What Are the Symptoms of GERD Disease? – A Comprehensive Overview
Uncover the key symptoms of GERD disease and understand its impact on health. Learn how to recognize signs and seek appropriate treatment in our detailed guide.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is a chronic digestive condition where stomach acid or bile flows back into the esophagus, leading to various uncomfortable symptoms. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for effective management and treatment. This article provides an analytical overview of the primary symptoms associated with GERD, helping individuals identify and address this prevalent condition.
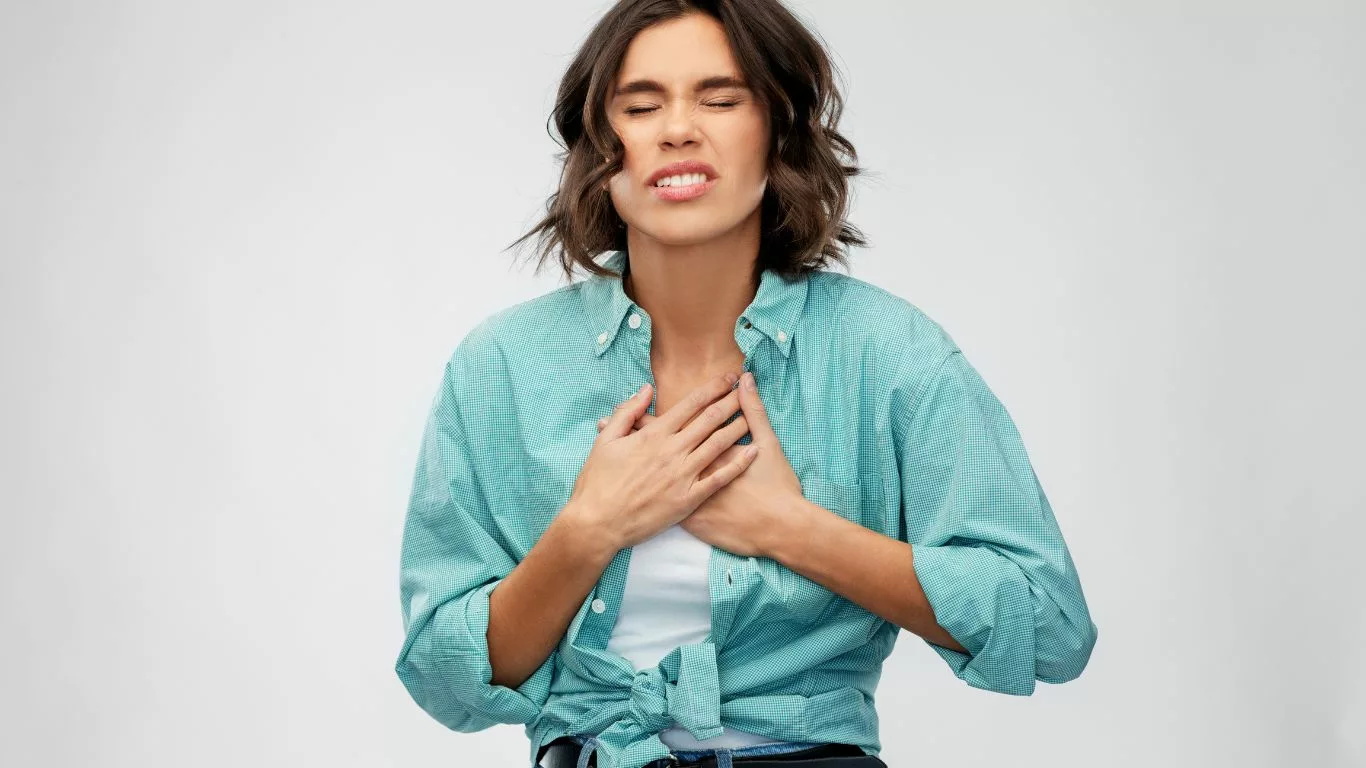

Common Symptoms of GERD
The symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) can vary significantly among individuals, making it important for patients to recognize the hallmark signs. These symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe complications that affect daily life. Below are several key symptoms commonly reported by individuals with GERD.
1. Heartburn
Heartburn is the most prevalent symptom of GERD. It is characterized by a burning sensation in the chest, often triggered by meals, especially large or fatty ones, or when lying down. This discomfort results from stomach acid irritating the lining of the esophagus, which is not designed to withstand the harsh acidity of gastric contents. The intensity of heartburn can vary, and it may be accompanied by a feeling of pressure or tightness in the chest. For some, heartburn may be a frequent occurrence, disrupting normal activities and causing distress.
2. Regurgitation
Regurgitation involves the sensation of acid or food backing up into the throat or mouth, often accompanied by a sour or bitter taste. This can occur shortly after eating or during sleep, leading to discomfort and potential sleep disturbances. The act of regurgitating can provoke a strong gag reflex and may leave individuals feeling embarrassed or anxious about eating in social settings. Persistent regurgitation may also lead to damage of the esophagus and throat, resulting in additional complications.
3. Dysphagia
Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, is another symptom experienced by individuals with GERD. This may manifest as a sensation of food being stuck in the throat or chest, which can lead to anxiety around eating. Some individuals may develop a fear of swallowing due to the discomfort associated with this symptom. In severe cases, dysphagia can result in unintentional weight loss, as the individual may avoid eating altogether to prevent discomfort.
4. Chronic Cough and Throat Irritation
A persistent cough, particularly at night or after meals, can signal the presence of GERD. This symptom may arise when stomach acid irritates the airways, causing a cough reflex. Individuals may also experience throat irritation or hoarseness due to acid exposure, leading to symptoms similar to those of allergies or infections. Chronic cough can significantly impact quality of life, causing disruptions in sleep and daily activities.
5. Asthma-like Symptoms
Some individuals with GERD may experience asthma-like symptoms, including wheezing, shortness of breath, and a sensation of tightness in the chest. These symptoms may worsen after eating or lying down, particularly if stomach acid enters the airways. For individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions, such as asthma, GERD can exacerbate symptoms and complicate management of their respiratory health.

