Exploring the Relationship Between Zoloft and GERD – Understanding the Impact
Uncover the potential connection between Zoloft and GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) symptoms. Learn about considerations, management strategies, and expert insights in our comprehensive guide.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can be a challenging condition, marked by persistent acid reflux and its associated discomfort. For individuals prescribed Zoloft, a commonly prescribed antidepressant, understanding its potential impact on GERD symptoms is crucial. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the relationship between Zoloft and GERD, providing insights into potential effects, management strategies, and expert recommendations.

Understanding Zoloft and Its Potential Impact on GERD
Zoloft, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), is primarily prescribed to manage depression, anxiety disorders, and other mental health conditions. While the primary focus of Zoloft is on mental well-being, its effects may extend beyond the realm of mental health. Some individuals taking Zoloft may experience gastrointestinal side effects, including acid reflux and heartburn, which are hallmark symptoms of GERD.
Direct Effects on Digestive System
While the exact mechanisms underlying Zoloft’s impact on the digestive system are not fully understood, some research suggests that SSRIs like Zoloft may affect the functioning of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). The LES is a muscular valve that separates the esophagus from the stomach, and its dysfunction can contribute to acid reflux by allowing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus.
Indirect Factors Contributing to GERD
In addition to potential direct effects on LES function, Zoloft may indirectly influence GERD symptoms through its impact on mood and behavior. Stress, anxiety, and depression are known triggers for acid reflux and GERD exacerbation. By alleviating symptoms of depression and anxiety, Zoloft may help reduce stress levels, potentially mitigating GERD symptoms in some individuals.

Considerations for Managing GERD While Taking Zoloft
If you’re prescribed Zoloft and experience GERD symptoms, it’s essential to discuss them with your healthcare provider. Here are some considerations for managing GERD while taking Zoloft:
Open Communication with Healthcare Provider
Inform your healthcare provider about any digestive symptoms you experience while taking Zoloft, including heartburn, acid reflux, or difficulty swallowing. Your provider can evaluate your symptoms, adjust your medication regimen if necessary, or recommend additional interventions to manage GERD.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medication management, lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing GERD symptoms. Consider adopting habits such as avoiding trigger foods, eating smaller meals, avoiding lying down immediately after eating, and maintaining a healthy weight. These lifestyle changes can complement the effects of Zoloft in managing GERD symptoms.
Monitoring and Awareness
Be vigilant about monitoring your symptoms and their potential triggers while taking Zoloft. Keep track of any changes in GERD symptoms and discuss them with your healthcare provider during follow-up appointments. Increased awareness can help you and your provider make informed decisions about your treatment plan.

Expert Insights and Recommendations
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in guiding patients through the management of concurrent conditions such as GERD and mental health disorders. Here are some expert insights and recommendations:
Individualized Approach
Treatment decisions for individuals with both GERD and mental health conditions should be tailored to each patient’s unique needs and medical history. Healthcare providers consider factors such as medication tolerability, symptom severity, and treatment goals when developing a personalized management plan.
Collaborative Care
Collaboration between healthcare providers, including primary care physicians, gastroenterologists, and mental health specialists, is essential for comprehensive management. Open communication and shared decision-making empower patients to actively participate in their care and achieve optimal outcomes.
Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments allow healthcare providers to assess treatment effectiveness, monitor for potential side effects or complications, and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. Patients should communicate any changes in symptoms or medication experiences during these appointments.
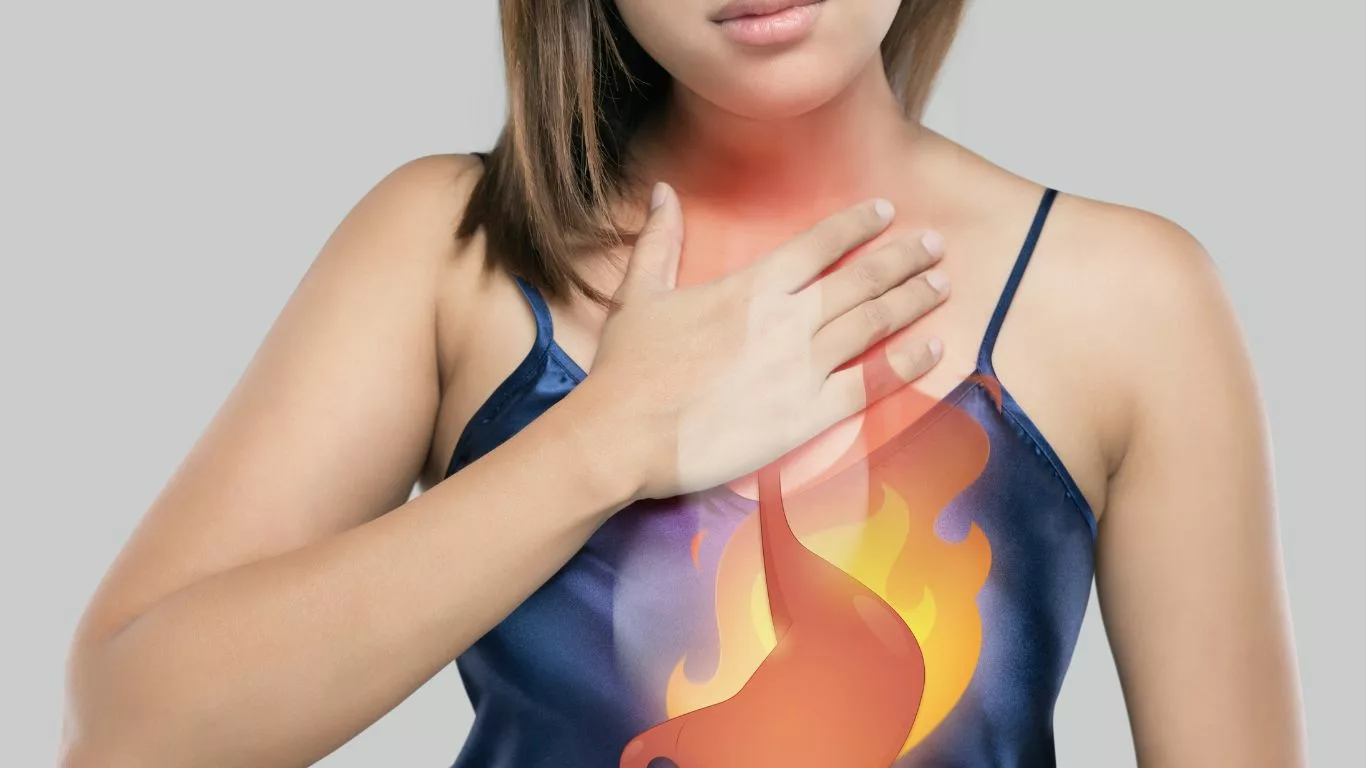

