“Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Treatment Options”
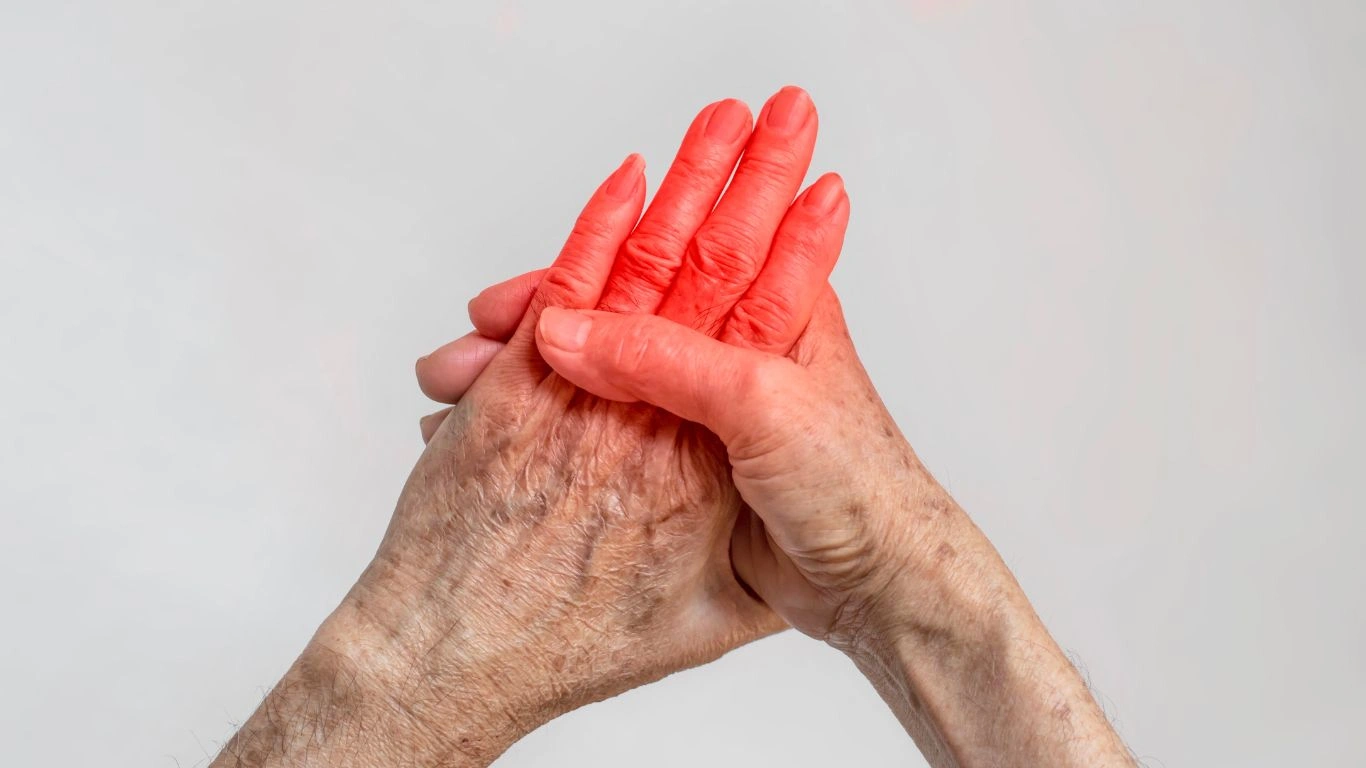
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the joints, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. It primarily targets the small joints in the hands, wrists, and feet. However, it can also affect larger joints like the knees and shoulders.
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?

RA occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissues. This leads to inflammation, joint damage, and potential disability. Over time, the condition can worsen if not properly managed, making early diagnosis crucial.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis

Common symptoms of RA include:
- Joint pain and swelling
- Morning stiffness
- Fatigue
- Reduced range of motion
- Fever and weight loss (in some cases)
These symptoms may vary in intensity and can change over time. Some individuals experience flare-ups, while others may go through periods of remission.
