Difference Between Asthma and Bronchitis: What’s the Real Distinction?
Wondering whether your coughing and wheezing are signs of asthma or bronchitis? Let’s break it down and clear up the confusion!
What Is Asthma?
Asthma is a chronic condition where the airways in the lungs are inflamed, making it harder to breathe. Think of it like the air passages getting irritated or constricted, which leads to difficulty breathing. People with asthma often have periods where they experience wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath, especially during physical activity, allergies, or exposure to irritants.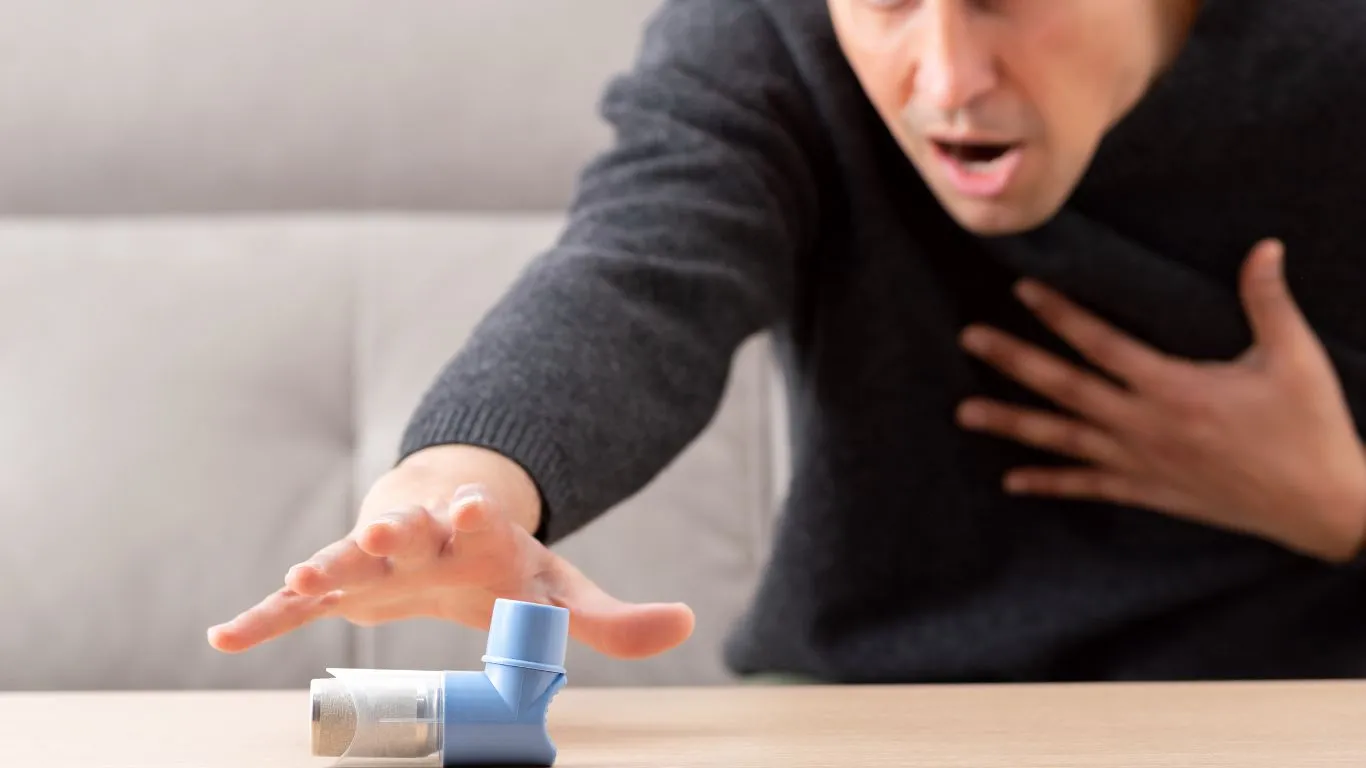 
What Is Bronchitis?
