Chronic GERD Symptoms and Solutions: A Complete Guide
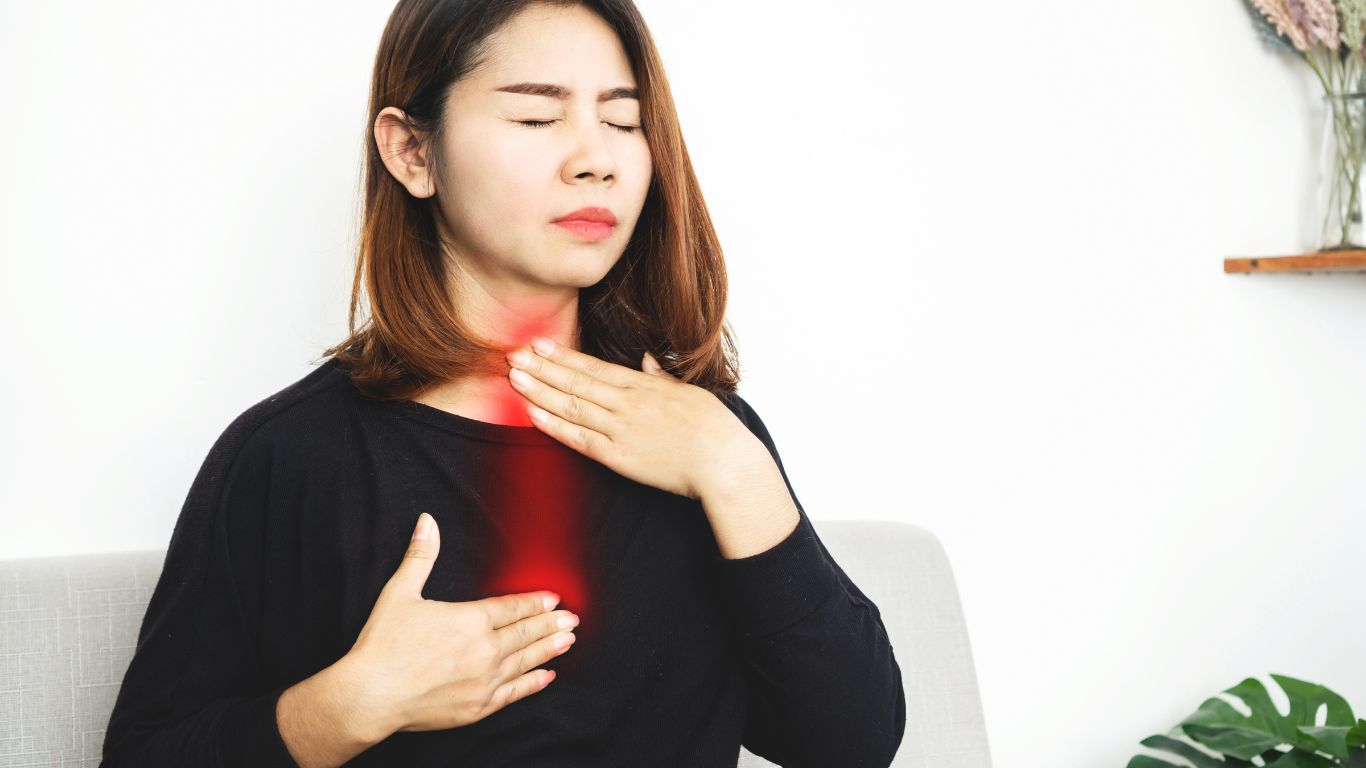
If you’re like me and have ever woken up in the middle of the night with a burning sensation in your chest or an awful taste in your mouth, you might already know the uncomfortable world of chronic GERD. I used to think it was just occasional heartburn — until it turned into something that started interfering with meals, sleep, and even social plans. Chronic Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is more than just a sour stomach; it’s a persistent condition that can lead to serious health complications if not properly managed. Let’s break it all down together.
What Makes GERD “Chronic”?