Less Common Symptoms
In addition to the common symptoms of GERD, the condition can manifest in less typical ways, affecting overall well-being.
1. Nausea
Nausea is a symptom that some individuals may experience, often occurring after eating. This feeling of needing to vomit can be distressing and may lead to a decreased appetite or aversion to certain foods. The nausea associated with GERD may be due to the irritation of the stomach lining or the esophagus.
2. Chest Pain
Chest pain related to GERD can mimic cardiac-related issues, making it crucial for individuals to differentiate between these symptoms. This pain may be sharp or dull and can be triggered by eating or lying down. Due to the serious nature of heart disease, any chest pain should be evaluated by a healthcare provider to rule out cardiac causes.

When to Seek Medical Attention
While occasional symptoms may be manageable with lifestyle adjustments, persistent or severe symptoms warrant medical evaluation. Key indicators include:
- Frequent heartburn: More than twice a week indicates a need for medical intervention.
- Severe chest pain or discomfort: This requires immediate evaluation to rule out serious conditions.
- Difficulty swallowing that worsens: Progressive dysphagia may signal complications that need addressing.
- Unexplained weight loss: This can be a sign of significant underlying issues.
- Symptoms that disrupt daily life or sleep: Persistent disruption may necessitate a reevaluation of management strategies.

Managing GERD Symptoms
Effective management of GERD typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and medical treatments.
1. Lifestyle Modifications
Implementing lifestyle changes can significantly reduce GERD symptoms. Avoiding large meals, refraining from lying down immediately after eating, and elevating the head during sleep are effective strategies. Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding tight clothing can also help minimize pressure on the stomach.
2. Dietary Changes
Identifying and avoiding trigger foods is crucial in alleviating symptoms. Common triggers include spicy dishes, citrus fruits, chocolate, fatty foods, and caffeinated beverages. Keeping a food diary can help individuals pinpoint specific foods that exacerbate their symptoms.
3. Medical Treatments
Over-the-counter antacids, H2-receptor antagonists, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are common medications prescribed to manage GERD symptoms. These medications help reduce stomach acid production and promote healing of the esophagus. Consulting a healthcare provider for tailored treatment is essential, as they can recommend appropriate medications and dosage based on individual health status and symptom severity.

Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms of GERD is vital for effective management and improved quality of life. With common symptoms like heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing, individuals can take proactive steps to address their health. Lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and medical treatments can effectively mitigate symptoms, allowing individuals to manage GERD successfully. If symptoms persist or worsen, seeking medical advice is crucial for appropriate evaluation and care.
Appendices
References
For further exploration of GERD and its symptoms, consider reviewing the following references:
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). (2021). Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD). Read Article
- American College of Gastroenterology. (2023). Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of GERD. Read Article
- American Gastroenterological Association. (2022). GERD: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Read Article
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about GERD symptoms:
- What should I do if I experience severe heartburn? If you experience severe heartburn, consider consulting a healthcare professional for evaluation and possible treatment options.
- Are there specific foods to avoid with GERD? Yes, common trigger foods include spicy dishes, citrus fruits, chocolate, and fatty foods. Identifying personal triggers can help manage symptoms.
- Can lifestyle changes really help manage GERD symptoms? Yes, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding large meals, and elevating the head during sleep can significantly reduce GERD symptoms.
Related Table
Here’s a summary table of key information regarding GERD symptoms:
| Aspect | Information |
|---|---|
| Common Symptoms | Heartburn, regurgitation, dysphagia, chronic cough, asthma-like symptoms |
| When to Seek Help | Frequent symptoms, severe chest pain, difficulty swallowing, unexplained weight loss |
| Management Strategies | Lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, medical treatments |
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article. Reliance on any information provided in this article is solely at your own risk.

Camellia Wulansari is a dedicated Medical Assistant at a local clinic and a passionate health writer at Healthusias.com. With years of hands-on experience in patient care and a deep interest in preventive medicine, she bridges the gap between clinical knowledge and accessible health information. Camellia specializes in writing about digestive health, chronic conditions like GERD and hypertension, respiratory issues, and autoimmune diseases, aiming to empower readers with practical, easy-to-understand insights. When she’s not assisting patients or writing, you’ll find her enjoying quiet mornings with coffee and a medical journal in hand—or jamming to her favorite metal band, Lamb of God.