Asthma and Acid Reflux Connection: What You Need to Know
Are you dealing with asthma and acid reflux at the same time? You’re not alone! Many people experience both conditions, and they often seem to go hand in hand. Understanding the connection between asthma and acid reflux can help you manage symptoms more effectively. Keep reading to learn more about this relationship and tips for managing both.
Introduction
If you’ve been diagnosed with both asthma and acid reflux (GERD), it’s easy to feel overwhelmed by the impact they can have on your daily life. Both conditions can affect your breathing and digestion, sometimes making it harder to feel your best. But here’s the thing: asthma and acid reflux are more connected than you might think. In this article, we’ll explore how these two conditions relate to one another and what you can do to manage both at the same time. 
How Asthma and Acid Reflux Are Connected
While asthma and acid reflux are separate conditions, they have a significant overlap. Here’s how they are connected:
1. Acid Reflux Can Trigger Asthma Symptoms
When stomach acid rises into the esophagus (a condition known as gastroesophageal reflux disease or GERD), it can sometimes reach the airways. This can cause inflammation and make asthma symptoms worse. For example, the acid can irritate the lungs and trigger an asthma attack or worsen symptoms like coughing and wheezing.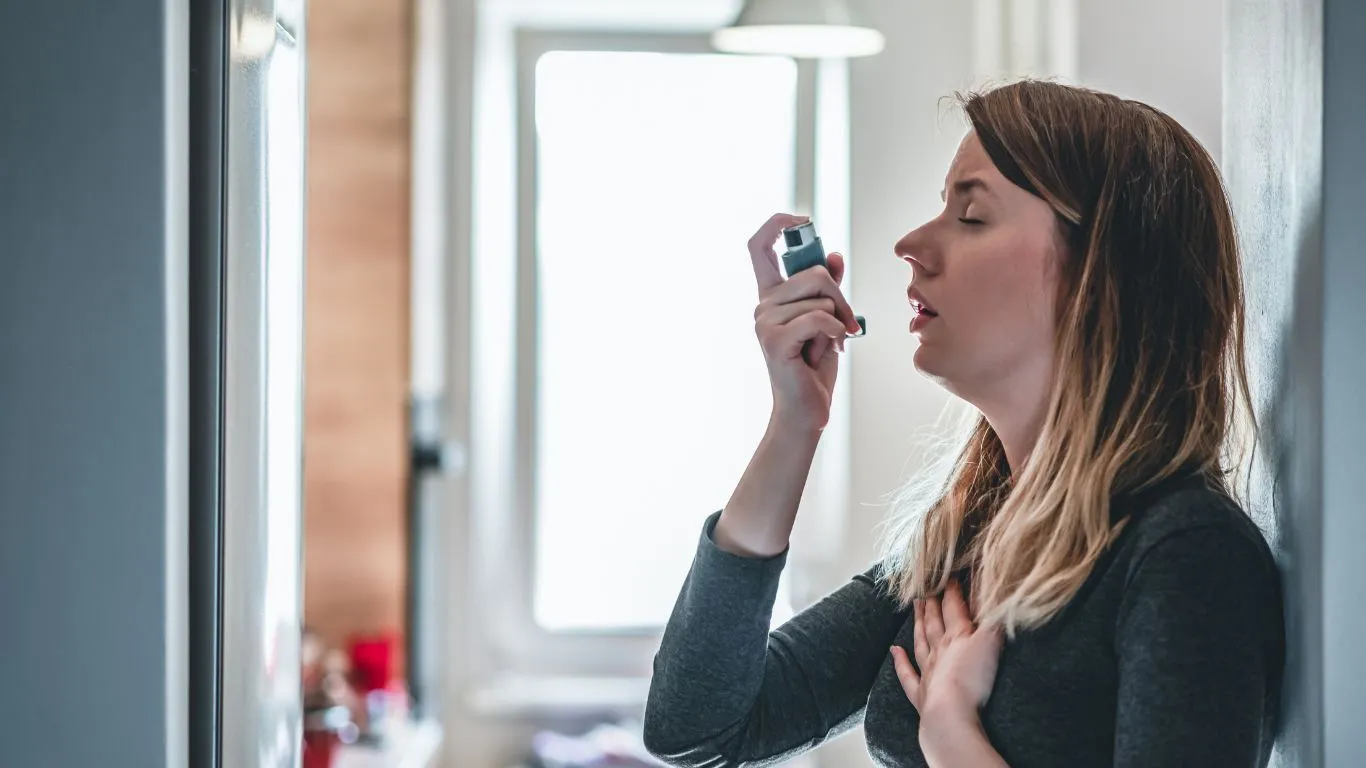 
2. Asthma Medications Can Worsen Acid Reflux
Some asthma medications, particularly inhaled bronchodilators, can relax the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). This muscle is supposed to keep stomach acid from traveling up the esophagus. When the LES relaxes too much, it allows acid to flow back into the esophagus, which leads to acid reflux. So, sometimes the treatment for asthma can actually contribute to acid reflux.
