GERD Chest Pain: How to Identify and Manage It Effectively
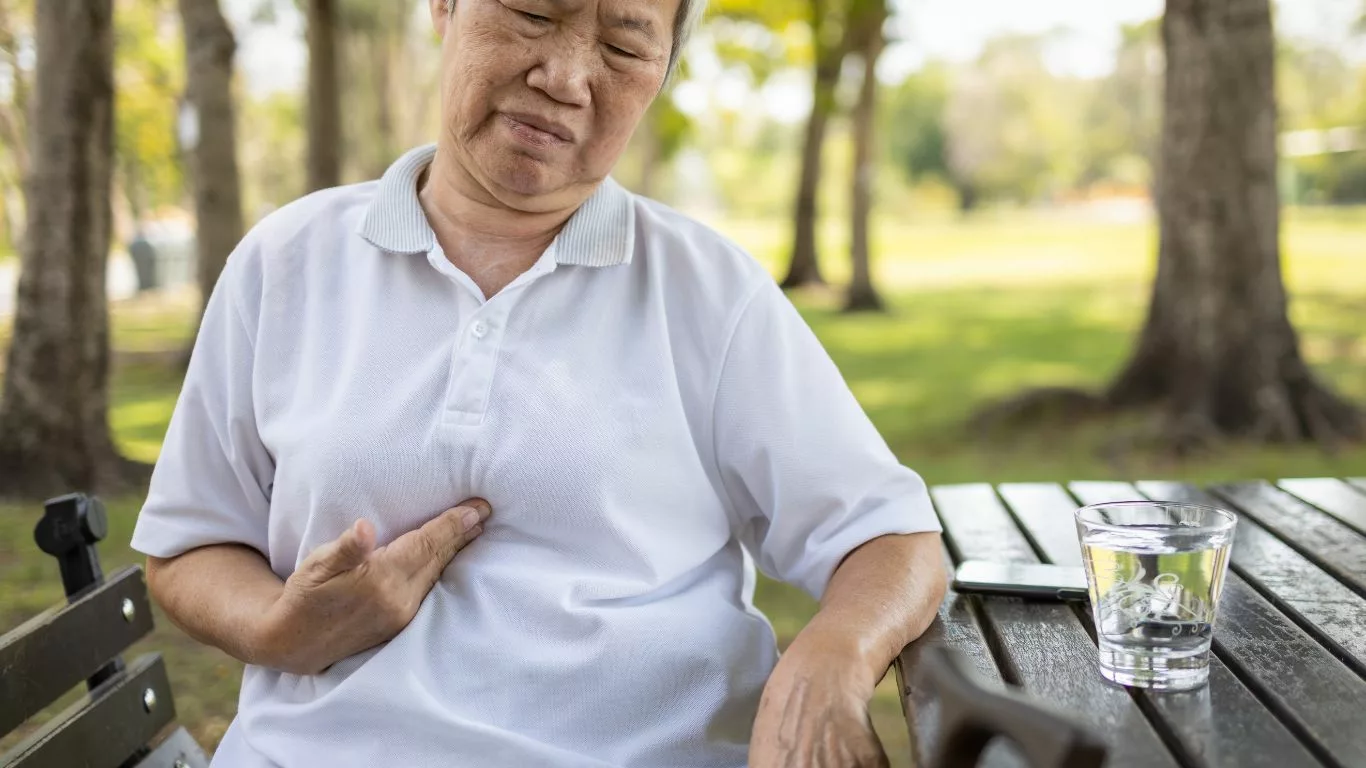
If you’ve ever felt a tight, burning sensation in your chest that made you wonder, “Is this heartburn or something more serious?” — you’re not alone. I’ve been there too, pacing the living room in the middle of the night, trying to convince myself it wasn’t a heart attack. Chest pain caused by GERD can mimic cardiac events so closely that it’s downright terrifying. The tricky part? It’s more common than most people realize, yet often misunderstood or misdiagnosed. Let’s unpack what’s really going on when GERD messes with your chest.
Why GERD Triggers Chest Pain

