How Humidity Affects Asthma – Understanding the Connection
Struggling with asthma and wondering how humidity plays a role? We’re breaking down exactly how humidity can affect your breathing and what you can do about it!
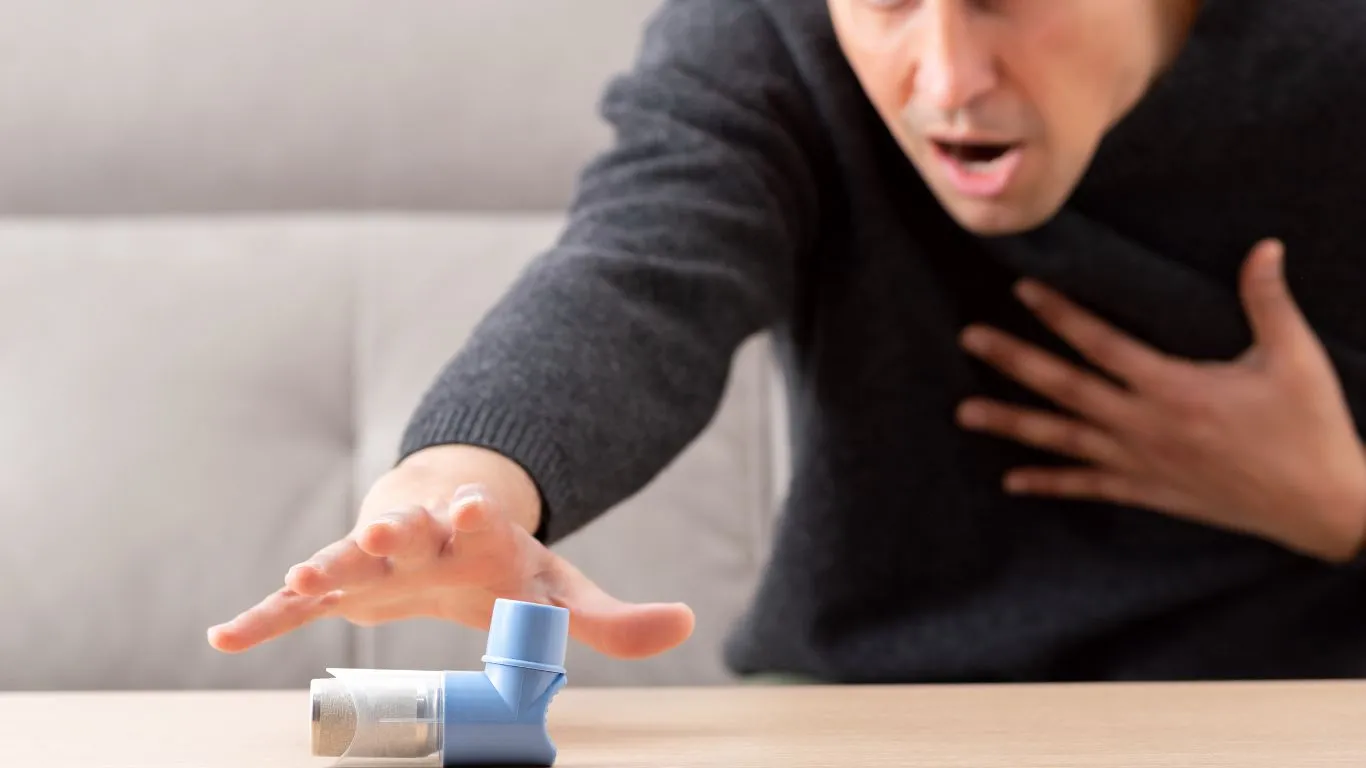
If you have asthma, you probably already know that certain weather conditions can make your symptoms worse. While cold air and strong winds are often discussed, there’s another sneaky factor that can trigger asthma flare-ups: humidity. Whether it’s too high or too low, the humidity in the air can impact your breathing and make managing asthma more challenging. In this guide, we’ll look at how humidity affects asthma, why it’s so important, and what you can do to stay on top of your symptoms.
What Is Humidity, and How Does It Affect the Air?
Before diving into how humidity specifically affects asthma, let’s first understand what humidity is. Humidity refers to the amount of water vapor in the air. The higher the humidity, the more moisture there is, making the air feel warmer and stickier. On the other hand, low humidity means the air is drier. Both extremes—too much moisture or too little—can have an impact on your respiratory system, especially if you have asthma.

How High Humidity Affects Asthma
When humidity is high, the air feels warmer and stickier. For people with asthma, high humidity can cause several problems.
1. Increased Airway Inflammation
High humidity can make the airways in the lungs more inflamed. The moisture in the air can make it harder to breathe because the air feels thicker, and your lungs have to work harder to get the oxygen they need. This can increase the likelihood of an asthma attack, especially if the humidity is combined with other triggers like allergens (dust mites, mold, etc.).
2. Mold and Dust Mites Thrive
Humidity provides a perfect environment for mold and dust mites to thrive. These are two major asthma triggers that can worsen symptoms. Mold grows in damp, humid environments—like bathrooms or basements—while dust mites flourish in places where moisture accumulates. When the humidity is high, these allergens are more likely to be present in the air, which could lead to increased asthma flare-ups.