Both asthma and acid reflux share some common risk factors. For example, obesity is a risk factor for both conditions. If you’re overweight, the extra pressure on the abdomen can increase the likelihood of acid reflux while also making asthma symptoms harder to manage. Smoking, stress, and a poor diet also contribute to both conditions.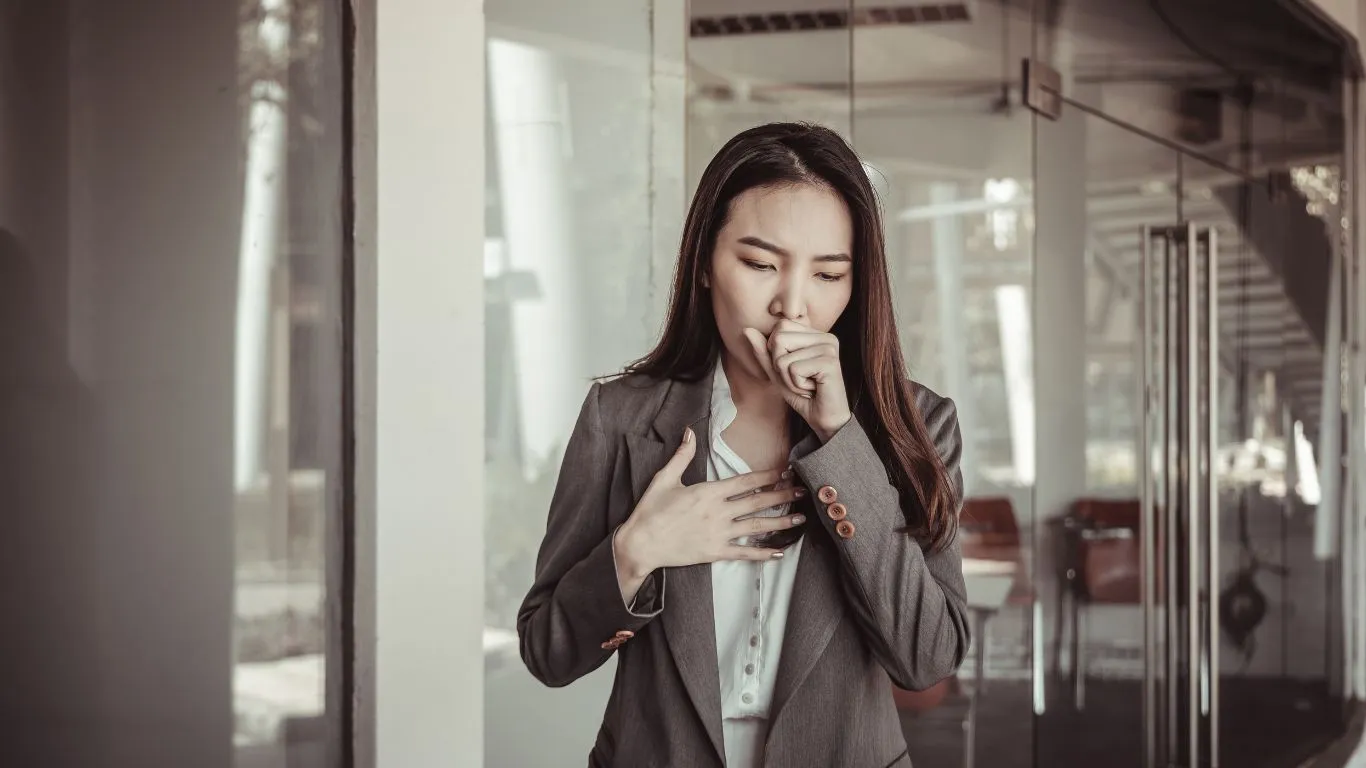 
Symptoms of Asthma and Acid Reflux
Understanding the symptoms of asthma and acid reflux can help you identify whether the two conditions are interacting. Here’s what to look out for:
Asthma Symptoms:
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing or a whistling sound when breathing
- Persistent coughing, especially at night or early in the morning
- Tightness in the chest
Acid Reflux Symptoms:
- Heartburn or a burning sensation in the chest or throat
- Sour or bitter taste in the mouth
- Difficulty swallowing
- Chronic cough, especially at night
- Regurgitation of food or liquid
If you notice that your asthma symptoms get worse after meals, especially if you’re lying down, it could be a sign that acid reflux is playing a role.