Chronic GERD is not your typical acid reflux that pops up after a spicy taco night. This version is more stubborn, often lasting longer than a few weeks and returning regularly even with basic over-the-counter antacids. According to NIDDK, GERD becomes chronic when the esophageal lining is frequently exposed to stomach acid, leading to inflammation or even tissue damage over time.
Common Chronic GERD Symptoms That Often Get Ignored
- Chest discomfort: Not quite a heart attack, but unnerving enough to make you second-guess.
- Chronic cough: Especially one that gets worse at night or after meals.
- Throat issues: Hoarseness, sore throat, or a constant need to clear your throat.
- Dysphagia: A fancy word for difficulty swallowing, but something that can be quite distressing.
- Regurgitation: The sensation of acid backing up into your throat or mouth, often bitter or sour-tasting.
Chronic symptoms can sneak up on you. What began as mild heartburn after heavy meals turned into daily discomfort for me. Over time, these signals pointed to something far more long-term. Recognizing early signs is crucial. Here’s a comprehensive guide to GERD symptoms you should never ignore.
What Causes Chronic GERD to Stick Around?
Not everyone with acid reflux will develop chronic GERD. But when it happens, several culprits are often at play:
- Weak lower esophageal sphincter (LES): This is the muscular ring that acts like a gate between your esophagus and stomach. When it’s loose or weakened, acid easily sneaks upward.
- Hiatal hernia: A condition where part of your stomach bulges through your diaphragm, making reflux more likely.
- Obesity: Extra abdominal pressure can push acid back up, especially after meals or when lying down.
- Smoking and alcohol: Both can weaken LES tone and increase acid production.
- Dietary triggers: Citrus, tomato-based sauces, chocolate, caffeine — you name it, GERD loves to crash the party.
There’s also growing evidence that chronic stress plays a role in worsening GERD symptoms by affecting digestion and stomach acid balance. It’s not just physical — your mental state can really stir the pot.
Updated Approaches to Diagnosing Chronic GERD

If your reflux issues aren’t responding to basic remedies or persist beyond a couple of weeks, it might be time to explore more advanced diagnostics. I waited too long and wish I’d pushed for more than just antacids early on.
How Doctors Typically Diagnose It Today
- Endoscopy: A scope is used to examine your esophagus for damage or inflammation.
- 24-hour pH monitoring: This tracks acid levels in the esophagus over an extended period — not comfortable, but really informative.
- Esophageal manometry: Measures how well your esophagus moves and how strong the LES is.
These tools help distinguish between occasional reflux and chronic GERD, which requires a more strategic and ongoing treatment plan.
Current Best Practices for Chronic GERD Management

Living with chronic GERD doesn’t mean you’re stuck in discomfort forever. Management has come a long way — and it’s about more than just popping pills. My gastroenterologist emphasized a layered approach, and honestly, that changed everything for me.
Lifestyle Adjustments That Actually Work
- Smaller meals, more often: Large meals increase pressure on your stomach and LES.
- Raise the head of your bed: Gravity can be your best friend when you’re fighting nighttime reflux.
- Avoid lying down right after eating: Give your digestive system some time to work before you hit the couch.
- Elimination diets: Cutting back on specific triggers can be surprisingly effective — trial and error helped me find mine.
Medications for Chronic Relief
You’ve got your over-the-counter options like antacids and H2 blockers. But for many chronic sufferers, doctors now rely on:
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): These reduce acid production and are often used long-term, though they’re not without risks.
- Prokinetics: These help the stomach empty faster, which can reduce reflux episodes.
For those with severe or refractory GERD, treatments like the LINX device or even fundoplication surgery may be considered. As always, consult with a gastroenterologist before trying or stopping any treatment.
In fact, this comprehensive guide from the Cleveland Clinic breaks down these options beautifully if you want more clinical insight.
Smart Diet Adjustments That Can Ease Chronic GERD