Bronchitis, on the other hand, is the inflammation of the bronchial tubes that carry air to your lungs. It usually happens because of an infection (viral or bacterial) or from irritants like smoke. It’s typically more of a short-term condition that leads to a persistent cough, mucus production, and sometimes even fever. There are two types: acute (which usually lasts for a few weeks) and chronic (which is ongoing and associated with smoking).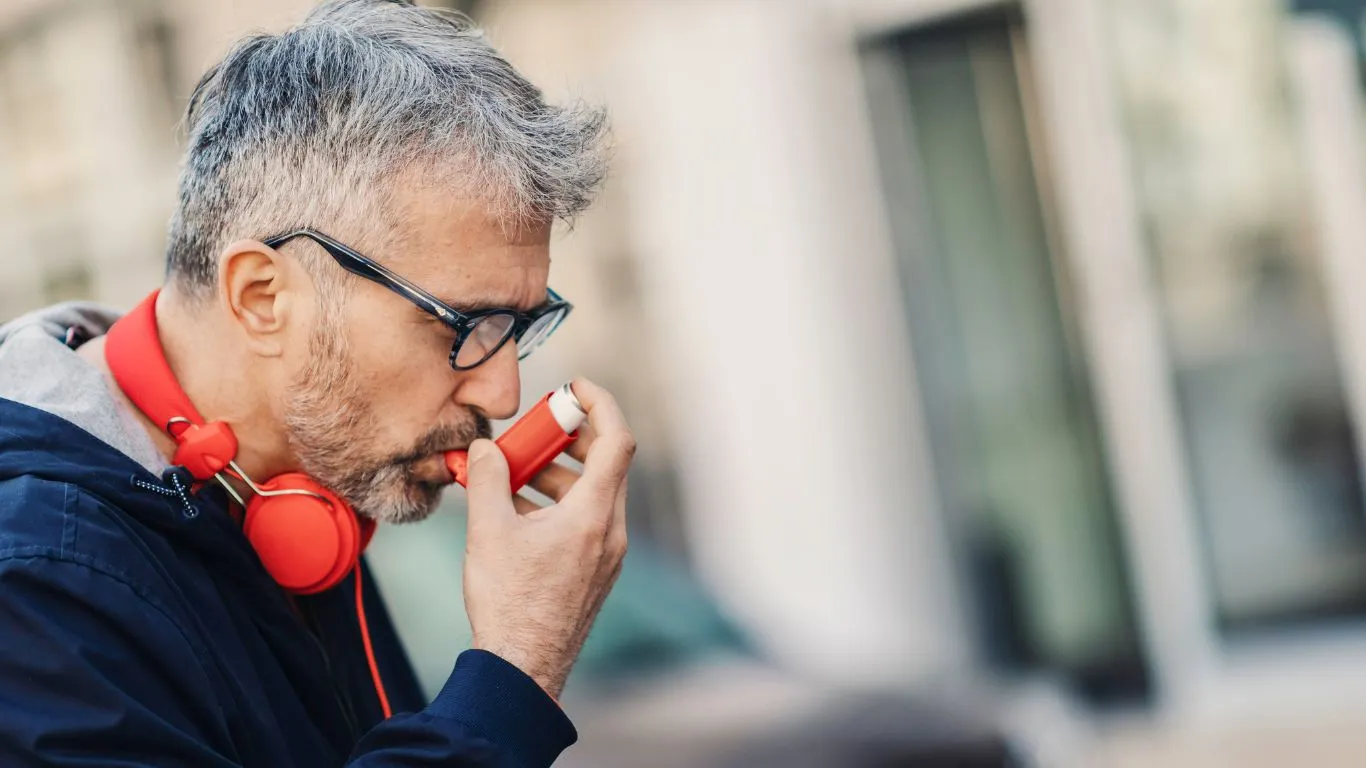 
Key Differences: Asthma vs. Bronchitis
While asthma and bronchitis might seem similar at first, there are some key differences to be aware of.
- Cause: Asthma is often triggered by allergens, air pollution, exercise, or cold air. In contrast, bronchitis is mainly caused by infections or prolonged exposure to irritants like cigarette smoke.
- Duration: Asthma is a chronic condition, meaning it lasts for a long time and can be managed but not cured. Bronchitis can be either short-term (acute) or long-term (chronic) depending on the type.
- Symptoms: Asthma symptoms tend to worsen at night or with exercise, while bronchitis usually comes with a persistent cough, mucus, and chest discomfort.
- Treatment: Asthma is typically treated with inhalers (like corticosteroids and bronchodilators) to open up the airways. Bronchitis treatment may involve antibiotics (for bacterial infections) and cough medicine, but asthma inhalers aren’t typically used for bronchitis.

Similarities Between Asthma and Bronchitis
Despite the differences, these two conditions share a few common symptoms:
- Persistent coughing
- Wheezing
- Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity
- Chest tightness
However, understanding the triggers and underlying causes of each can help you figure out what’s going on.
How to Know Which One You Have
So, how do you know whether you’ve got asthma or bronchitis? The best thing to do is see a doctor. They’ll listen to your symptoms, look at your medical history, and may even run tests (like lung function tests or chest X-rays) to figure out what’s going on. 
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between asthma and bronchitis is crucial for effective treatment and symptom management. While they share some similar symptoms, their causes and long-term impacts are quite different. If you’re unsure, visiting your healthcare provider is always a good idea!
Appendices
References
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI). (2024). Asthma and Bronchitis: Key Differences. Read Article
- American Lung Association. (2024). Bronchitis and Asthma: Understanding Your Diagnosis. Read Article
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Asthma vs. Bronchitis: Symptoms and Treatment. Read Article
FAQs
- Can asthma and bronchitis occur together? Yes, it’s possible for someone with asthma to develop bronchitis, especially if they’re exposed to irritants like smoke or viruses. This can make managing both conditions a bit trickier.
- Is bronchitis contagious? Acute bronchitis, caused by a viral infection, can be contagious. It’s best to avoid close contact with others while you’re sick.
- How do I know if my cough is asthma-related? If your cough comes with wheezing or shortness of breath, it could be asthma. A doctor can confirm this with lung function tests.
- Can bronchitis turn into asthma? Bronchitis doesn’t usually turn into asthma, but chronic bronchitis can increase your risk of developing other lung conditions, including asthma.
- Can smoking cause both asthma and bronchitis? Yes, smoking is a major trigger for both conditions. It can worsen asthma symptoms and also lead to chronic bronchitis.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and does not substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment. Individual needs may vary, and personalized care is important for managing asthma or bronchitis.

Bianca Nala is a compassionate Nurse Practitioner with a strong background in primary and respiratory care. As a health writer for Healthusias.com, she combines her clinical expertise with a talent for clear, relatable storytelling to help readers better understand their health. Bianca focuses on topics like asthma, COPD, chronic cough, and overall lung health, aiming to simplify complex medical topics without losing accuracy. Whether she’s treating patients or writing articles, Bianca is driven by a single goal: making quality healthcare knowledge accessible to everyone.