Managing Asthma and Acid Reflux Together
Managing both asthma and acid reflux can feel like juggling two health conditions at once, but with the right strategies, you can reduce flare-ups and improve your quality of life.
1. Keep Your GERD in Check
- Medications: Talk to your doctor about medications that can help control acid reflux, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2 blockers. These can reduce stomach acid and prevent it from reaching the esophagus.
- Dietary Changes: Certain foods can trigger acid reflux. Try to avoid spicy, fatty, or fried foods, citrus, chocolate, and caffeine. Instead, focus on a diet that’s easy on your stomach, like bland, non-acidic foods.
- Eat Smaller Meals: Large meals can trigger acid reflux, so try eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day to reduce the strain on your digestive system.
2. Control Your Asthma
- Inhalers: Make sure to use your asthma inhalers as prescribed. If your symptoms are worsening, talk to your doctor about adjusting your treatment plan.
- Avoid Triggers: Common asthma triggers include allergens, cold air, smoke, and exercise. Avoiding these triggers can help you reduce asthma flare-ups.
- Breathing Exercises: Certain breathing exercises can help manage asthma. Techniques like pursed-lip breathing or diaphragmatic breathing may help you breathe more easily and prevent shortness of breath.
3. Work With Your Healthcare Provider
If you’re struggling with both asthma and acid reflux, it’s crucial to work closely with your doctor. They can help you find the right balance between controlling your asthma and managing acid reflux. This might include a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and ongoing monitoring of your symptoms.
4. Elevate Your Head While Sleeping
Acid reflux symptoms often worsen at night, especially if you lie flat. Try elevating the head of your bed or using a wedge pillow to keep your upper body raised while you sleep. This can help prevent acid from flowing back into your esophagus while also promoting better airflow for asthma.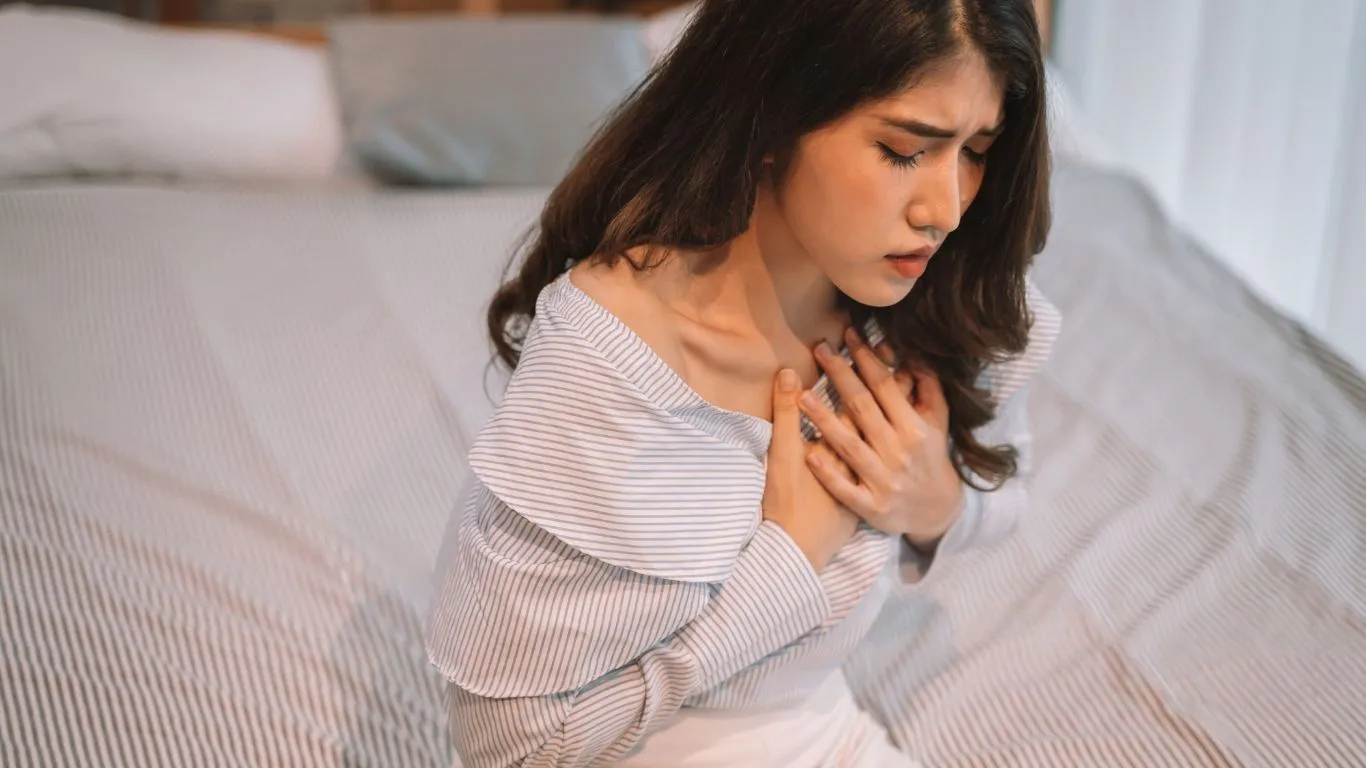 
When to Seek Help
While it’s common to experience both asthma and acid reflux, certain symptoms should prompt a visit to your healthcare provider. If you notice any of the following, it’s important to seek medical advice:
- Frequent or severe asthma attacks
- Persistent heartburn that doesn’t improve with over-the-counter medications
- Difficulty swallowing or a feeling of food getting stuck
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Worsening of asthma symptoms after meals
