“Can Asthma Cause Swelling in the Chest? Learn Effective Control Tips”
Asthma is a condition that affects millions of people around the world, and as a Pulmonary Nurse, I’ve seen firsthand how challenging it can be for patients to manage. A common question I hear from patients is: “Can asthma cause swelling in the chest?” It’s a great question because chest tightness and discomfort are often associated with asthma, but many people wonder whether they’re dealing with something more serious, like swelling. In this article, we’ll dive into how asthma can affect the chest, the symptoms that might indicate swelling, and how to recognize the signs.
Understanding Asthma and Its Effects on the Chest
When we talk about asthma, we’re referring to a chronic condition that affects the airways, causing them to become inflamed and narrowed. This inflammation can lead to wheezing, shortness of breath, coughing, and chest tightness. But here’s the thing: chest tightness is often confused with other types of discomfort, and it’s sometimes misinterpreted as “swelling.” So, can asthma actually cause swelling in the chest? Let’s break this down.
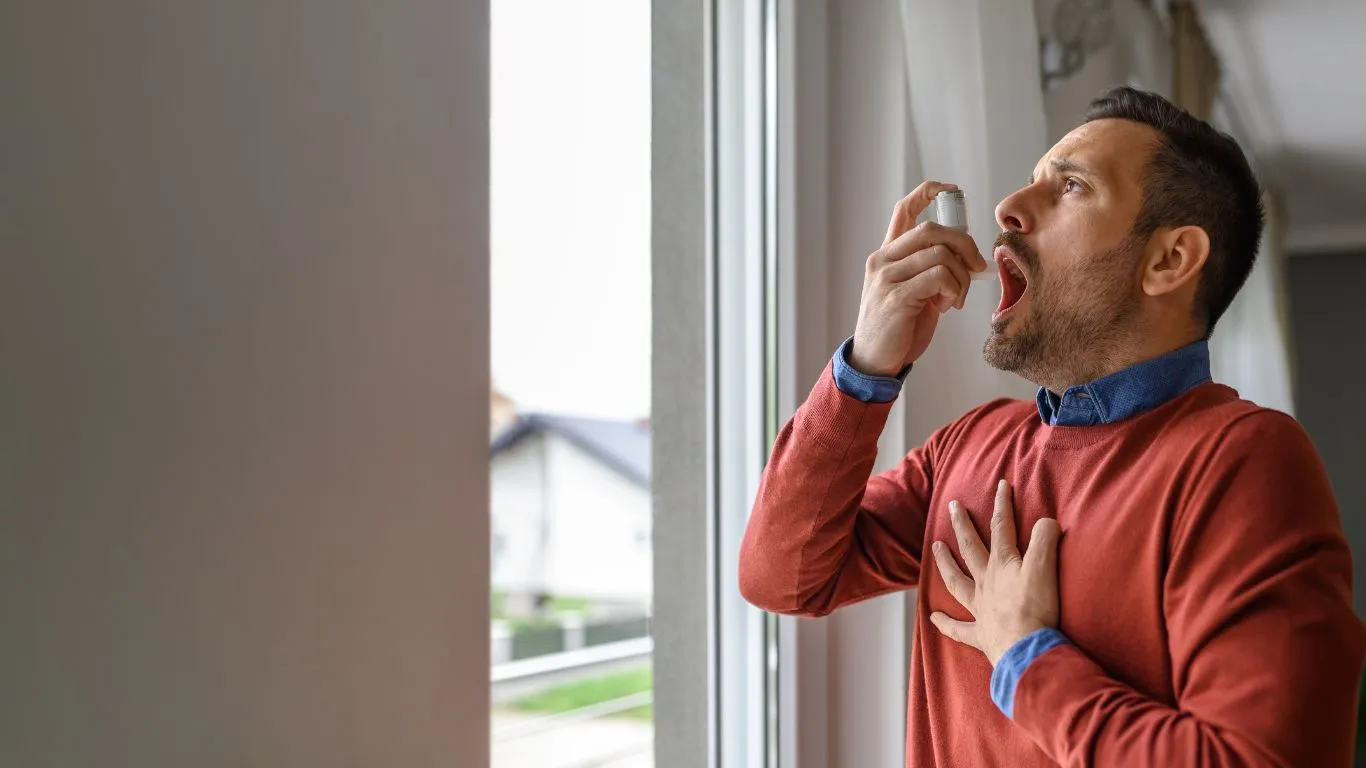

