this guide, we dive deep into what these conditions are, how they affect your body, and how you can manage them effectively. Let’s break it all down.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is just one of the many autoimmune diseases that can significantly impact your quality of life. It’s a chronic condition that primarily affects the joints, causing pain, swelling, and even permanent damage over time. But RA doesn’t just stop at the joints—it’s a whole-body condition. That means understanding what’s going on behind the scenes can help you manage symptoms better and work with your healthcare team to find the right treatment.

If you or a loved one is dealing with RA or another autoimmune disease, understanding the ins and outs can be really helpful. In this guide, we’ll cover what autoimmune diseases like RA are, how they work, and what steps you can take to manage them.
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
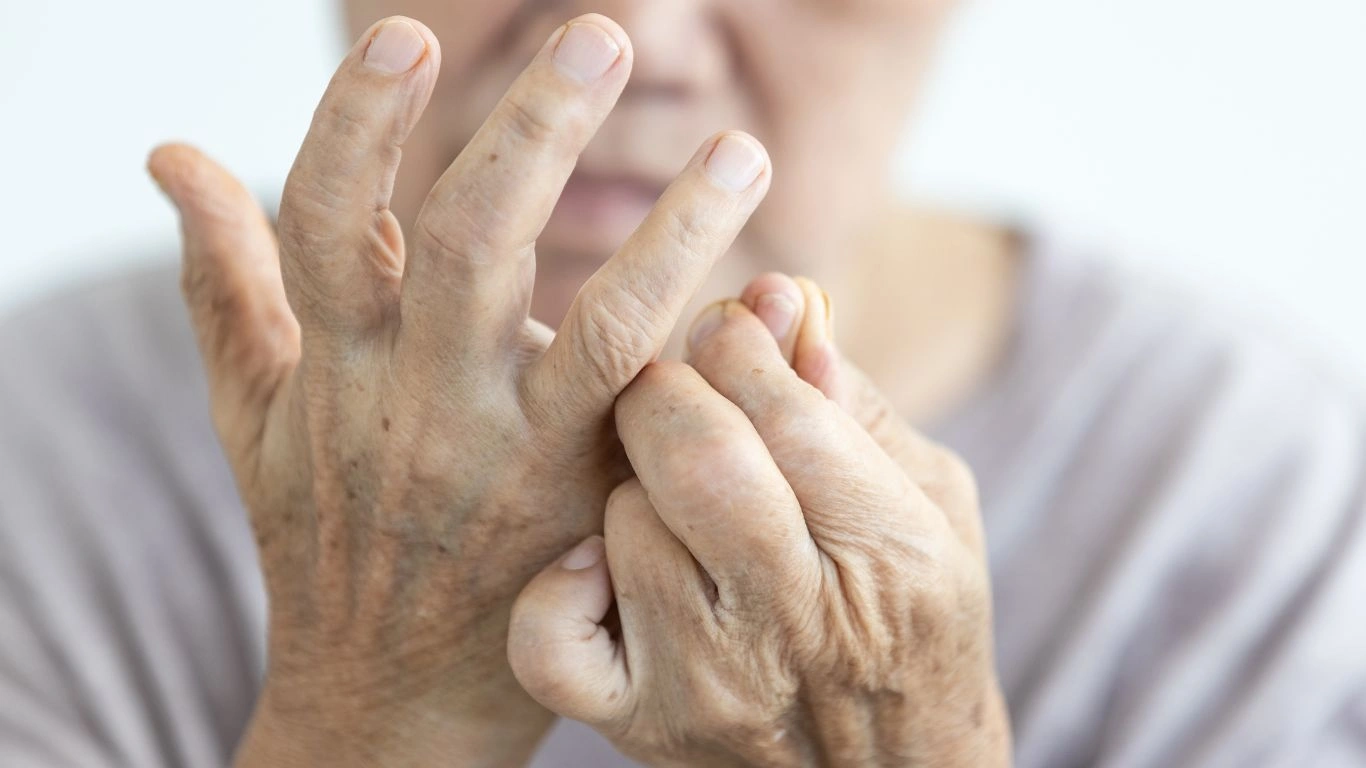
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease where your body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy tissue, particularly the joints. This leads to inflammation, which causes pain and swelling. Over time, this inflammation can damage joints, leading to deformities and loss of function.
Unlike osteoarthritis (which is caused by wear and tear on the joints), RA is driven by an immune response. It usually affects both sides of the body, meaning if one knee or wrist is affected, the other one likely is too. RA often hits in flare-ups, where the symptoms become worse, followed by periods of remission where symptoms improve.

