GERD Symptoms in Young Adults – A Comprehensive Guide
In this guide, we will dive into the details of GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) symptoms in young adults, how it affects daily life, and what you can do to manage the discomfort. If you or someone you know is dealing with GERD, you’re not alone. We’ll break down everything from the causes to the treatment options, with real-life examples and easy-to-understand advice.

What is GERD?
Before we dive into the symptoms, let’s first clarify what GERD is. GERD stands for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, and it happens when stomach acid or bile irritates the food pipe lining. Basically, it’s when your stomach contents push back into your esophagus, leading to that all-too-familiar burning sensation, chest pain, and other uncomfortable symptoms. While many people associate GERD with older adults, it can affect young people, too.
The good news is that you don’t have to just “live with it.” Recognizing the symptoms early on and knowing what to do can make a huge difference. So, let’s talk about those symptoms in more detail.

Common GERD Symptoms in Young Adults
Young adults may not typically be the first group that comes to mind when we think of GERD. However, this condition is on the rise among younger populations, partly due to lifestyle choices, stress, and dietary habits. So, if you’re dealing with any of the following symptoms, you might want to pay closer attention:
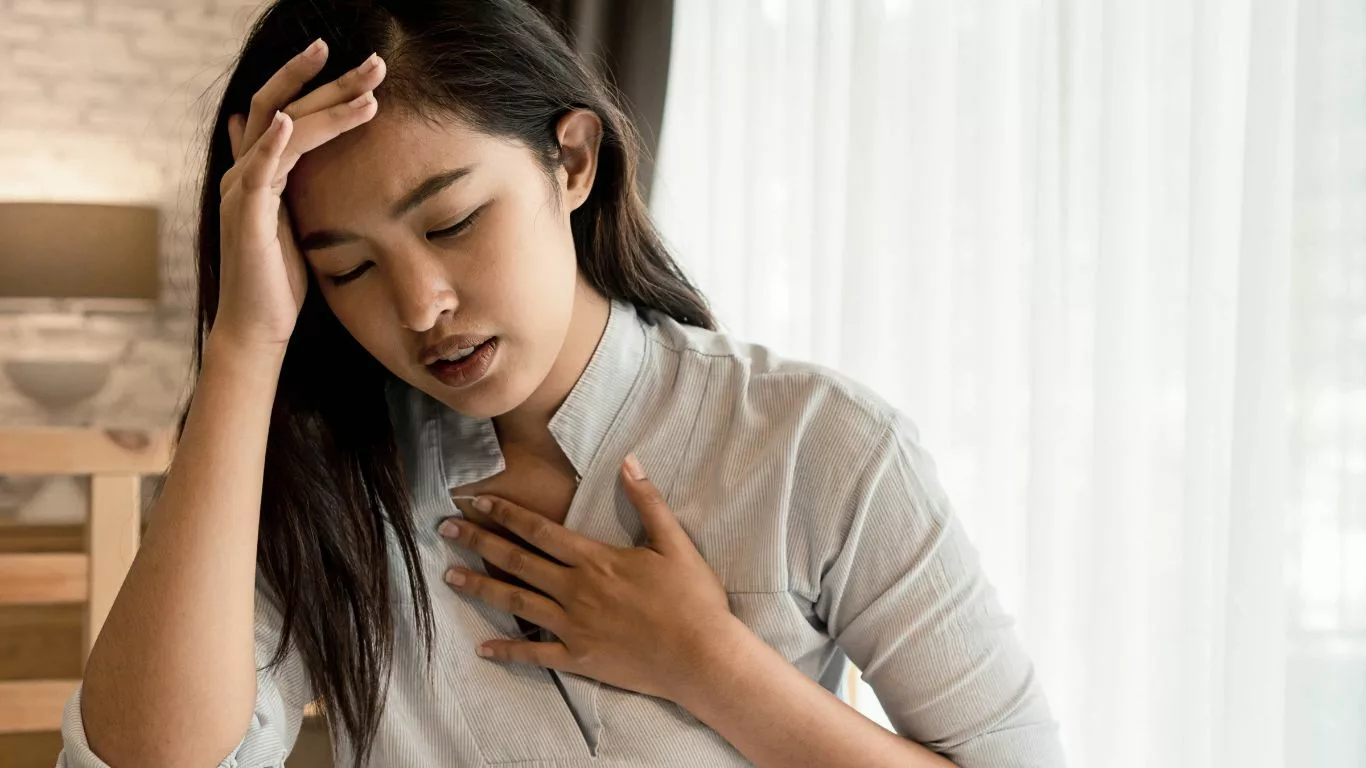
1. Heartburn
This is the classic symptom that most people associate with GERD. Heartburn is a burning sensation that rises from the stomach into the chest and sometimes even the throat. It’s often worse after eating, lying down, or bending over. You may have noticed that certain foods like pizza, spicy meals, or chocolate make it worse—this is because they can trigger acid reflux.