What is Chest Tightness in Asthma?
Chest tightness is one of the hallmark symptoms of asthma. When the airways constrict due to inflammation, it can feel like there’s a weight on your chest, making it harder to breathe. However, this sensation of tightness doesn’t actually involve swelling in the way we think of it in terms of other health conditions like allergic reactions or injuries. Instead, the sensation comes from the muscles around your airways contracting, making it feel like your chest is tight or compressed.
Think of it like this: if you were to squeeze a balloon, you’d notice it would become harder for the air to move through. This is similar to how asthma works – when the muscles around your airways tighten, it becomes more difficult for air to flow in and out, creating a feeling of tightness in the chest. While it can feel uncomfortable and even scary, it’s important to know that this is a common symptom of asthma.
Can Asthma Cause Swelling in the Chest?
Now, let’s address the main concern: can asthma actually cause swelling in the chest? The short answer is no, asthma doesn’t typically cause swelling in the chest in the traditional sense. However, the inflammation and narrowing of the airways that asthma causes can create a sensation similar to swelling. The muscles, tissues, and airways are inflamed, which might lead to the feeling of puffiness or fullness in the chest, especially during an asthma flare-up.
This is where it gets a bit tricky: inflammation doesn’t always mean “swelling” like you would see if you had a sprained ankle, for example. Instead, it’s the internal irritation and constriction that makes your chest feel tight or like it’s swelling. While this discomfort can feel similar to what you’d experience with actual swelling, it’s not the same thing. If you’re ever unsure about whether your asthma symptoms are different from usual, always seek medical advice to be safe.
How Do You Know if Your Chest Feels Swollen from Asthma or Something Else?
It can be tough to differentiate between the sensations of asthma-related chest tightness and actual swelling. The good news is that there are some key signs that can help you figure it out. If you’re experiencing any of the following, it might indicate that your asthma is flaring up and not that you’re dealing with swelling:
- Wheezing: This high-pitched sound when breathing is a clear sign that your airways are constricted.
- Coughing: Asthma often causes persistent coughing, especially at night or during physical activity.
- Shortness of Breath: If you feel winded or out of breath even during mild activity, your asthma might not be under control.
- Chest Tightness: As mentioned earlier, tightness is common with asthma and is caused by inflammation in the airways.
On the other hand, actual swelling, like what you might experience with an allergic reaction or injury, can cause visible signs such as redness, heat, and actual puffiness that you can feel or see. If you notice these symptoms, it’s best to seek medical attention right away to rule out other conditions.
Can Asthma Cause Swelling Due to Allergies?
Allergies are a common trigger for asthma attacks, and in some cases, they can lead to swelling in the chest. When you’re allergic to something, your immune system reacts by releasing chemicals that can cause inflammation, which can then make your asthma symptoms worse. In severe cases, this could lead to swelling in the throat or chest, although it’s not as common as other symptoms like difficulty breathing.
If you have asthma and also suffer from allergies, you might be more prone to experiencing swelling in the throat, which can give the sensation that your chest is swelling as well. This is why managing both asthma and allergies is so important for preventing flare-ups. If you’re finding that your symptoms are getting worse, or if you notice any swelling that doesn’t go away, you should contact your doctor for guidance.

When Should You Be Concerned About Chest Discomfort?
If you’re experiencing persistent chest discomfort, whether it’s from asthma or something else, it’s crucial to take it seriously. Sometimes, chest tightness can be a sign of a more serious condition, such as a heart problem, so it’s important not to ignore any new or unusual symptoms. If your chest tightness or discomfort is accompanied by dizziness, pain radiating to your arm or jaw, or confusion, get medical help immediately. These could be signs of something more serious, and it’s always better to be cautious.
Managing Asthma to Reduce Chest Tightness and Discomfort
Managing asthma is key to reducing symptoms like chest tightness, and the good news is that there are many ways to keep things under control. As a pulmonary nurse, I always emphasize the importance of a tailored asthma management plan. It’s not one-size-fits-all. The medications and strategies that work best for you will depend on how severe your asthma is and what triggers it. Let’s dive into some effective ways to manage asthma and reduce that feeling of tightness in the chest.

Medication: The Foundation of Asthma Control
The first step in managing asthma is often through medication. While it might not completely eliminate symptoms, it’s the foundation of controlling your asthma and preventing flare-ups. There are two main types of medications that play a role in asthma management:
- Quick-relief (rescue) inhalers: These are used to relieve sudden symptoms like chest tightness. They work by quickly relaxing the muscles around your airways, opening them up to allow easier breathing. This is usually what people grab when they’re having an asthma attack.
- Long-term control medications: These are taken daily to reduce inflammation in the airways and prevent symptoms from occurring in the first place. These medications help keep asthma under control and reduce the frequency and severity of attacks.
As someone who’s worked with asthma patients for years, I always remind them that consistency is key. It’s easy to forget about your maintenance medications when you’re feeling fine, but not taking them regularly can lead to flare-ups and increase the risk of chest tightness or swelling-like sensations when asthma acts up.
Recognizing Asthma Triggers
A big part of managing asthma is identifying and avoiding triggers. Asthma can be exacerbated by various things – allergens, irritants, changes in weather, exercise, and even stress. Over the years, I’ve noticed that many patients overlook certain triggers, especially when they’re subtle. For example, cold air or a change in humidity can sometimes worsen asthma symptoms, making it feel like your chest is getting tight.
One of my personal tips for my patients is to keep a symptom diary. This might sound a bit old-fashioned, but it works wonders. By jotting down the time of day, what you’ve eaten, weather conditions, or anything you’ve been exposed to, you can start to see patterns in your symptoms. From there, it’s easier to adjust your environment and daily routine to avoid things that trigger your asthma.

