Chronic Asthma vs Acute Asthma – Understanding the Differences
So, you’re trying to figure out what’s up with chronic asthma vs acute asthma, right? Maybe you’ve heard the terms thrown around but aren’t sure how they’re different. Let’s break it down in simple terms so you can get a clear picture of what’s going on with your breathing!
When people talk about asthma, they often bring up two types: chronic asthma and acute asthma. But what’s the deal with each of these, and how do they affect your lungs? Let’s dive in and explain the differences, why it matters, and how it impacts treatment.
Chronic Asthma: The Long-Term Breathing Buddy
Chronic asthma is basically the asthma that sticks around. It’s long-term and can last for years or even a lifetime. This type of asthma often comes and goes in flare-ups, but the underlying condition is always there, waiting to cause trouble. People with chronic asthma tend to have more frequent symptoms, and they can vary from mild to severe. You might notice things like wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing—especially at night or in the early morning. These symptoms don’t usually go away completely but can be managed with the right treatment. 
Why Does Chronic Asthma Happen?
The exact cause of chronic asthma isn’t fully understood, but it’s believed to be a mix of genetics and environmental factors. Things like allergens (dust, pollen, mold), irritants (smoke, pollution), and even exercise can trigger flare-ups. It’s a chronic condition, meaning it’s always there, just waiting to be triggered.
What Treatment Looks Like
Managing chronic asthma is all about control. It’s not so much about curing it (unfortunately), but more about keeping symptoms at bay. Medications like inhalers (steroid or bronchodilator) are the go-to treatment. These help keep your airways open and reduce inflammation. You might also need to stay on top of your environment, avoiding triggers, and sometimes using long-term control medications, like corticosteroids or leukotriene modifiers, to keep things in check.
Acute Asthma: The Sudden and Intense Attack
On the flip side, we have acute asthma, which is often a sudden flare-up of asthma symptoms. It’s like your asthma showing up out of nowhere and making everything feel much worse, fast. Acute asthma attacks can be triggered by the same things as chronic asthma—like allergens, respiratory infections, or exercise—but the difference is that they happen unexpectedly and can escalate quickly. During an acute asthma attack, the airways become inflamed and constricted, leading to intense difficulty breathing. If you’re having an acute asthma attack, you might notice: – Extreme wheezing or shortness of breath – Tightness in your chest – Trouble talking or walking without gasping for air – Coughing, especially at night 
Why Does Acute Asthma Happen?
Acute asthma attacks often occur when your asthma is poorly controlled, or if you’ve been exposed to a significant trigger. But sometimes, they can happen even if your asthma was under control. Things like a cold or flu can also throw everything off, making acute attacks more likely.
What Treatment Looks Like
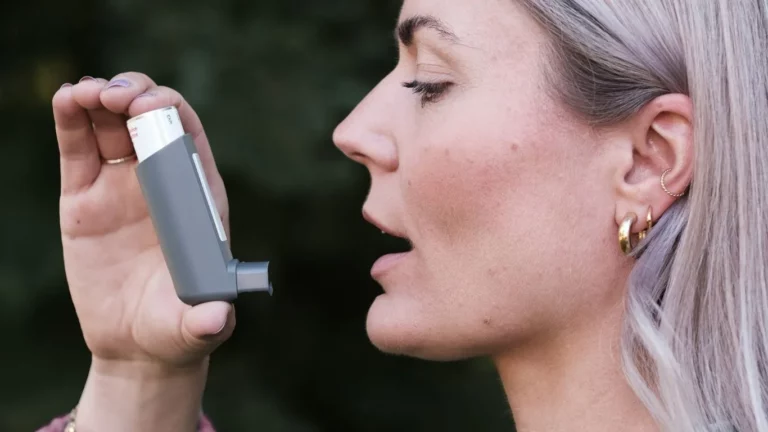
If you’re experiencing an acute asthma attack, it’s all about quick relief. Bronchodilators, which are short-acting inhalers, are the go-to meds to relax and open the airways fast. This is usually the first thing you’ll grab when you’re in trouble, and it can make a huge difference. But if the attack is more severe, you may need to go to the hospital. The goal during an acute attack is to get you breathing better as quickly as possible, sometimes with the help of oxygen therapy or stronger medications.
Key Differences Between Chronic and Acute Asthma
Now that we’ve covered both, let’s summarize the main differences: – Duration: Chronic asthma is a long-term condition, while acute asthma refers to short-term attacks. – Symptoms: Chronic asthma symptoms are ongoing but can be managed. Acute asthma attacks are sudden and intense. – Management: Chronic asthma requires long-term management, like daily medications and lifestyle changes. Acute asthma needs quick-relief treatment and might require emergency care. – Triggers: Both types of asthma can be triggered by similar things like allergens or irritants, but acute asthma attacks are often more unpredictable.
How To Manage Both Types of Asthma
If you’ve got asthma, whether chronic or acute, it’s important to keep things under control. Here’s a simple game plan for managing both types: 1. Know Your Triggers: Keep a list of what sets off your asthma. This could be pet dander, dust, smoke, cold air, etc. Try to avoid or minimize exposure to these things. 2. Keep Your Meds Handy: For chronic asthma, always have your controller meds (like inhaled steroids) and quick-relief inhalers (like albuterol) within reach. 3. Monitor Your Symptoms: Use a peak flow meter to track your lung function. If you notice any decline, take action and see your doctor. 4. Stay Active, But Smart: Exercise is good for your lungs, but if you have asthma, you may need to take it easy or use your inhaler before a workout.
Conclusion: Stay in Control of Your Asthma
Understanding the differences between chronic and acute asthma is key to managing your health. Chronic asthma requires long-term care, but with the right approach, you can minimize flare-ups and lead a normal life. Acute asthma, on the other hand, needs quick intervention to keep you from feeling overwhelmed. If you’ve been feeling like your asthma is out of control, make sure to talk to your doctor. They can help you figure out the best treatment plan to keep your lungs in tip-top shape. 
Appendices
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can acute asthma attacks be prevented? While acute asthma attacks can’t always be prevented, knowing your triggers and managing your chronic asthma with the right medications can help reduce the risk of sudden attacks. 2. Is chronic asthma always severe? Not necessarily. Chronic asthma can range from mild to severe, and some people with chronic asthma may experience only occasional flare-ups. 3. What should I do during an acute asthma attack? Use your quick-relief inhaler immediately. If your symptoms don’t improve quickly, seek medical help right away. 4. Can stress trigger an asthma attack? Yes, stress can contribute to asthma flare-ups for some people. It’s important to manage stress through relaxation techniques and lifestyle adjustments. 5. Is there a cure for chronic asthma? Unfortunately, there’s no cure for chronic asthma, but it can be managed effectively with the right treatment and lifestyle changes.
References
– National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (2023). Asthma Overview. Read More – Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America (2024). Chronic vs Acute Asthma: What’s the Difference? Read More – American Lung Association (2023). Asthma: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments. Read More
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider to discuss your asthma symptoms, triggers, and treatment options.

Bianca Nala is a compassionate Nurse Practitioner with a strong background in primary and respiratory care. As a health writer for Healthusias.com, she combines her clinical expertise with a talent for clear, relatable storytelling to help readers better understand their health. Bianca focuses on topics like asthma, COPD, chronic cough, and overall lung health, aiming to simplify complex medical topics without losing accuracy. Whether she’s treating patients or writing articles, Bianca is driven by a single goal: making quality healthcare knowledge accessible to everyone.