The Role of Antihistamines in Asthma Management: What You Should Know
Ever wonder if antihistamines play a part in managing asthma? You’re not alone! Let’s dive into how they work and if they can help you breathe easier.
If you’re living with asthma, you’re probably already familiar with the whole allergy-asthma connection. Things like pollen, dust, and pet dander can trigger asthma attacks and make it hard to breathe. But did you know that antihistamines could help in managing asthma symptoms? Yeah, it’s true! But here’s the thing—antihistamines are typically used for allergies, not asthma directly. So, how do they fit into asthma management? Let’s break it down!

What Are Antihistamines?
Before we get into how they relate to asthma, it’s important to understand what antihistamines are. These are medications that help block histamines, which are chemicals in your body that are released when you’re exposed to allergens. Think of histamines as the body’s way of saying, “Hey, something’s not right!” This can cause symptoms like sneezing, itching, and swelling, which are typical in allergies. When antihistamines step in, they basically turn down the volume on that reaction.
Now, if you have asthma, your airways can become inflamed and constricted, making it tough to breathe. For some folks with asthma, allergies can make that even worse. So, you might be wondering, “How can antihistamines help with asthma?”
Can Antihistamines Help with Asthma?
Here’s where it gets interesting. Antihistamines aren’t a cure for asthma, but they can help control asthma symptoms, especially if allergies are a trigger for your asthma attacks.
How Antihistamines Work for Asthma
For people whose asthma is triggered by things like pollen, pet dander, or dust mites (yep, those tiny little things are trouble!), antihistamines can help ease the allergic reactions that worsen asthma. For example, if you’re allergic to dust mites and it’s triggering asthma symptoms, taking an antihistamine could reduce sneezing and nasal congestion, which helps open up the airways a little bit. This might prevent a full-blown asthma attack from happening or reduce the severity of one.
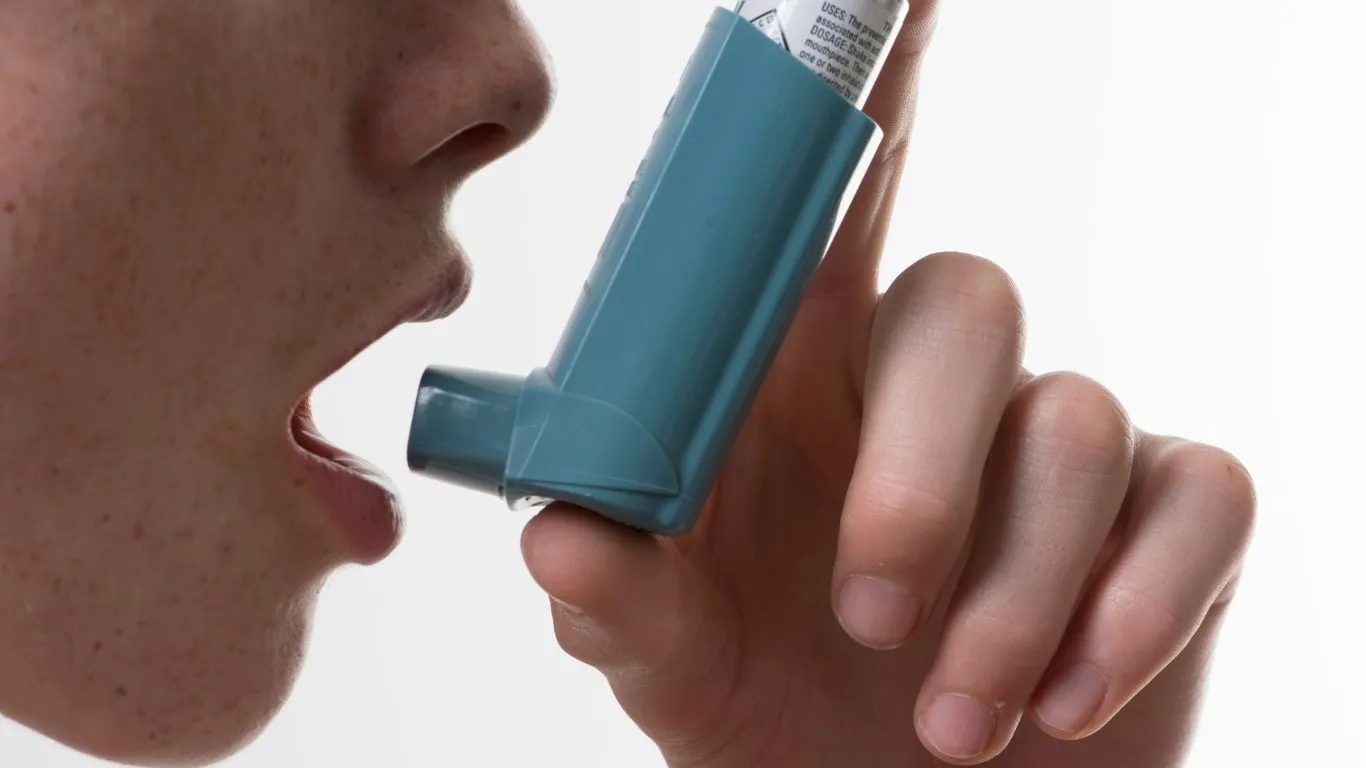
But—and here’s the catch—antihistamines alone won’t stop an asthma attack. They work best when combined with other asthma treatments like bronchodilators (those inhalers that help open your airways) or corticosteroids (the inhaled meds that reduce inflammation in your lungs).