It’s Not Your Heart—It’s Your Esophagus
GERD, or gastroesophageal reflux disease, happens when stomach acid escapes upward into the esophagus. Unlike the stomach, the esophageal lining isn’t built to handle acid. The result? Inflammation, irritation, and—you guessed it—pain. The chest pain caused by GERD can be intense and located right behind the breastbone, leading many people to fear they’re experiencing a cardiac episode.
How Acid Reflux Causes That Burning Sensation
When acid flows back up, it stimulates nerve endings in the esophagus. Some of these nerves are linked to the same network that communicates heart pain to the brain, so it’s no surprise the symptoms feel similar. This is why differentiating GERD chest pain from cardiac pain can be so challenging without medical help.
Contributing Triggers That Make It Worse
- Large or fatty meals
- Lying down too soon after eating
- Smoking and alcohol
- Caffeine and carbonated beverages
- Tight clothing (you’d be surprised how often this makes things worse!)
Common Symptoms That Accompany GERD Chest Pain

It’s Not Always Just the Pain
I used to think chest pain was the only sign I needed to watch for, but I quickly learned GERD is a shapeshifter. It shows up in sneaky ways that often catch people off guard.
- Burning sensation: Often described as a fire creeping up the chest, especially after meals.
- Regurgitation: That bitter acid taste rising into the throat. Ugh, the worst!
- Difficulty swallowing: A tightening or the sensation of food getting stuck.
- Chronic cough or throat clearing: Especially at night.
- Shortness of breath or wheezing: This one overlaps with asthma-like symptoms.
How to Know It’s GERD and Not a Heart Attack
This is one area you never want to self-diagnose recklessly. Chest pain is always a red flag that deserves attention. However, there are clues that suggest GERD over cardiac causes:
- The pain gets worse when lying down or after eating
- Antacids relieve the pain
- No radiating pain to arms or jaw
- No sweating or shortness of breath (though GERD can sometimes cause mild versions)
If there’s ever a doubt, get checked out. A visit to the ER is better than second-guessing your heart.
When Chest Pain Becomes a Daily Struggle

Chronic GERD Pain: What It Feels Like
There was a point in my life when chest pain became a daily visitor. I started associating meals with fear. The pressure, the tightness, the heat—it all blended into a miserable routine. Chronic GERD-related chest pain tends to feel dull, persistent, and often occurs with other symptoms like throat irritation or bloating.
The Mental Toll It Takes
Let’s not gloss over this. GERD doesn’t just mess with your body—it shakes your confidence. It makes you second-guess your health. According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), GERD can significantly affect quality of life, from anxiety to disrupted sleep and even depression.
Related Issues That Worsen Chest Pain
Tests and Diagnosis: Getting the Right Answers

How Doctors Confirm GERD as the Culprit
When I finally sought help, the process started with some simple questions and escalated to more advanced tests. Your doctor might suggest:
- Upper endoscopy: A flexible tube looks at the esophagus for damage.
- pH monitoring: Measures acid in your esophagus over 24 hours. Annoying? Yes. Worth it? Definitely.
- Esophageal manometry: Checks the strength and function of esophageal muscles.
If you’re curious about what a thorough diagnostic process looks like, check out our GERD diagnosis guide from our core pillar articles.
Managing GERD Chest Pain: Lifestyle Adjustments That Make a Difference

Small Changes, Big Relief
When I first started battling GERD chest pain, I threw every medication at it—antacids, PPIs, you name it. But the real game-changer? Shifting my daily habits. Managing GERD isn’t just about what pill you take—it’s about how you live. And it turns out, a lot of the triggers were hiding in plain sight.
- Eat smaller meals: Overeating was a guaranteed way to bring on the fire. I switched to eating more frequently, but smaller portions.
- Stay upright after meals: No more couch-naps right after lunch. I make it a rule to stay upright for at least 2 hours post-meal.
- Elevate the head of your bed: I added a wedge pillow—lifesaver. Gravity actually helps keep stomach acid in check while you sleep.
- Limit trigger foods: Spicy dishes, caffeine, chocolate—yes, chocolate (heartbreaking, I know).
Clothing and Posture Matter Too
It sounds minor, but tight clothes—especially around the waist—can increase abdominal pressure and make reflux worse. I had to retire a few pairs of jeans I used to love. Also, poor posture (especially slouching at a desk) puts extra pressure on your stomach. A more mindful sitting habit helped reduce my symptoms noticeably.
Treatment Options: Medications and More