Managing Exercise-Induced Asthma
For those with asthma, exercise can be a double-edged sword. On the one hand, physical activity is important for overall health and lung function. On the other hand, exercise can sometimes trigger asthma symptoms, including chest tightness, coughing, or shortness of breath. If you’re dealing with exercise-induced asthma, it’s important to take precautions and work with your healthcare provider to create an exercise plan that suits your needs.
I’ve worked with many athletes who have asthma, and with the right approach, they’ve been able to continue training and competing. Some general tips for managing exercise-induced asthma include:
- Use your inhaler before exercise: If your doctor recommends it, using a quick-relief inhaler about 15 minutes before exercise can help prevent symptoms from arising.
- Warm-up and cool down: A proper warm-up helps your lungs gradually adjust to the exertion, and cooling down allows your body to return to its resting state without stress on your airways.
- Choose the right exercise: Activities that involve short bursts of exertion, like swimming or walking, might be easier on your airways than prolonged, intense exercise like running.
- Avoid extreme weather: Exercise in cold or hot air can irritate the airways and worsen asthma symptoms. If possible, try to exercise indoors or when the weather is milder.
It’s about finding what works for your body while still enjoying physical activity. You shouldn’t have to give up on exercise altogether, but you do need to take proactive steps to avoid triggering your asthma symptoms.
The Role of Breathing Exercises and Lifestyle Adjustments
When it comes to asthma, sometimes it’s not just about medication – it’s about how you live your life. Breathing exercises can be incredibly helpful in managing chest tightness and improving lung function. Techniques like diaphragmatic breathing and pursed-lip breathing can help you control your breath, calm your nerves, and reduce the feeling of tightness in your chest. These exercises may seem simple, but they can make a big difference in how you feel on a daily basis.

Stress Management and Asthma
One factor that’s often overlooked when managing asthma is stress. Emotional stress can actually trigger asthma symptoms or make them worse, leading to that familiar tightness in the chest. I’ve seen this time and time again in my practice. When you’re stressed, your body’s response can include shallow breathing, which in turn puts more strain on your lungs.
That’s why stress management is an important part of asthma care. Techniques like mindfulness, meditation, or even just taking time for yourself to relax can help lower your stress levels and make it easier to manage asthma. Remember, your mind and body are connected, so managing your mental health is just as crucial as managing your physical health.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Finally, maintaining a healthy weight plays a significant role in managing asthma symptoms. Excess weight can put additional strain on your lungs and chest, making it harder for you to breathe and increasing the risk of experiencing chest tightness. A healthy diet, regular exercise (as long as it’s asthma-friendly), and staying active can help keep your weight in check and, in turn, improve your asthma symptoms.
Ultimately, asthma is a manageable condition. By combining medications, lifestyle changes, stress management, and a bit of trial and error to identify triggers, you can significantly reduce the discomfort that often comes with asthma, including that feeling of tightness or “swelling” in the chest.
When to Seek Medical Help for Asthma-Related Chest Tightness
As someone who has spent years working closely with asthma patients, I can tell you that recognizing when your symptoms require medical attention is absolutely crucial. Chest tightness from asthma is one thing, but if it’s severe or persistent, or if it comes with other alarming symptoms, it’s time to reach out to a healthcare provider. Trust your body – if something feels off or if your usual management strategies don’t seem to be helping, don’t hesitate to get checked out.

