Heat vs. Ice for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Discover Effective Pain Relief Strategies
Living with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) can be incredibly challenging, especially when managing pain and discomfort. As a Rheumatology Nurse Practitioner, I’ve seen firsthand how debilitating the pain can be for my patients. One of the most common questions I get asked is about managing pain effectively – particularly, when it comes to using heat versus ice. It’s a debate that many people with RA, and those who support them, find themselves having: Does heat provide better relief for stiffness and aching joints, or does ice help reduce inflammation more effectively? In this post, we’ll dive deep into the science behind heat and ice therapy and explore how each treatment can be used in the management of rheumatoid arthritis pain.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Impact on the Body

Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own joints, leading to inflammation, pain, and damage. The joints most commonly affected include the wrists, knees, and fingers, but RA can impact nearly any joint in the body. This inflammation can cause stiffness, swelling, and a feeling of warmth in the affected areas. Over time, if left untreated, it can result in joint deformity and loss of function.
Understanding this process is crucial when determining the best approach to pain management. The type of pain associated with RA can vary depending on the severity of the flare-up, the location of inflammation, and how long the individual has been living with the disease. Some patients experience constant pain, while others have more periodic flare-ups that cause sudden, intense discomfort. One thing is certain: managing this pain is key to maintaining a good quality of life.
Heat Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Relief

How Heat Helps with RA Pain
Heat therapy is often recommended for those with rheumatoid arthritis to help soothe stiff and aching muscles. The gentle warmth can be incredibly comforting, particularly in the morning when joints are often at their stiffest. When heat is applied to the body, it causes blood vessels to dilate, increasing circulation to the affected area. This increased circulation helps to reduce muscle spasms and promotes healing by delivering more oxygen and nutrients to the tissues.
Heat is especially helpful for individuals experiencing stiffness due to the buildup of waste products in the tissues around the joints. It can also help relieve pain by relaxing the muscles surrounding the inflamed joint. However, heat should be used cautiously when there’s active inflammation. Applying heat directly to an inflamed joint could worsen swelling, so it’s important to assess whether heat is appropriate for the situation.
Best Practices for Using Heat Therapy
- Warm compresses: You can apply a warm towel or heating pad directly to the affected area for 15 to 20 minutes. Make sure it’s not too hot to avoid burns.
- Warm baths or showers: A nice warm bath can be a great way to relax stiff joints and muscles, especially in the morning.
- Heat wraps: Some people with RA find relief from heat wraps, which are specially designed to wrap around joints and apply consistent, soothing warmth.
Ice Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Relief