Over-the-Counter Options
OTC meds became my go-to during flare-ups. But be warned—they’re a band-aid, not a cure.
- Antacids: Quick relief (think Tums), but don’t last long.
- H2 blockers: Longer-lasting but take more time to kick in.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): Great for long-term acid suppression, but not meant for indefinite use without a doctor’s supervision.
Prescription Medications
If OTC isn’t cutting it, doctors may prescribe stronger versions or combinations. In my case, a short round of prescription-strength omeprazole paired with lifestyle changes helped reset my system.
Surgical and Non-Surgical Interventions
In severe or treatment-resistant cases, doctors may recommend options like:
- LINX device: A magnetic ring implanted around the LES (lower esophageal sphincter) to prevent acid reflux.
- Fundoplication: A surgical procedure to tighten the LES using the top of your stomach.
Most people with GERD won’t need surgery, but it’s reassuring to know solutions exist if medication and lifestyle adjustments aren’t enough. Learn more about GERD surgery options here.
When to See a Doctor (Seriously, Don’t Wait)

Red Flags That Need Medical Attention
Chest pain is never something to mess around with. Even if you suspect GERD, there are symptoms that absolutely warrant a trip to the doctor or ER:
- Severe or crushing chest pain
- Pain radiating to jaw, arms, or neck
- Shortness of breath, dizziness, or fainting
- Black or bloody stools (a sign of GI bleeding)
Don’t self-diagnose or ignore the signs. I once put off seeing a doctor for weeks until the pain became unbearable—and it turned out I had developed mild esophagitis. A quick scope and treatment plan fixed it, but earlier action would’ve saved a lot of pain (and sleepless nights).
How Long Does GERD Chest Pain Last?

Understanding the Duration
The length of GERD chest pain varies wildly. Some people feel a dull ache for hours, others have sharp pain that comes and goes within minutes. In my experience, it typically ramped up after meals and lingered until I made changes—both with diet and position.
According to the Mayo Clinic, persistent heartburn and chest pain that last more than twice a week may indicate chronic GERD and requires medical treatment to avoid complications like Barrett’s esophagus.
Tracking Triggers Can Help
I started keeping a journal—jotting down meals, symptoms, timing, stress levels. Over time, it became clear what foods were troublemakers and what habits needed tweaking. That awareness gave me back control.
What Happens If You Leave It Untreated?

Complications You Don’t Want
Ignoring chest pain tied to GERD isn’t just uncomfortable—it’s dangerous. Long-term reflux can lead to:
- Esophagitis: Ongoing inflammation of the esophagus lining
- Strictures: Narrowing of the esophagus that makes swallowing tough
- Barrett’s esophagus: A precancerous condition from repeated acid damage
If you’re dealing with persistent chest discomfort, don’t write it off as “just reflux.” Managing GERD early helps prevent a chain of more serious digestive issues. For more on long-term outcomes, you can read about GERD complications here.
If you’re still unsure what’s causing your chest discomfort or feel like your GERD is getting worse even with changes, take action sooner rather than later. Understanding the difference between benign heartburn and something more serious could literally be life-saving.

Camellia Wulansari is a dedicated Medical Assistant at a local clinic and a passionate health writer at Healthusias.com. With years of hands-on experience in patient care and a deep interest in preventive medicine, she bridges the gap between clinical knowledge and accessible health information. Camellia specializes in writing about digestive health, chronic conditions like GERD and hypertension, respiratory issues, and autoimmune diseases, aiming to empower readers with practical, easy-to-understand insights. When she’s not assisting patients or writing, you’ll find her enjoying quiet mornings with coffee and a medical journal in hand—or jamming to her favorite metal band, Lamb of God.