Let’s be real — one of the hardest parts of living with chronic GERD is saying goodbye to your favorite foods. I had to kiss spicy ramen and my late-night pizza sessions goodbye. But, once I made peace with it and swapped those for GERD-friendly alternatives, my symptoms significantly calmed down.
What to Add and Avoid
Here’s what helped me and many others:
- Add: Oatmeal, bananas, green vegetables, ginger, and lean proteins like turkey or chicken.
- Avoid: Citrus fruits, onions, garlic, tomatoes, caffeine, and anything deep-fried or dripping in fat.
You might find this GERD food guide a good place to start adjusting your meals without sacrificing taste.
Simple Meals That Worked Wonders
Honestly, I was surprised how satisfying simple meals became:
- Grilled salmon with steamed broccoli and brown rice
- Oats with almond milk and a touch of honey
- Boiled potatoes with sautéed zucchini (no garlic!)
Portion control is a big deal, too. Eating until you’re 80% full, and chewing slowly — those were game changers for me.
Long-Term Treatment Options for Chronic GERD

Let’s talk long-haul. Chronic GERD is, well, chronic. So short-term fixes like antacids are usually not enough. If medications like PPIs are not cutting it or are leading to side effects (I had nasty bloating after long-term use), there are more targeted strategies available.
Advanced Interventions You Should Know About
- LINX Procedure: A small magnetic ring is implanted to reinforce the LES muscle. It’s FDA-approved and quite popular now.
- Fundoplication: Surgical technique to strengthen the LES by wrapping the top of the stomach around it — sounds extreme, but for some, it’s life-changing.
- Endoscopic therapies: Less invasive and suitable for early cases, they aim to restore valve function with techniques like radiofrequency stimulation.
If your GERD has become stubborn and you’ve tried every natural remedy under the sun, this detailed breakdown on permanent relief is worth a read.
Complications of Chronic GERD You Shouldn’t Ignore

When GERD sticks around long enough without proper care, it’s not just annoying — it’s dangerous. Trust me, I ignored it for a while, and that led to esophageal inflammation so bad I couldn’t even handle soft bread.
Common Long-Term Risks
- Esophagitis: Inflammation that leads to pain, ulcers, and even bleeding.
- Barrett’s Esophagus: A precancerous condition where esophageal cells start to change due to ongoing acid exposure.
- Strictures: Narrowing of the esophagus which makes swallowing a painful challenge.
Even Mayo Clinic warns that untreated GERD can increase the risk of esophageal cancer. That’s why taking it seriously, especially if it’s chronic, isn’t just about comfort — it’s about long-term health.
Strategies to Live Well With Chronic GERD

Living with chronic GERD doesn’t mean living in fear. I’ve adapted. You can too. It’s about creating a GERD-safe lifestyle that still feels like you.
Habits That Helped Me the Most
- Mindful eating: Slowing down during meals and chewing thoroughly made more of a difference than I expected.
- Stress management: I started doing 10-minute breathing exercises after meals — it actually worked.
- Tracking symptoms: Keeping a reflux journal helped me see patterns in what triggered my flare-ups.
- Staying upright: Posture matters more than we think, especially after eating. I keep a gentle walk routine after dinner now.
Integrating Holistic Tools
More people, including myself, are now turning to supportive tools like herbal teas, probiotics, and yoga. I was skeptical at first, but honestly, even adding the right probiotics gave me relief I didn’t get from meds alone.
All said and done, managing chronic GERD is about being proactive and intentional. You don’t have to overhaul your life overnight — small changes add up. From your meals to your mindset, it all plays a role.

Camellia Wulansari is a dedicated Medical Assistant at a local clinic and a passionate health writer at Healthusias.com. With years of hands-on experience in patient care and a deep interest in preventive medicine, she bridges the gap between clinical knowledge and accessible health information. Camellia specializes in writing about digestive health, chronic conditions like GERD and hypertension, respiratory issues, and autoimmune diseases, aiming to empower readers with practical, easy-to-understand insights. When she’s not assisting patients or writing, you’ll find her enjoying quiet mornings with coffee and a medical journal in hand—or jamming to her favorite metal band, Lamb of God.