High Blood Pressure in Athletes – What You Need to Know
As athletes, we often think of ourselves as being in top shape, but high blood pressure can still sneak up on us. Whether you’re a professional competitor or a weekend warrior, understanding how high blood pressure impacts your performance and health is crucial. In this article, we’ll break down how hypertension affects athletes and what you can do about it.
When we think of athletes, we picture strong bodies, fast recovery, and impressive performance. But what if high blood pressure—something typically associated with older adults—starts to show up in younger, seemingly healthy athletes? It may seem surprising, but hypertension (high blood pressure) can actually impact athletes at any level. Here’s a deep dive into this issue and how to manage it for optimal health and performance.
What Is High Blood Pressure?

High blood pressure, or hypertension, is when the force of blood against the walls of your arteries is consistently too high. Blood pressure is measured using two numbers: systolic (the pressure when the heart beats) and diastolic (the pressure when the heart rests between beats). If these numbers stay elevated for an extended period, it can lead to serious health issues, such as heart disease or stroke.
For adults, normal blood pressure is generally considered to be around 120/80 mmHg. Anything higher is considered elevated or high. For athletes, maintaining normal blood pressure is essential not only for overall health but also for peak athletic performance.
How High Blood Pressure Affects Athletes
You might be wondering, “Why would an athlete, who’s physically fit, be concerned about high blood pressure?” Well, being an athlete doesn’t automatically protect you from high blood pressure, especially as you push your body to its limits. High blood pressure can affect athletes in several ways:
- Decreased Oxygen Delivery
High blood pressure can cause the heart to work harder to pump blood, which can reduce the oxygen delivered to muscles during intense exercise. This means athletes may experience fatigue sooner than expected, impacting their performance.
- Risk of Heart Disease
Over time, if left unchecked, high blood pressure can cause damage to the heart and arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease. In athletes, this could lead to problems with endurance and even more severe cardiovascular issues if not properly managed.
- Reduced Recovery Time
With high blood pressure, your body may take longer to recover from workouts and competitions. This happens because the cardiovascular system isn’t as efficient at circulating blood, which is crucial for delivering nutrients and oxygen to muscles after exertion.
- Increased Risk of Injury
High blood pressure can cause changes in how your muscles and joints perform, potentially increasing the likelihood of injury. As an athlete, preventing injuries is a top priority, so hypertension could become a serious concern.

Causes of High Blood Pressure in Athletes
Even though regular exercise can actually help lower blood pressure, athletes are still at risk of developing hypertension. So, what are the common causes of high blood pressure in athletes?
- Genetics
Some athletes may have a family history of high blood pressure, which could predispose them to developing the condition, regardless of their fitness level.
- Overtraining
Pushing your body beyond its limits without proper rest and recovery can lead to increased blood pressure. Overtraining syndrome can cause stress on the heart and elevate blood pressure.
- Stress
Athletes often deal with stress, whether it’s from competitions, training schedules, or personal life. Stress triggers the release of hormones like adrenaline, which can increase blood pressure temporarily and contribute to long-term hypertension if it’s chronic.
- Diet and Lifestyle
Despite their physical fitness, some athletes may still struggle with poor dietary choices, such as consuming too much salt, caffeine, or alcohol, which can contribute to high blood pressure.
Managing High Blood Pressure as an Athlete
The good news is, if you have high blood pressure, there are plenty of ways to manage it and still maintain peak athletic performance. Here’s how:
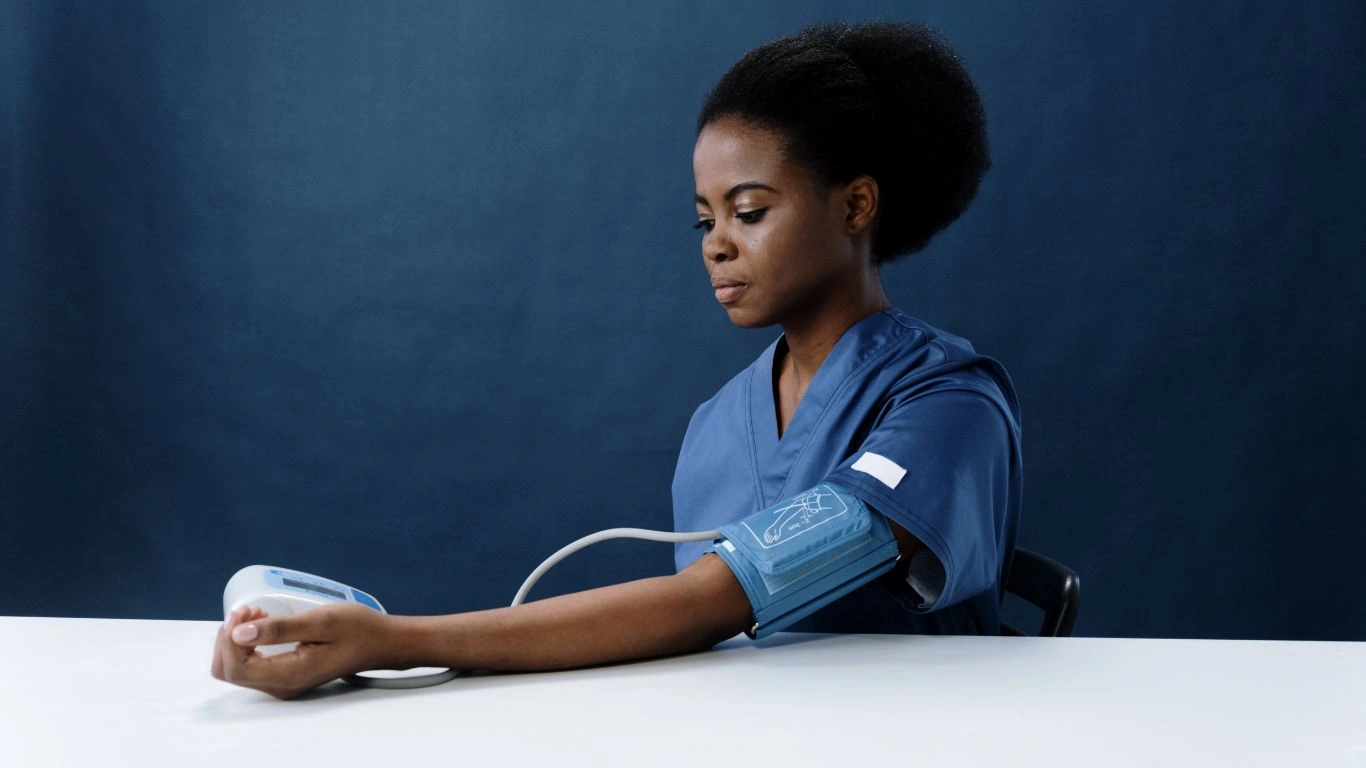
- Regular Monitoring
As an athlete, it’s crucial to monitor your blood pressure regularly. Keep track of it before, during, and after training sessions. This will help you spot any changes and address them early.
- Optimal Rest and Recovery
Allowing your body ample time to recover from intense training is essential. Overtraining is a leading cause of high blood pressure in athletes, so make sure you’re getting enough rest between workouts and sleep each night.
- Balanced Diet
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help manage blood pressure. Avoid too much sodium, alcohol, and caffeine, all of which can spike blood pressure. Staying hydrated is also crucial for maintaining good cardiovascular health.
- Stress Management
Practice mindfulness techniques, meditation, and deep breathing exercises to keep stress in check. Mental health is just as important as physical health for an athlete, and reducing stress can help lower blood pressure.
- Consult with a Healthcare Professional
If you’ve been diagnosed with high blood pressure, it’s important to work with a healthcare provider. A sports medicine doctor or cardiologist can help tailor a plan that keeps your blood pressure in check while you continue to pursue your athletic goals.

