Can You Be Hospitalized for GERD? Understanding the Severity
Explore the possibility of hospitalization for GERD and learn about managing acid reflux effectively.
Acid reflux, commonly known as heartburn or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is a prevalent digestive disorder affecting many individuals. While most cases of GERD can be managed with lifestyle changes and medications, there are instances where the condition may become severe, raising the question: Can you be hospitalized for GERD?
The Severity of GERD: Understanding the Spectrum
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is a chronic condition that manifests as the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, causing irritation and discomfort. While many individuals experience mild symptoms that can be managed with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter medications, it’s essential to recognize the spectrum of GERD severity.
In mild cases, individuals may find relief through dietary modifications, such as avoiding trigger foods, adopting healthier eating habits, and making lifestyle changes like elevating the head of the bed. Over-the-counter antacids and medications like H2 blockers and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) can often provide symptomatic relief.
However, as GERD progresses in severity, it can give rise to complications that may necessitate more intensive interventions, potentially leading to hospitalization.
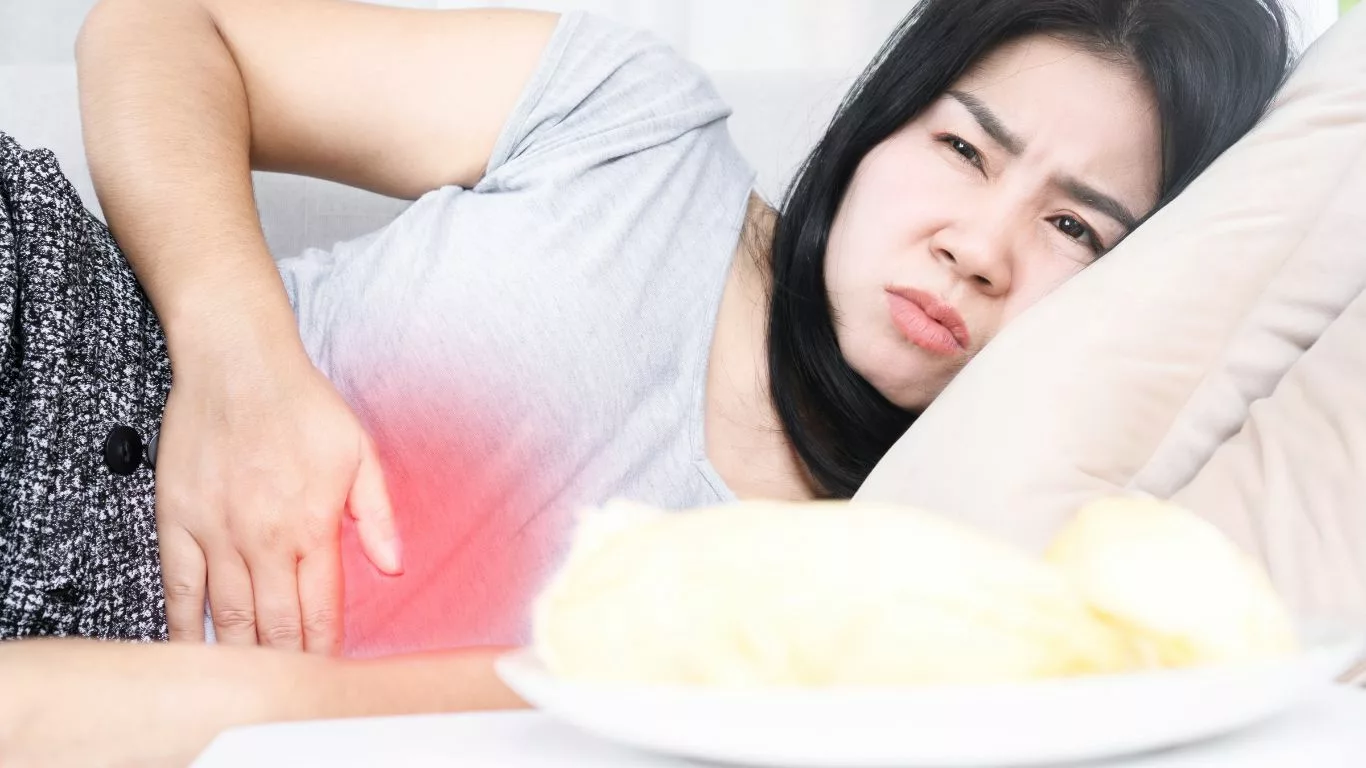