How Ice Helps with RA Pain
On the other hand, ice therapy is a go-to remedy for many people suffering from RA, especially when inflammation is at its peak. Cold therapy can help numb the area and reduce swelling, making it particularly useful during an RA flare-up when joints are visibly swollen and painful. The cold works by constricting blood vessels and slowing the flow of blood to the inflamed area, which helps to reduce the amount of fluid and inflammation that builds up in the joints.
Ice can also help relieve pain by temporarily numbing the area, providing a distraction from the constant ache and discomfort that often accompanies RA. For those who experience a lot of joint stiffness in the morning, applying ice for a short time can bring much-needed relief.
Best Practices for Using Ice Therapy
- Cold packs: Wrap an ice pack or frozen peas in a towel and apply it to the affected joint for 15 to 20 minutes. Avoid direct contact with the skin to prevent frostbite.
- Cold baths: Submerging the affected joints in a cold bath can help reduce swelling, but be sure to limit the exposure to about 10 minutes at a time.
- Contrast therapy: Alternating between hot and cold therapy (known as contrast therapy) can be particularly effective in reducing both pain and swelling. Start with heat for about 5-10 minutes, then switch to ice for 10-15 minutes.
Which Is Better for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Heat or Ice?
So, which is better for managing rheumatoid arthritis pain: heat or ice? The answer depends largely on the specific symptoms you’re dealing with. Both therapies have their place in pain management, and the best approach often involves a combination of both.
If you’re dealing with stiffness and chronic pain, heat therapy may be the better choice to promote relaxation and increase blood flow to the joints. If you’re experiencing acute inflammation and swelling, ice therapy may be more beneficial to reduce the swelling and numb the pain.
Ultimately, it’s important to listen to your body. Some people find that heat works better in the mornings when their joints are stiff, while others prefer ice during a flare-up to manage inflammation. The goal is to experiment and find what works best for your unique symptoms.
In the next section, we’ll dive deeper into how combining these two therapies can enhance your pain management routine and provide additional tips on maximizing their effectiveness. Stay tuned!
Combining Heat and Ice for Maximum Pain Relief
Now that we’ve explored the individual benefits of heat and ice therapy, let’s talk about how these two methods can be combined for even more effective pain relief. As I mentioned before, both heat and ice serve different purposes. Heat is fantastic for soothing stiff joints and muscles, while ice works wonders for reducing inflammation. But, what if you could use both in a way that maximizes their benefits?
In my experience as a Rheumatology Nurse Practitioner, many of my patients with RA find that alternating between heat and ice works like a charm. The combination, also known as contrast therapy, is a great way to take advantage of the strengths of both methods. The theory behind contrast therapy is that by switching between heat and ice, you get the benefits of increased blood flow and reduced swelling, which can help improve joint function and relieve pain.
How Does Contrast Therapy Work?
Here’s how contrast therapy works: you start with heat, which promotes circulation, relaxes muscles, and eases stiffness. After a short period, you switch to ice, which reduces swelling and numbs the pain. The idea is that the quick switch between heat and cold causes your blood vessels to expand and contract, creating a pumping effect that helps move fluid out of the joints and bring in fresh, oxygenated blood.
This alternating method is not only soothing but can also be incredibly effective in managing both chronic pain and inflammation. Think of it as a “reset” for your joints. Of course, it’s important to pay attention to your body’s signals. If at any point the heat or ice makes you feel uncomfortable, stop the therapy immediately. Everyone’s tolerance is different, and what works for one person may not be ideal for another.
Best Practices for Contrast Therapy
- Start with heat: Apply heat for 5-10 minutes to warm up the muscles and joints. This will help loosen up the area and prepare it for the cold therapy.
- Switch to ice: After the heat, immediately switch to ice for 5-10 minutes. The cold will help reduce inflammation and numb the pain.
- Repeat the cycle: You can repeat the heat and ice cycle two or three times, but be sure to end with ice if inflammation is your main concern.
- Always protect your skin: Never apply heat or ice directly to the skin. Use a towel or cloth to protect your skin from burns or frostbite.
Other Effective Techniques for Managing RA Pain