Conclusion
Asthma and acid reflux often go hand in hand, and understanding the connection between the two is key to managing both conditions. By addressing both asthma and acid reflux with the right treatments and lifestyle changes, you can improve your quality of life and reduce the impact of these chronic conditions.
Appendices
FAQs
- Can acid reflux cause asthma attacks? Yes, acid reflux can trigger asthma attacks by irritating the airways and lungs, leading to symptoms like coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
- How do asthma medications affect acid reflux? Some asthma medications, particularly bronchodilators, can relax the lower esophageal sphincter, making it easier for acid to travel up into the esophagus and cause reflux.
- Can I treat both asthma and acid reflux at the same time? Yes, treating both conditions together is essential for managing symptoms. Your doctor can help you develop a treatment plan that addresses both asthma and acid reflux.
- What lifestyle changes can help with both asthma and acid reflux? Eating smaller meals, avoiding trigger foods, maintaining a healthy weight, and controlling asthma triggers can help manage both conditions.
- Are there any foods I should avoid with both asthma and acid reflux? Yes, foods that trigger acid reflux, such as spicy, fried, and citrus foods, can also exacerbate asthma symptoms. It’s best to avoid these and focus on a balanced diet.
References
- National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID). (2023). Asthma and Acid Reflux.
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Managing Asthma and GERD Together.
- American College of Gastroenterology. (2024). GERD and Asthma: Understanding the Connection.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and does not substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and treatment plans. Individual needs may vary, and professional consultation is essential for accurate diagnosis and care.

Bianca Nala is a compassionate Nurse Practitioner with a strong background in primary and respiratory care. As a health writer for Healthusias.com, she combines her clinical expertise with a talent for clear, relatable storytelling to help readers better understand their health. Bianca focuses on topics like asthma, COPD, chronic cough, and overall lung health, aiming to simplify complex medical topics without losing accuracy. Whether she’s treating patients or writing articles, Bianca is driven by a single goal: making quality healthcare knowledge accessible to everyone.