Understanding GERD Attacks: Symptoms, Triggers, and Management
Explore everything you need to know about GERD attacks, including their symptoms, triggers, and practical management tips for better digestive health and reduced discomfort.
GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) is a chronic digestive condition that affects millions worldwide. GERD attacks, characterized by sudden and intense episodes of acid reflux, can disrupt daily life and cause significant discomfort. This guide will delve into the causes, symptoms, and effective strategies to manage GERD attacks, empowering you to lead a healthier, more comfortable life.

What is a GERD Attack?
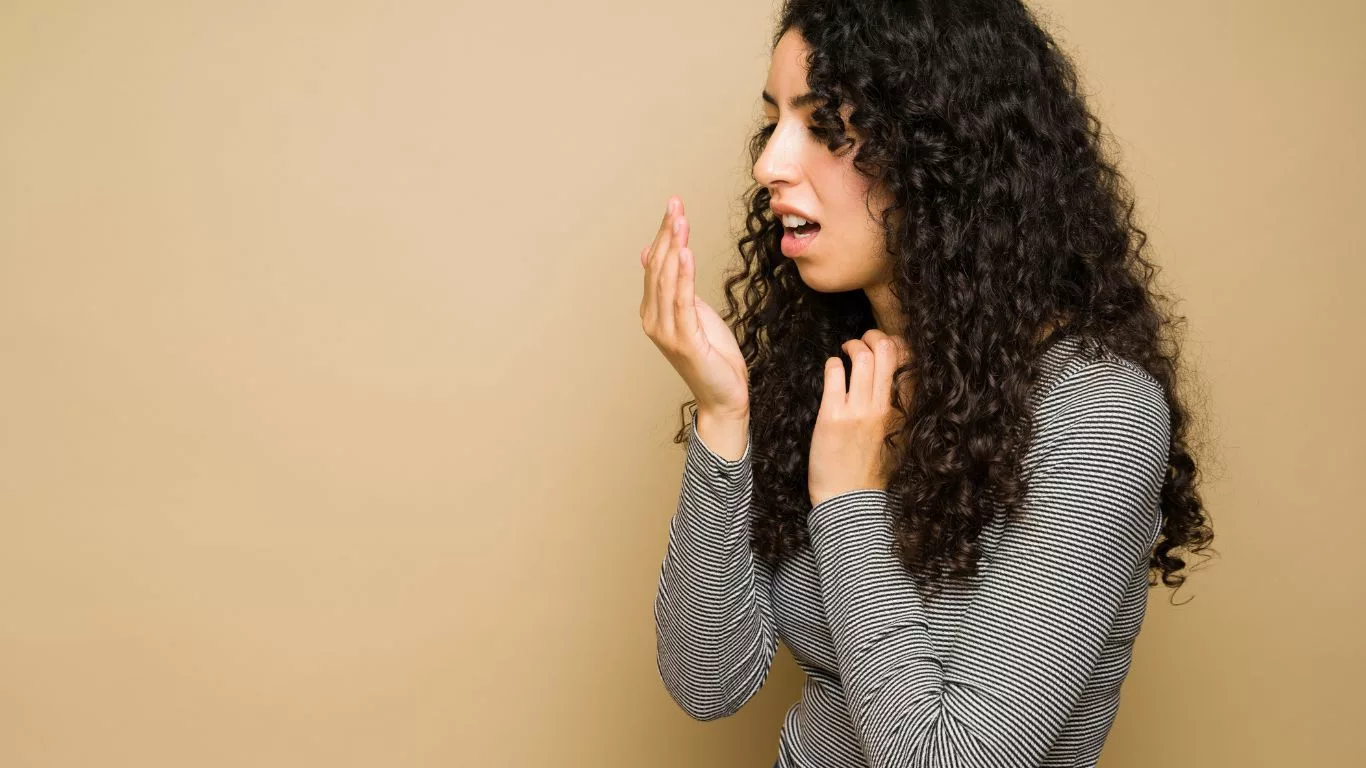
A GERD attack occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation. While occasional acid reflux is normal, GERD attacks are more severe and chronic, often requiring medical attention and lifestyle adjustments.
Common Symptoms of GERD Attacks
GERD attacks can manifest in various ways, impacting both the digestive system and overall well-being. Here are the most common symptoms:
- Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest, often worse after eating or when lying down.
- Regurgitation: The sensation of acid or food coming back up into the throat or mouth.
- Dysphagia: Difficulty swallowing, sometimes accompanied by a feeling of food being stuck in the throat.
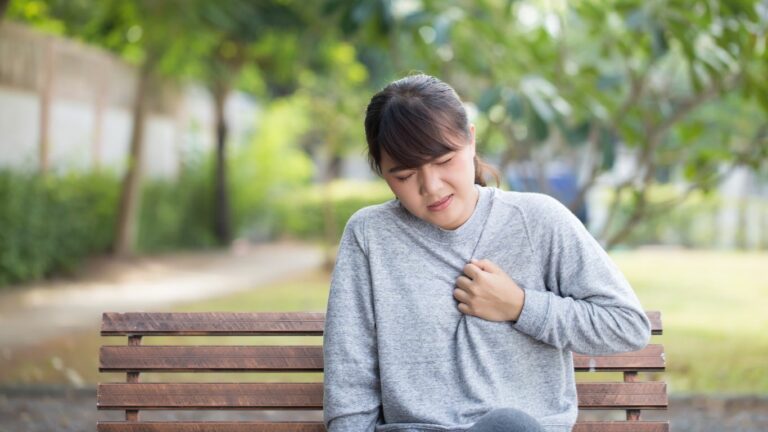
- Chest Pain: Discomfort or pain in the chest, which may mimic a heart attack.
- Chronic Cough: Persistent coughing caused by acid irritating the throat and airways.
Triggers of GERD Attacks
Identifying and avoiding triggers is crucial for managing GERD. Some common triggers include:
1. Dietary Factors
Certain foods and beverages can relax the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), allowing acid to escape the stomach. Common culprits include:
- Spicy foods
- Fatty or fried foods
- Citrus fruits
- Carbonated beverages
- Alcohol
2. Lifestyle Choices
Unhealthy habits can exacerbate GERD symptoms. Smoking, overeating, and lying down immediately after meals are significant contributors.
3. Medical Conditions
Pregnancy, obesity, and certain medications can increase abdominal pressure, leading to GERD attacks.