Can Exercise Help Lower High Blood Pressure?
Yes, it absolutely can. Regular, moderate-intensity exercise helps to strengthen the heart, improve circulation, and lower overall blood pressure. It’s one of the best ways to manage hypertension. However, it’s important to balance hard training with recovery, as excessive training without proper rest can contribute to elevated blood pressure.
Should Athletes Be Concerned About Blood Pressure Medication?
For some athletes with high blood pressure, medications may be necessary. Common medications like beta-blockers, diuretics, or ACE inhibitors are often prescribed to lower blood pressure. While these can help manage hypertension, athletes should be aware of how these medications might affect their performance. Some medications may reduce endurance, while others might lead to dehydration or muscle cramps. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to find the best option for your specific needs.

Appendices
References
For more detailed information on high blood pressure and its impact on athletes, check out the following resources:
- American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM). (2023). Hypertension and Exercise: A Comprehensive Guide.
- Fagard, R. H. (2022). Exercise, Blood Pressure, and Cardiovascular Risk. European Heart Journal, 44(1), 15-23.
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). High Blood Pressure and Athletes: What You Should Know. Mayo Clinic Health Library.
FAQs
- Can high blood pressure affect athletic performance?
Yes, high blood pressure can reduce oxygen delivery to muscles and slow recovery, which can impair athletic performance.
- What should athletes do if they are diagnosed with high blood pressure?
It’s important to monitor blood pressure regularly, maintain a healthy lifestyle with proper diet and rest,and consult a healthcare provider for personalized management.
- Does exercise worsen high blood pressure?
While excessive or overtraining can worsen high blood pressure, regular, moderate-intensity exercise is beneficial for lowering blood pressure in the long term.
- Are blood pressure medications safe for athletes?
Blood pressure medications can be safe, but some may affect performance. It’s important to consult with a doctor to choose the best medication based on your specific athletic needs.
- Can athletes with high blood pressure compete in sports?
Yes, most athletes with controlled high blood pressure can safely participate in sports. It’s important to manage the condition with lifestyle changes and medications as needed.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is intended for educational purposes only and should not substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized treatment and guidance regarding blood pressure management.

Dr. Gwenna Aazee is a board-certified Internal Medicine Physician with a special focus on hypertension management, chronic disease prevention, and patient education. With years of experience in both clinical practice and medical writing, she’s passionate about turning evidence-based medicine into accessible, actionable advice. Through her work at Healthusias.com, Dr. Aazee empowers readers to take charge of their health with confidence and clarity. Off the clock, she enjoys deep dives into nutrition research, long walks with her rescue pup, and simplifying medical jargon one article at a time.