Common Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The symptoms of RA vary from person to person, but some of the most common ones include:
- Joint Pain and Swelling: Especially in smaller joints like the wrists, knees, and fingers.
- Morning Stiffness: Feeling stiff and less mobile when you first wake up is common with RA.
- Fatigue: Chronic tiredness that doesn’t go away with sleep is a major symptom.
- Fever: Some people with RA experience low-grade fever.
- Loss of Appetite: Unexplained weight loss or a lack of appetite is common.
It’s important to note that RA can affect more than just your joints. Over time, it can impact other organs, including the lungs, heart, and eyes.
What Are Autoimmune Diseases?
An autoimmune disease happens when your immune system goes rogue and attacks your own body, mistaking healthy cells for harmful invaders. RA is just one example of these diseases, but there are many others, including lupus, multiple sclerosis, and type 1 diabetes.
In autoimmune diseases, the immune system isn’t working the way it should. Instead of fighting off bacteria, viruses, and other threats, it mistakenly targets the body’s tissues and organs. This can lead to inflammation, pain, and sometimes permanent damage.

Other Common Autoimmune Diseases
While RA is one of the most well-known autoimmune conditions, there are many others that affect different parts of the body. Some of the most common include:
- Lupus: This disease affects the skin, joints, kidneys, and other organs. It can cause fatigue, joint pain, and a characteristic butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and nose.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): MS attacks the nervous system, leading to symptoms like muscle weakness, difficulty walking, and coordination problems.
- Celiac Disease: This disease causes the body to react to gluten, leading to digestive problems and nutrient deficiencies.
- Type 1 Diabetes: The immune system attacks the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels.
How Do Autoimmune Diseases Affect the Body?
Autoimmune diseases often lead to chronic inflammation. This inflammation is what causes most of the symptoms, including pain, swelling, and stiffness. Over time, untreated inflammation can damage tissues and organs. For example, with RA, the inflammation in the joints can cause irreversible damage, including deformities and loss of joint function.
In some cases, autoimmune diseases can affect the entire body, as with lupus or MS. This makes it tricky to manage these conditions since they involve multiple organ systems, and the symptoms can be very diverse.
Appendices
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Can RA be cured? Unfortunately, there is no cure for RA. However, treatments can help control symptoms and prevent further damage to the joints.
- What’s the difference between RA and osteoarthritis? RA is an autoimmune disease that attacks healthy tissues, while osteoarthritis is caused by wear and tear on the joints.
- Can diet help with RA symptoms? While no specific diet cures RA, eating anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce symptoms and improve joint health.
- Are there natural remedies for RA? Some people find relief from RA symptoms with supplements like omega-3 fatty acids, but it’s important to consult with your doctor before trying new treatments.
- How can I prevent joint damage from RA? Early diagnosis and effective treatment are key to preventing long-term joint damage. Medications like DMARDs and biologics are often used to slow disease progression.
References
- American College of Rheumatology. (2024). “What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?” Read Article
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS). (2023). “Rheumatoid Arthritis.” Read Article
- Smith, J., & Anderson, L. (2022). “Understanding Autoimmune Diseases.” Journal of Rheumatology, 48(3), 256-270. Read Article
Disclaimer: The information in this article is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider before making any changes to your treatment plan or lifestyle.