3. Difficulty Breathing and Shortness of Breath
When the air is thick with moisture, it can feel harder to breathe, especially for those with asthma. The increased moisture content in the air can make the lungs work harder to process oxygen, causing shortness of breath, wheezing, and coughing—common asthma symptoms.
How Low Humidity Affects Asthma
While high humidity can cause a lot of discomfort, low humidity isn’t necessarily better for asthma either. Dry air can have a different set of challenges for those with asthma.
1. Dryness of Airways
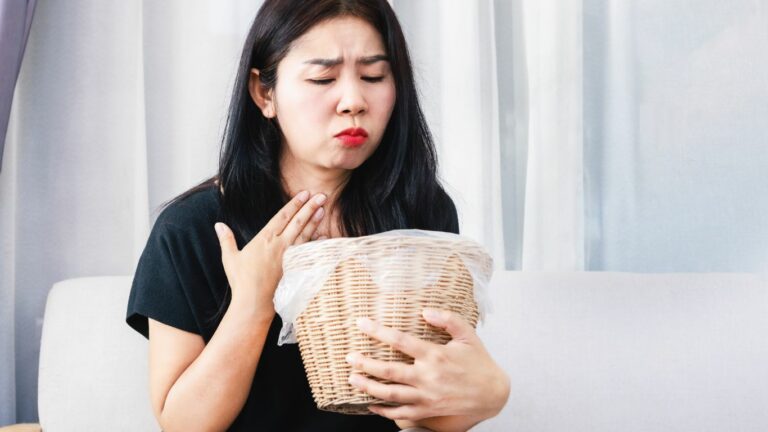
Low humidity can cause the airways to become dry and irritated. When the air lacks moisture, it can dry out the mucous membranes in your nose and throat, making it harder for your body to filter out allergens, viruses, and bacteria. This can lead to irritation in the lungs, coughing, and wheezing, all of which can trigger asthma symptoms.
2. Increased Risk of Respiratory Infections
Dry air can also increase the risk of respiratory infections. Since the mucous membranes in the airways dry out, it becomes easier for germs to enter the lungs and trigger asthma attacks. In cold, dry air, your body has to work harder to filter out these invaders, which can lead to more frequent asthma flare-ups during the winter months.

3. Higher Exposure to Irritants
Low humidity often coincides with winter months, when you might be using heating systems in your home. These systems can make the air even drier, increasing the risk of irritation in your respiratory system. Dust and other irritants can also become more common in dry environments, which can worsen asthma symptoms.
The Best Humidity Levels for Asthma
You might be wondering: what’s the ideal humidity level to avoid triggering asthma symptoms? Experts generally recommend keeping indoor humidity levels between 30% and 50%. This range helps prevent the growth of mold and dust mites while also keeping the airways from becoming too dry.
To manage asthma effectively, it’s important to monitor the humidity levels in your home, especially in areas where you spend a lot of time (like your bedroom or living room).
Practical Tips for Managing Asthma in Humid Weather
If you live in a humid area or are dealing with fluctuating humidity levels, here are a few practical tips to help you manage your asthma:
1. Use a Dehumidifier
In areas with high humidity, using a dehumidifier can help remove excess moisture from the air. This can reduce the growth of mold and dust mites, which are key asthma triggers. It also helps create a more comfortable breathing environment.
2. Keep Your Home Clean
Regular cleaning is essential to reducing allergens in your home. Dusting, vacuuming, and washing bed linens frequently can help remove dust mites and other allergens that can thrive in humid conditions.
3. Stay Hydrated
In dry environments, staying hydrated helps keep your airways moist, which makes it easier to breathe. Drinking plenty of water can help prevent irritation caused by dry air and maintain healthy mucus production in the respiratory system.
4. Use an Air Purifier
Air purifiers can help filter out dust, pollen, and other allergens from the air. This is particularly important during high humidity months when allergens are more prevalent.
5. Monitor Humidity Levels
Investing in a humidity monitor can help you keep track of the moisture levels in your home. If the humidity goes above 50%, you may want to use a dehumidifier, and if it drops below 30%, consider using a humidifier to prevent your airways from drying out.
Conclusion
Humidity, whether high or low, can significantly affect people with asthma. While high humidity promotes the growth of allergens like mold and dust mites, low humidity can lead to dryness and respiratory irritation. By monitoring humidity levels and taking steps to control the environment around you, you can help manage your asthma symptoms more effectively and breathe easier.
Appendices
References
For more information about asthma and environmental factors, check out these resources:
- American Lung Association. (2023). “Humidity and Asthma: Understanding the Connection.” Read Article
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2022). “Asthma and Environmental Triggers.” Read Article
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). “Managing Asthma with Environmental Control.” Read Article
FAQs
- How does humidity affect asthma symptoms?
High humidity can worsen asthma by triggering airway inflammation and promoting allergens like mold and dust mites. Low humidity can dry out airways, causing irritation and coughing.
- What humidity level is best for asthma?
The ideal indoor humidity level is between 30% and 50%. This range helps reduce the growth of allergens while keeping your airways comfortable.
- Can a humidifier help with asthma?
Yes! A humidifier can help in dry environments by adding moisture to the air, preventing your airways from becoming too dry and irritated.
- Can high humidity make asthma worse?
Yes, high humidity can trigger asthma symptoms by increasing airway inflammation and causing allergens like mold to thrive.
- How can I reduce asthma triggers from humidity?
Use a dehumidifier, keep your home clean, stay hydrated, and monitor humidity levels to reduce asthma triggers caused by humidity.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and does not substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with your doctor or asthma specialist for personalized asthma management and care.

Bianca Nala is a compassionate Nurse Practitioner with a strong background in primary and respiratory care. As a health writer for Healthusias.com, she combines her clinical expertise with a talent for clear, relatable storytelling to help readers better understand their health. Bianca focuses on topics like asthma, COPD, chronic cough, and overall lung health, aiming to simplify complex medical topics without losing accuracy. Whether she’s treating patients or writing articles, Bianca is driven by a single goal: making quality healthcare knowledge accessible to everyone.