Signs That Your Asthma Is Not Under Control
While chest tightness and discomfort are common with asthma, there are certain signs that indicate your asthma may not be as well-controlled as you think. If you experience any of the following symptoms, it might be time to revisit your asthma management plan with your healthcare provider:
- Frequent or worsening symptoms: If your chest tightness is becoming more frequent, or if your asthma symptoms are progressively getting worse despite medication, it’s important to consult with your doctor.
- Increased reliance on rescue inhalers: If you find yourself needing to use your quick-relief inhaler more often, it could be a sign that your asthma is not being managed effectively.
- Nighttime awakenings: Waking up at night due to asthma symptoms is a clear indication that your asthma is not under control and should be addressed.
- Difficulty speaking or doing normal activities: If your chest tightness or breathing problems are affecting your ability to speak or perform daily tasks, this is a warning sign that immediate attention may be needed.
Sometimes, even with proper medication and management, your asthma can still flare up. That’s why it’s so important to have a proactive and responsive approach to your asthma care. In my experience, patients who are aware of when things are getting worse tend to have better long-term outcomes because they seek help sooner rather than later.
Long-Term Asthma Care and How to Live Well with Asthma
Asthma is a chronic condition, but that doesn’t mean it has to control your life. With the right approach, you can live a full, active life, despite the challenges asthma may throw your way. As a Pulmonary Nurse, I’ve seen countless patients thrive despite having asthma, and it all comes down to proper management, understanding your triggers, and making healthy lifestyle choices.
Building an Asthma Action Plan
One of the most important tools you can have when it comes to managing asthma is a personalized asthma action plan. This plan outlines exactly what to do when you experience symptoms, how to use your medications, and when to seek help. Having this plan gives you peace of mind and helps you feel more in control of your asthma, especially when chest tightness or other symptoms flare up unexpectedly.
In my practice, I always work with patients to help them build and understand their asthma action plan. It’s not just about the medications – it’s also about recognizing your symptoms early and knowing when to take action. You should always have a clear understanding of:
- When to take your quick-relief medication.
- When to adjust your long-term control medications based on your symptoms.
- When to call for help or visit the doctor if your asthma symptoms worsen.
Your asthma action plan is your roadmap to feeling your best. It empowers you to manage your condition proactively rather than reactively. It’s one of the easiest ways to reduce anxiety and avoid severe asthma attacks.
Creating a Support System
Living with asthma can feel isolating at times, especially when you’re dealing with severe symptoms. But it doesn’t have to be. Surrounding yourself with a support system of family, friends, and even healthcare professionals can make a huge difference in your asthma journey. I encourage all my patients to communicate openly with their loved ones about their condition, so they can offer help when needed and understand what’s going on if you need to make adjustments to your routine.
Additionally, connecting with others who have asthma through support groups – either in-person or online – can offer valuable emotional support. I’ve had patients tell me that talking to someone else who understands what they’re going through has helped reduce their anxiety about their condition. It’s comforting to know that you’re not alone in this.
Exploring New Treatment Options for Asthma
As the field of respiratory care continues to evolve, new treatment options for asthma are constantly being explored. Advances in biologic therapies, which target specific molecules in the immune system, have been a game-changer for many patients with severe asthma. These treatments are usually considered for patients whose asthma is difficult to control with standard medications.
Biologic Medications: A Breakthrough for Severe Asthma
Biologic medications have revolutionized the way we approach asthma care. These treatments are designed to target the underlying causes of asthma, particularly inflammation, in a more precise way than traditional medications. While they’re not suitable for everyone, biologics have been shown to significantly improve asthma control in patients with severe, persistent asthma that doesn’t respond well to inhalers alone.
As someone who’s seen the impact of biologic therapies firsthand, I can tell you that these treatments have been life-changing for many of my patients. They’re usually administered by injection and work by reducing inflammation in the airways and lowering the frequency of asthma attacks. The best part? They come with fewer side effects than some of the older asthma medications.
However, biologics are not a cure-all, and they tend to be prescribed only after other treatments have been tried and found to be ineffective. If you’re interested in exploring biologics or other new treatments, it’s important to have an in-depth discussion with your doctor about whether it’s the right option for you.
The Future of Asthma Care
The future of asthma care is bright. Researchers continue to uncover new ways to understand and treat asthma, from personalized medicine that tailors treatments to your genetic makeup to cutting-edge therapies that aim to stop asthma at the molecular level. It’s an exciting time to be in the field of respiratory health, and I’m optimistic that these advances will lead to even better outcomes for people living with asthma.

References and Resources
If you’re looking for more information about asthma, here are some trusted resources you can explore:
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for general educational purposes and should not be taken as medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional regarding your specific health concerns and asthma management. Individual treatment plans may vary, and only your doctor can provide personalized recommendations based on your health history and current condition.

Bianca Nala is a compassionate Nurse Practitioner with a strong background in primary and respiratory care. As a health writer for Healthusias.com, she combines her clinical expertise with a talent for clear, relatable storytelling to help readers better understand their health. Bianca focuses on topics like asthma, COPD, chronic cough, and overall lung health, aiming to simplify complex medical topics without losing accuracy. Whether she’s treating patients or writing articles, Bianca is driven by a single goal: making quality healthcare knowledge accessible to everyone.