While heat and ice therapy are great options for managing rheumatoid arthritis pain, they are just two tools in the toolbox. Many patients with RA also find relief through other complementary techniques that can enhance the effects of temperature therapy. As a Rheumatology Nurse Practitioner, I always encourage my patients to explore a variety of strategies to manage their pain effectively. Here are some of the other techniques that can work well alongside heat and ice:
Gentle Exercise and Stretching
One of the most powerful tools for managing RA pain is regular exercise. I know, it might sound counterintuitive to move when your joints are swollen and inflamed, but gentle movement can actually help keep your joints flexible and reduce pain over time. In fact, low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, or yoga are fantastic for people with RA because they get the body moving without putting unnecessary stress on the joints.
Stretching is also key. Keeping your joints limber and your muscles flexible can help minimize stiffness and discomfort. Even something as simple as a few minutes of stretching every morning or evening can make a noticeable difference. I’ve had patients who tell me that a daily stretching routine helps them manage their morning stiffness and makes it easier to get through the day.
Heat and Ice Therapy Along with Anti-Inflammatory Medications
For many RA patients, temperature therapy is just one part of the treatment plan. Medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can be used alongside heat and ice therapy to target inflammation at the source. Combining medication with physical therapies provides a comprehensive approach to managing the disease and alleviating symptoms.
As always, it’s important to consult your healthcare provider before adjusting any medications or starting a new pain management strategy. A well-rounded approach to managing RA should be tailored to your unique needs, and your doctor can help you develop the best plan for your situation.
Incorporating Lifestyle Changes for Long-Term Relief
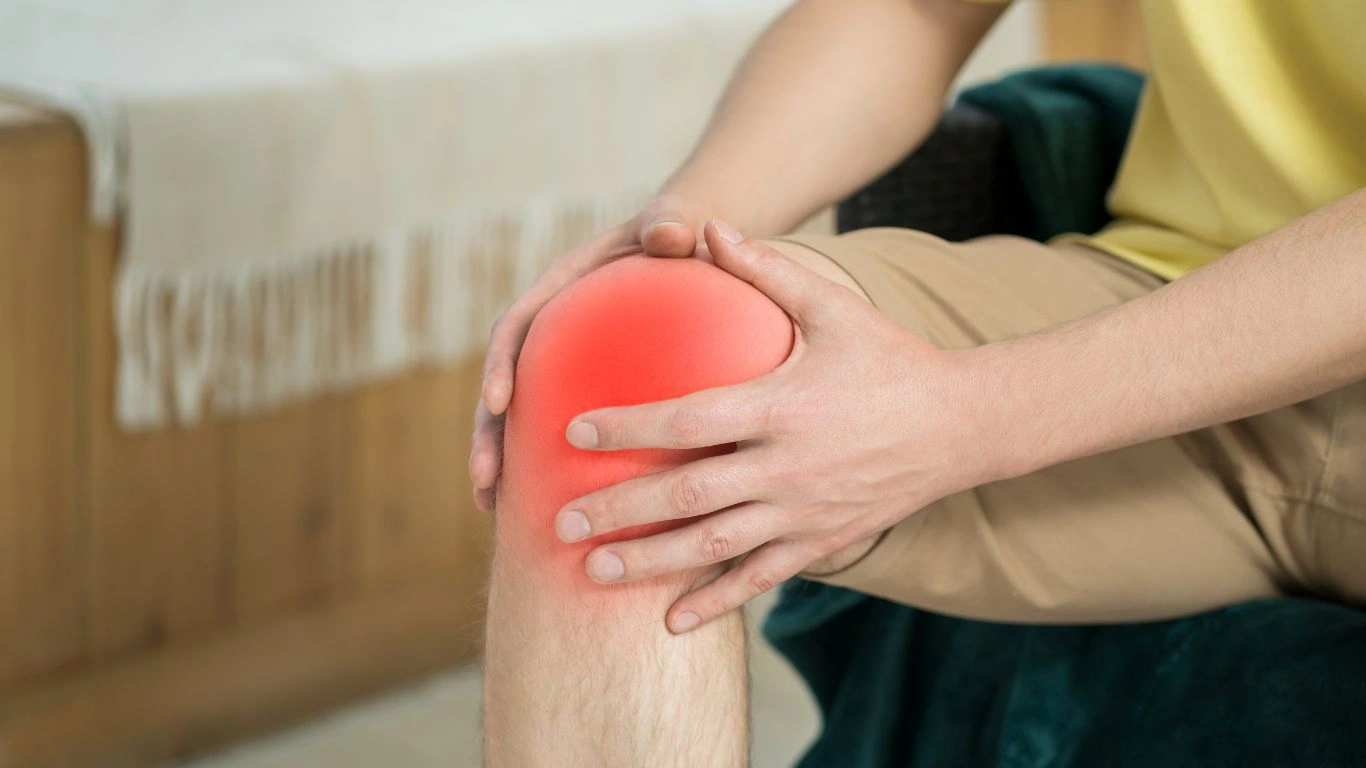
In addition to physical therapies and medications, making a few lifestyle changes can go a long way in managing rheumatoid arthritis. I always stress the importance of a healthy, balanced diet, regular sleep, and stress management in my practice. When you’re dealing with a chronic condition like RA, taking care of your overall well-being is just as important as managing the physical symptoms.
Healthy Diet for Joint Health
Eating an anti-inflammatory diet can help reduce the overall burden on your joints. I often recommend foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts), antioxidants (like berries and leafy greens), and whole grains. Avoiding processed foods and refined sugars can also help lower inflammation and support better joint health. Remember, your body is working hard to fight inflammation from within, and fueling it with the right nutrients can make a huge difference in how you feel.
Managing Stress
Stress can exacerbate RA symptoms, so finding ways to manage stress is crucial. I encourage patients to explore relaxation techniques like deep breathing exercises, meditation, or mindfulness practices. These techniques help reduce the body’s overall stress levels and can prevent flare-ups from becoming more severe.
Incorporating these lifestyle changes into your routine, along with heat and ice therapy, can help you feel more in control of your RA. It’s all about finding a balance that works for you and taking a proactive approach to managing your health.
When to Seek Professional Help for Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain

While heat and ice therapy can certainly provide relief, it’s important to remember that rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, progressive condition. As a Rheumatology Nurse Practitioner, I’ve seen many patients manage their pain effectively with at-home treatments, but there are times when you may need to seek professional help. It’s crucial to be aware of the signs that your RA may require more intensive intervention.
Recognizing When Your Pain Isn’t Typical
It’s easy to get used to living with some level of discomfort when you’ve had RA for a while. However, there are certain signs that indicate a change in the progression of the disease or that your pain management strategy needs to be reevaluated.
If you notice any of the following, it’s important to contact your healthcare provider as soon as possible:
- Uncontrolled pain: If your pain persists despite using heat, ice, and medications, it may indicate that your RA is flaring up or that your current treatment plan isn’t sufficient.
- Increased joint swelling: Swelling that doesn’t subside with ice therapy or anti-inflammatory medications should be monitored closely. Persistent swelling can lead to joint damage if left unchecked.
- Loss of joint function: If you’re experiencing difficulty moving your joints or notice a decrease in your range of motion, it may be time to consult your doctor. This could be a sign of joint damage or a need for adjustments in your treatment.
- Fever or fatigue: These symptoms can indicate that your RA is in an active flare, which may require stronger medications or changes in your treatment approach.
If any of these signs appear, don’t hesitate to reach out to your rheumatologist or healthcare provider. They can offer additional therapies, medications, or recommendations that can help manage your symptoms more effectively.
Long-Term Strategies for Managing RA Pain

Managing rheumatoid arthritis pain isn’t just about immediate relief—it’s about finding long-term strategies that help you maintain an active, fulfilling life despite the challenges of the disease. While heat and ice therapy can be valuable tools in your pain management toolkit, there are other strategies that should be part of a comprehensive long-term approach. I always encourage my patients to take a holistic approach to their care, considering both physical and emotional aspects of their health.
Medication and Disease Modifying Therapies
For many people with RA, medications play a central role in controlling symptoms and slowing the progression of the disease. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are often prescribed to reduce inflammation and prevent joint damage. These medications can be incredibly effective, but they often take time to show results. In the meantime, it’s important to use other therapies—like heat, ice, and physical therapy—to manage pain and keep your joints functioning as well as possible.
Biologic drugs are another option for people with more severe RA. These medications target specific parts of the immune system to reduce inflammation and prevent joint damage. Biologics can be a game-changer for those who haven’t responded to traditional DMARDs, but they do come with their own set of considerations, including potential side effects and costs. A thorough discussion with your healthcare provider is key to determining whether biologics are right for you.
Physical and Occupational Therapy
Physical therapy (PT) and occupational therapy (OT) can be incredibly helpful for people with RA, particularly those dealing with chronic pain and stiffness. A physical therapist can help you strengthen the muscles surrounding your joints, improve your range of motion, and teach you techniques to prevent further joint damage. An occupational therapist can work with you on strategies to make daily tasks easier, like using assistive devices or learning joint protection techniques.
Both PT and OT focus on improving function and maintaining independence. I’ve seen firsthand how a good therapist can make a huge difference in a patient’s quality of life. These therapies are an essential part of the long-term management of RA and can complement your other treatment strategies, including medication and pain relief techniques like heat and ice therapy.
Mind-Body Connection: Addressing Emotional Health
Rheumatoid arthritis is not just a physical condition—it can have a significant impact on mental and emotional health. Chronic pain, fatigue, and the unpredictability of RA flares can take a toll on your mood, leading to feelings of frustration, anxiety, or depression. Addressing your emotional health is an essential part of managing RA over the long term.
Mindfulness practices like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help reduce stress, improve emotional resilience, and even alleviate physical symptoms of RA. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is another tool that can help people with RA cope with the psychological aspects of chronic pain and disease management. Many healthcare providers now offer integrated care teams that include mental health professionals who specialize in chronic illness, making it easier to address both the physical and emotional aspects of RA.
Resources and Support for People with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Living with rheumatoid arthritis can feel isolating at times, but it’s important to remember that you don’t have to go through it alone. There are many resources and support systems available to help you manage your condition. Whether it’s through online forums, local support groups, or educational materials, connecting with others who understand your journey can provide invaluable support.
The Arthritis Foundation is an excellent resource for people with RA. They offer a wealth of information about managing symptoms, living with arthritis, and finding local support groups. The American College of Rheumatology also provides resources for both patients and healthcare providers, offering up-to-date research and guidelines on RA management. Additionally, National Institutes of Health (NIH) offers comprehensive research findings and news about new treatments for RA.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is intended for general informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read in this article.

Tarra Nugroho is a dedicated Nurse Practitioner with a strong foundation in family and preventive care. She brings both compassion and clinical expertise to her practice, focusing on patient-centered care and health education. As a contributor to Healthusias.com, Tarra translates medical knowledge into clear, empowering articles on topics like women’s health, chronic disease management, and lifestyle medicine. Her mission is simple: help people feel seen, heard, and informed—both in the clinic and through the content she creates. When she’s not caring for patients, Tarra enjoys weekend hikes, plant-based cooking, and curling up with a good health podcast.