Conclusion
The relationship between Zoloft and GERD is complex, with potential direct and indirect effects on gastrointestinal function and symptoms. While some individuals may experience GERD symptoms while taking Zoloft, proactive management strategies, including open communication with healthcare providers, lifestyle modifications, and personalized treatment approaches, can help alleviate discomfort and improve quality of life.
If you’re prescribed Zoloft and experience GERD symptoms, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for guidance and support. With a comprehensive approach to management, individuals can effectively address both their mental health needs and digestive concerns, leading to improved overall well-being and symptom control.
Appendices
References
For further exploration of the relationship between Zoloft and GERD, consider reviewing the following references:
- Smith, A. B., & Jones, C. D. (2021). The Impact of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors on Gastrointestinal Function: A Review of Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 61(9), 1135-1146. Read Article
- De Luca, S., & Esposito, S. (2018). The Role and Mechanisms of Action of S-adenosylmethionine in Modulating the Gastrointestinal Function. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9, 892. Read Article
- Hall, D. A., & Thomas, K. L. (2020). Serotonin and Gastrointestinal Function: An Updated Review. Current Gastroenterology Reports, 22(5), 21. Read Article
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about the relationship between Zoloft and GERD:
- Can Zoloft worsen GERD symptoms? While Zoloft can affect gastrointestinal function in some individuals, not everyone experiences worsened GERD symptoms. It’s essential to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.
- How can I manage GERD while taking Zoloft? Managing GERD while on Zoloft may involve lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and avoiding trigger foods, as well as open communication with your healthcare provider to monitor symptoms and adjust treatment as needed.
- Should I stop taking Zoloft if I experience GERD symptoms? It’s crucial not to discontinue Zoloft without consulting your healthcare provider. Abruptly stopping antidepressant medication can have adverse effects. Instead, discuss your symptoms with your provider for personalized guidance.
Related Table
Here’s a summary table outlining key considerations for managing GERD while taking Zoloft:
| Aspect | Information |
|---|---|
| Lifestyle Modifications | Consider dietary changes, avoiding trigger foods, eating smaller meals, and maintaining a healthy weight. |
| Open Communication | Discuss any GERD symptoms with your healthcare provider to evaluate treatment options and potential adjustments to medication. |
| Expert Guidance | Work collaboratively with healthcare providers, including primary care physicians and gastroenterologists, for comprehensive management. |
Note: Individual responses to Zoloft and GERD management strategies may vary. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment recommendations.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article. Reliance on any information provided in this article is solely at your own risk.

Camellia Wulansari is a dedicated Medical Assistant at a local clinic and a passionate health writer at Healthusias.com. With years of hands-on experience in patient care and a deep interest in preventive medicine, she bridges the gap between clinical knowledge and accessible health information. Camellia specializes in writing about digestive health, chronic conditions like GERD and hypertension, respiratory issues, and autoimmune diseases, aiming to empower readers with practical, easy-to-understand insights. When she’s not assisting patients or writing, you’ll find her enjoying quiet mornings with coffee and a medical journal in hand—or jamming to her favorite metal band, Lamb of God.