How to Manage GERD Attacks
Managing GERD requires a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and sometimes medical intervention. Here are some practical strategies:
1. Lifestyle Changes
- Elevate the head of your bed to prevent nighttime reflux.
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals instead of large meals.
- Avoid eating at least 2-3 hours before bedtime.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce abdominal pressure.
2. Dietary Adjustments
Focus on GERD-friendly foods such as:
- Lean proteins (e.g., chicken, turkey)
- Non-citrus fruits (e.g., bananas, melons)
- Whole grains
- Low-fat dairy products
3. Medical Treatment
If lifestyle and dietary changes are insufficient, medical options may be necessary:
- Antacids: Provide quick relief by neutralizing stomach acid.
- H2 Blockers: Reduce acid production.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): Block acid production and promote healing.

Preventing GERD Attacks
Prevention is the best approach to minimize GERD attacks. Here are some tips:
- Avoid known triggers and keep a food diary to identify personal culprits.
- Practice stress-reducing activities like yoga or meditation.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Chew food thoroughly and eat slowly to aid digestion.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience frequent or severe GERD attacks, consult a healthcare provider. Persistent symptoms can lead to complications such as esophagitis, Barrett’s esophagus, or esophageal cancer.

Conclusion
GERD attacks can be disruptive, but with the right strategies, you can manage and even prevent them. By understanding your triggers, making lifestyle and dietary changes, and seeking medical advice when necessary, you can achieve better digestive health and live more comfortably.
Appendices
References
- American Gastroenterological Association (AGA). (2024). GERD: Symptoms and Treatment. Read Article
- Smith, R. (2023). Acid Reflux: Dietary Tips and Triggers. Journal of Digestive Health, 40(1), 45-50. Read Article
FAQs
- What triggers GERD attacks? Common triggers include fatty foods, caffeine, alcohol, and lying down after eating.
- How can I relieve GERD symptoms quickly? Over-the-counter antacids and drinking water can provide quick relief.
- Is GERD curable? While GERD can’t be cured entirely, it can be effectively managed with lifestyle and medical treatments.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Consult your doctor for personalized recommendations.

Camellia Wulansari is a dedicated health writer specializing in digestive disorders, contributing valuable insights and information to the health and wellness community. With a passion for promoting well-being through knowledge, Camellia serves as a reliable source of expert content on healthusias.com.