Which Antihistamines Are Best for Asthma?
Not all antihistamines are created equal. There are two main types:
- First-generation antihistamines: These are older medications, like diphenhydramine (think Benadryl). They’re effective at treating allergy symptoms, but they can make you really drowsy and aren’t usually recommended for people with asthma because they can dry out your airways, which could make breathing worse.
- Second-generation antihistamines: These newer versions, like loratadine (Claritin) and cetirizine (Zyrtec), are less likely to cause drowsiness, and they’re typically a better choice for people with asthma. They target specific receptors to block histamine without the side effects of the older meds.
Antihistamines and Asthma Control
When allergies are under control, it might be easier to keep asthma flare-ups at bay. Taking an antihistamine before heading into an environment with lots of allergens—like a dusty room or a pet-heavy area—could help prevent the allergic reaction that could lead to an asthma attack.
But remember: antihistamines are part of the puzzle, not the whole solution. You still need to follow your asthma action plan, use prescribed inhalers as directed, and keep your allergies in check.

Should Antihistamines Be Part of Your Asthma Treatment Plan?
Good question! If allergies are a significant trigger for your asthma, it’s definitely worth considering antihistamines. But, and this is key, you should always consult with your doctor before adding anything new to your asthma treatment plan. They’ll know if antihistamines will help based on your specific situation, your asthma severity, and any other medications you might be taking.
Plus, if your asthma is more severe or not well-controlled, antihistamines alone won’t cut it. You’ll need to focus on other treatments that target the asthma itself, like inhaled corticosteroids or biologic treatments. Always keep your healthcare provider in the loop!
Potential Side Effects of Antihistamines
Like any medication, antihistamines come with their own set of potential side effects. Some of the more common ones include:
- Drowsiness: This is more common with first-generation antihistamines, so if you’re using them, be prepared for a nap! (It’s not ideal when you need to be alert.)
- Dry mouth: This can be a bit uncomfortable and could make your airways feel even more irritated.
- Dizziness or headaches: Some people report feeling a little off after taking antihistamines.
It’s always a good idea to start slow and see how your body reacts. If you experience any negative effects, reach out to your doctor and consider trying a different antihistamine or adjusting the dosage.
Other Ways to Manage Asthma and Allergies Together
Along with antihistamines, here are some additional tips for managing both asthma and allergies:
- Keep your living space clean: Regular dusting and vacuuming (with a HEPA filter) can help reduce allergens like dust mites.
- Use air purifiers: These can filter out pollen, dander, and other airborne allergens that might trigger asthma.
- Avoid outdoor allergens when possible: If it’s pollen season, try to stay inside, especially on windy days. You might also want to keep windows closed during high pollen times.
Conclusion
So, are antihistamines a good option for asthma management? The short answer is: maybe! If allergies are a major trigger for your asthma, antihistamines can help reduce those symptoms, which might make managing asthma a little easier. But remember, they’re not a substitute for other asthma treatments like inhalers. Always chat with your doctor about the best way to manage both asthma and allergies to keep your breathing as easy as possible.
Appendices
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about the role of antihistamines in asthma management:
- Can antihistamines cure asthma?
No, antihistamines can help reduce allergy symptoms, but they won’t treat asthma directly. Asthma medications like bronchodilators and corticosteroids are needed for that. - Which antihistamines are safest for asthma sufferers?
Second-generation antihistamines like loratadine (Claritin) or cetirizine (Zyrtec) are generally recommended because they don’t cause drowsiness and are less likely to dry out your airways. - Do I still need to use my inhaler if I take antihistamines?
Yes! Antihistamines can help with allergies but won’t prevent asthma flare-ups on their own. Keep using your prescribed asthma treatments. - Can I take antihistamines daily for asthma?
Antihistamines are often safe for daily use if you have allergies, but it’s best to check with your doctor, especially if you have any other health conditions. - What are the side effects of antihistamines for asthma?
Some antihistamines can cause drowsiness, dry mouth, and dizziness, particularly the first-generation types. Always monitor how your body reacts.
References
For further information on asthma management and antihistamine use, check out these resources:
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2023). Asthma and Allergy. Read Article
- American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology. (2022). Antihistamines and Asthma. Read Article
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). Asthma Medications. Read Article
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or a healthcare professional for advice tailored to your individual situation.