Causes and Risk Factors of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The exact cause of RA is unknown, but several factors may increase the risk of developing the condition:
- Genetics
- Gender (women are more likely to develop RA)
- Age (most commonly develops between 30-60 years)
- Smoking and exposure to pollutants
- Infections
While these factors can increase the likelihood of developing RA, not everyone with these risk factors will develop the disease.
Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis
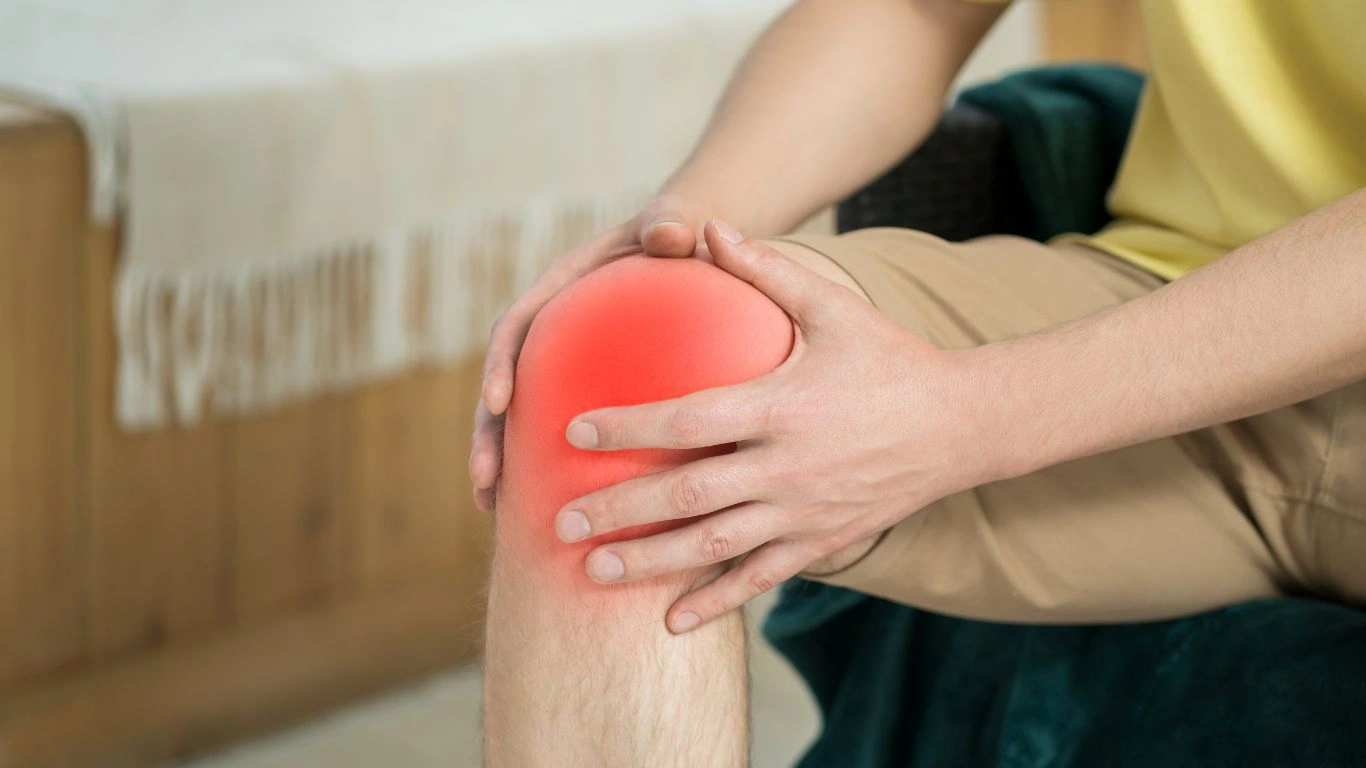
Treatment for RA aims to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and prevent joint damage. Some common treatment options include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
- Biologic therapies
- Physical therapy
- Joint surgery (in severe cases)
Early treatment is key to preventing long-term damage and improving quality of life. Talk to your doctor about the best treatment plan for your situation.
Remember, while RA is a lifelong condition, with the right care, people living with RA can manage their symptoms and continue leading active lives. Keep an open line of communication with your healthcare provider to adjust treatment as needed.