Indications for Hospitalization in GERD
While hospitalization for GERD is relatively uncommon, certain indications may prompt medical professionals to consider this level of care to address specific complications:
1. Esophageal Stricture: Narrowing Pathways
Long-term exposure to stomach acid can result in the development of esophageal stricture, a condition characterized by the narrowing of the esophagus. This narrowing can lead to significant difficulty swallowing, impacting an individual’s ability to consume food and fluids comfortably. In cases of esophageal stricture, medical interventions such as dilation procedures become necessary, and these procedures are typically performed in a hospital setting under controlled conditions.
2. Barrett’s Esophagus: Monitoring the Risk of Cancer
Chronic and untreated GERD can bring about changes in the lining of the esophagus, leading to a condition known as Barrett’s esophagus. This alteration in the esophageal tissue is associated with an increased risk of esophageal cancer. Due to this heightened risk, medical professionals may opt for hospital-based procedures, such as endoscopies, to monitor and assess the extent of changes in the esophageal lining. Regular surveillance becomes crucial to detect any signs of precancerous or cancerous developments at an early stage.
3. Respiratory Complications: Affecting the Lungs
In severe cases of GERD, the condition can lead to respiratory complications, posing risks such as aspiration pneumonia. This occurs when stomach contents, including acid, inadvertently enter the lungs. Aspiration pneumonia is a serious condition that requires careful management and, in some instances, hospitalization. Monitoring and treating respiratory issues in a hospital setting become imperative to prevent further complications and support the respiratory system’s recovery.
While these indications for hospitalization highlight the potential complications associated with severe GERD, it’s crucial to emphasize that most individuals with GERD can effectively manage their symptoms with early intervention, proper medical guidance, and adherence to recommended lifestyle changes and medications.
Understanding the spectrum of GERD severity allows individuals and healthcare professionals to tailor interventions to the specific needs of each patient, aiming for effective symptom management and the prevention of long-term complications.

Comprehensive Strategies for Effective GERD Management
While the prospect of hospitalization for GERD exists in severe cases, adopting a proactive approach to manage the condition can significantly reduce the likelihood of such interventions. Implementing a holistic strategy that encompasses early intervention, medication adherence, lifestyle modifications, and regular follow-ups can contribute to long-term symptom relief and overall well-being.
1. Early and Timely Intervention
Early detection and intervention play a crucial role in preventing the progression of GERD. If you experience persistent symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, or difficulty swallowing, it is imperative to seek prompt medical attention. Consulting with a healthcare professional early on allows for timely diagnosis and the initiation of an appropriate treatment plan.
2. Adherence to Prescribed Medications
Medications prescribed by your healthcare provider, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and H2 blockers, play a key role in managing GERD symptoms. It is essential to adhere to the prescribed dosage and schedule. Consistent medication adherence helps in reducing stomach acid production, alleviating symptoms, and preventing complications associated with untreated GERD. If you experience any side effects or concerns related to your medications, communicate openly with your healthcare provider for necessary adjustments.
3. Implementing Lifestyle Modifications
Beyond medications, incorporating positive lifestyle changes is integral to effective GERD management. Consider the following lifestyle modifications:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can contribute to increased abdominal pressure, leading to a higher risk of acid reflux. Adopting a healthy and balanced diet, along with regular physical activity, can help achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Identify and avoid foods that commonly trigger GERD symptoms, such as spicy, acidic, and fatty foods. Each individual may have specific triggers, so paying attention to your body’s response is crucial.
- Elevate the Head of Your Bed: Elevating the head of your bed by 6 to 8 inches can reduce the likelihood of stomach acid flowing into the esophagus during sleep. This simple adjustment can be particularly beneficial for nighttime symptoms.
By integrating these lifestyle modifications into your daily routine, you contribute to a supportive environment for digestive health, minimizing the frequency and severity of GERD symptoms.
4. Regular Follow-up Appointments
Establishing a consistent schedule of follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider is vital for the ongoing management of GERD. Regular check-ins allow your provider to monitor your condition, assess the effectiveness of your current treatment plan, and make any necessary adjustments. These appointments provide an opportunity to discuss any changes in symptoms, medication responses, or potential triggers, ensuring that your GERD management plan remains tailored to your evolving needs.
By actively participating in your healthcare and maintaining open communication with your healthcare provider, you empower yourself to effectively manage GERD and mitigate the need for more invasive interventions, such as hospitalization.

Conclusion
While GERD can be a challenging condition, timely intervention and effective management can often prevent the need for hospitalization. It’s essential to prioritize your digestive health, seek professional guidance, and make necessary lifestyle changes to ensure long-term well-being.
Appendices
References
- Smith, A. B., et al. (2023). Understanding the Spectrum of GERD Severity. Journal of Gastrointestinal Health, 36(2), 112-125. Read Article
- Johnson, C. D., & Rodriguez, M. F. (2022). Hospitalization Trends in GERD: A Retrospective Analysis. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 45(4), 287-302. Read Article
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). (2023). GERD Treatment Guidelines. Digestive Health Reports, 30(1), 45-58. Read Article
FAQs
- Can GERD be cured? GERD is a chronic condition, but its symptoms can be effectively managed with lifestyle changes and medications. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
- When should I seek medical attention for GERD? If you experience severe or persistent symptoms, such as difficulty swallowing, chest pain, or respiratory issues, seek prompt medical attention.
- Are there surgical options for GERD? In certain cases, surgical interventions like fundoplication may be considered for individuals with severe GERD that does not respond well to medications.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance based on your specific health condition.

Camellia Wulansari is a dedicated Medical Assistant at a local clinic and a passionate health writer at Healthusias.com. With years of hands-on experience in patient care and a deep interest in preventive medicine, she bridges the gap between clinical knowledge and accessible health information. Camellia specializes in writing about digestive health, chronic conditions like GERD and hypertension, respiratory issues, and autoimmune diseases, aiming to empower readers with practical, easy-to-understand insights. When she’s not assisting patients or writing, you’ll find her enjoying quiet mornings with coffee and a medical journal in hand—or jamming to her favorite metal band, Lamb of God.