Real-life example: “I thought I just had a heavy dinner once and felt that burning sensation in my chest for hours. It was intense and kept me up at night. I started noticing it more after eating certain foods like fried chicken or pasta.” – Sarah, 23
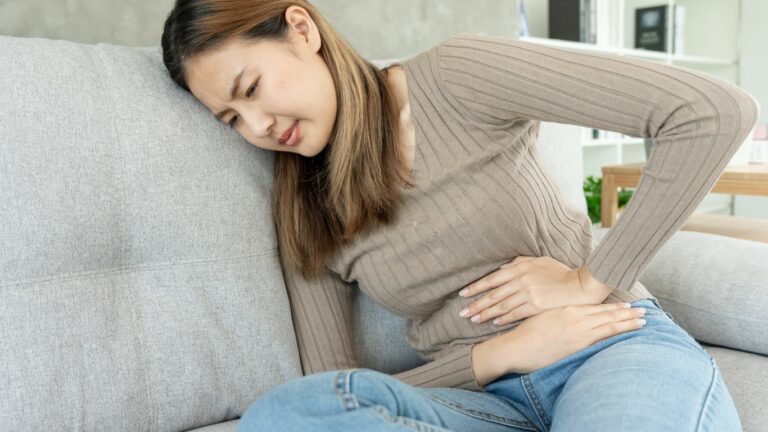
2. Regurgitation
This is when food or liquid comes back up into your mouth from your stomach. It can be a bitter or sour taste and is often referred to as acid reflux. If this happens frequently, it can lead to complications like tooth erosion or damage to the esophagus lining.
3. Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia)
You might feel like food is stuck in your throat, or that swallowing is uncomfortable. This could be due to irritation in the esophagus, which can narrow or become inflamed over time. This symptom is especially common if GERD is left untreated.
4. Chest Pain
While chest pain can be linked to a variety of causes, GERD is a common culprit. It’s often mistaken for a heart attack or other heart-related issues, especially if the pain occurs after eating or when lying down. If you experience chest pain, it’s important to seek medical attention to rule out any serious conditions.
5. Chronic Cough or Hoarseness
If you find yourself coughing frequently, especially at night, GERD could be the cause. Stomach acid that travels up into the esophagus and throat can irritate the airways, causing a chronic cough or a hoarse voice. This is sometimes mistaken for allergies or a common cold, but if it lingers, GERD could be to blame.

Causes of GERD in Young Adults
GERD in young adults can be triggered by several lifestyle and physiological factors. Here’s a closer look at the common causes:
1. Dietary Habits
Certain foods can contribute to GERD by relaxing the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a muscle that prevents acid from moving up into the esophagus. Foods like citrus fruits, spicy dishes, chocolate, caffeine, and fatty meals can trigger GERD symptoms.
2. Obesity
Being overweight or obese increases the risk of developing GERD. Extra weight puts pressure on the stomach, making it easier for acid to escape and irritate the esophagus.
3. Stress
Stress plays a huge role in GERD for young adults. Many of us deal with anxiety, work, and school pressures that can exacerbate stomach acid production. Plus, stress often leads to poor eating habits, like eating late at night or consuming comfort foods that trigger GERD.
4. Smoking and Alcohol
Both smoking and alcohol can relax the LES, making it easier for stomach acid to reflux into the esophagus. If you’re a smoker or regularly drink alcohol, this can contribute to your GERD symptoms.
5. Eating Before Bed
Eating large meals or snacking close to bedtime can trigger GERD. Lying down after eating makes it easier for acid to travel back up into the esophagus. Try to wait at least 2-3 hours after eating before lying down.
How to Manage GERD in Young Adults
Living with GERD doesn’t mean you have to suffer through every symptom. Here are a few practical tips for managing GERD in young adults:
1. Adjust Your Diet
The first step to managing GERD is to identify foods that trigger your symptoms and avoid them. Opt for smaller, more frequent meals instead of large ones. Focus on lean proteins, whole grains, and vegetables. Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
2. Elevate Your Head While Sleeping
If you experience acid reflux at night, elevate the head of your bed by about 6 to 8 inches. This can help prevent stomach acid from traveling up into your esophagus while you sleep.
3. Lose Weight (If Necessary)
If you’re carrying excess weight, losing a few pounds can help reduce pressure on your stomach and reduce GERD symptoms.
4. Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol
Both smoking and alcohol are big GERD triggers, so quitting smoking and reducing alcohol consumption can make a significant difference.
5. Over-the-Counter Antacids
Over-the-counter medications like antacids can help neutralize stomach acid. However, if you find yourself relying on them regularly, it might be time to consult a doctor.
6. Consult a Doctor
If your symptoms persist or worsen, it’s time to see a healthcare professional. They might prescribe stronger medications like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or recommend other treatments like lifestyle changes or even surgery in severe cases.
Conclusion
GERD symptoms in young adults can be a real hassle, but understanding what’s going on and making simple changes can help manage the discomfort. From adjusting your diet to stress management and avoiding triggers, there are several ways to reduce GERD’s impact on your life. Don’t ignore the symptoms—addressing them early on can save you a lot of trouble in the long run. If you’re experiencing severe symptoms or they’re interfering with your daily activities, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider for guidance.
Appendices
FAQs
- Can GERD be cured in young adults? GERD can be managed with lifestyle changes and medications, but it often requires ongoing management rather than a complete cure.
- What foods should I avoid with GERD? Common triggers include spicy foods, chocolate, citrus, caffeine, and fatty or fried foods.
- How do I know if I have GERD? Frequent heartburn, regurgitation, chest pain, and difficulty swallowing are common symptoms of GERD.
- Is GERD common in young adults? Yes, GERD is becoming more common in young adults due to factors like diet, stress, and obesity.
- Can GERD cause long-term damage? If untreated, GERD can lead to complications like esophageal damage, ulcers, or even cancer in rare cases.
- What over-the-counter medications are safe for GERD? Antacids, H2 blockers, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are commonly used to manage GERD symptoms.
- Can I still eat spicy food if I have GERD? It’s best to avoid spicy food as it can irritate your esophagus and trigger symptoms.
- How can I prevent GERD from worsening? Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding triggers, and managing stress can help prevent GERD from getting worse.
- Is it safe to take medication for GERD during pregnancy? Always consult your doctor before taking any GERD medication during pregnancy.
- Can stress worsen GERD symptoms? Yes, stress can increase stomach acid production and worsen GERD symptoms.
References
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). (2023). Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Read More
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). GERD: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment. Read More
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and does not substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment tailored to your individual needs.

Camellia Wulansari is a dedicated Medical Assistant at a local clinic and a passionate health writer at Healthusias.com. With years of hands-on experience in patient care and a deep interest in preventive medicine, she bridges the gap between clinical knowledge and accessible health information. Camellia specializes in writing about digestive health, chronic conditions like GERD and hypertension, respiratory issues, and autoimmune diseases, aiming to empower readers with practical, easy-to-understand insights. When she’s not assisting patients or writing, you’ll find her enjoying quiet mornings with coffee and a medical journal in hand—or jamming to her favorite metal band, Lamb of God.