Managing GERD Back Pain: Effective Solutions
Explore effective solutions for managing GERD-related back pain. Discover lifestyle adjustments, treatment options, and expert advice in our comprehensive guide.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) affects millions worldwide, causing not only discomfort in the chest but also unexpected symptoms like back pain. If you’re among those experiencing this, understanding how to alleviate GERD-related back pain is crucial for your well-being. In this detailed guide, we’ll delve into various strategies to help you find relief and improve your quality of life.
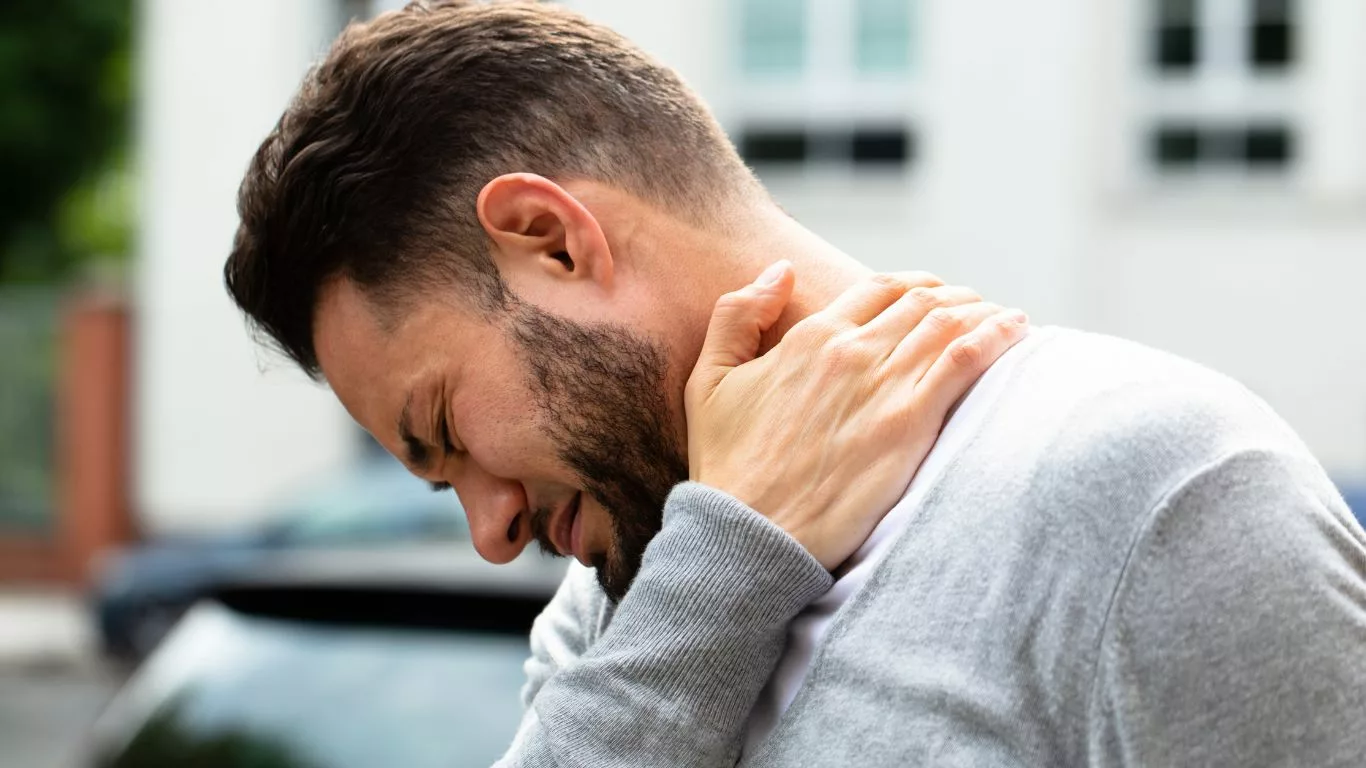

Understanding GERD and Back Pain
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic condition characterized by the reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus, leading to irritation and inflammation of the esophageal lining. While heartburn is the hallmark symptom of GERD, the condition can also manifest as back pain, adding to the complexity of its presentation. The proximity of the esophagus to the spine means that irritation from acid reflux can radiate to the back, causing discomfort that ranges from mild to debilitating. This back pain may be felt between the shoulder blades, in the upper or lower back, or even in the neck, further complicating diagnosis and treatment.

Lifestyle Adjustments for Relief
Adopting certain lifestyle changes can play a pivotal role in alleviating GERD symptoms, including back pain. Here are some comprehensive adjustments to consider:
Dietary Changes
Adjusting your diet is often the first line of defense against GERD symptoms. Avoiding trigger foods such as spicy dishes, fatty meals, citrus fruits, and caffeinated beverages can help minimize acid reflux episodes. Instead, focus on incorporating more alkaline-forming foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your diet. These foods promote digestive health and reduce the likelihood of acid reflux.
Elevate Your Sleeping Position
Changing your sleeping habits can significantly reduce nighttime reflux and alleviate associated back pain. Elevating the head of your bed by six to eight inches using bed risers or placing a wedge pillow under your mattress can prevent stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus while you sleep. Alternatively, investing in an adjustable bed frame allows you to customize your sleeping position to maintain optimal elevation and minimize reflux symptoms.
Manage Stress
Stress management is essential for mitigating GERD symptoms, including back pain. Stress triggers physiological responses that can exacerbate acid reflux, making relaxation techniques vital for symptom control. Incorporate stress-reducing practices such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, progressive muscle relaxation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies and activities that bring joy and fulfillment. By reducing stress levels, you can lower the likelihood of experiencing GERD flare-ups and associated back discomfort.

Treatment Options for GERD Back Pain
In addition to lifestyle modifications, several treatment options can provide relief from GERD-related back pain:
Medications
Medications play a crucial role in managing GERD symptoms and associated back pain. Over-the-counter antacids, such as Tums or Maalox, can provide quick relief by neutralizing stomach acid. H2 blockers, like famotidine (Pepcid) or ranitidine (Zantac), work by reducing the production of acid in the stomach, thereby alleviating irritation in the esophagus.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), such as omeprazole (Prilosec) or esomeprazole (Nexium), are potent acid suppressors that can effectively control GERD symptoms and promote healing of the esophageal lining. Your healthcare provider can help determine the most suitable medication regimen based on the severity of your symptoms and medical history.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy offers non-invasive techniques to alleviate back pain associated with GERD. A skilled physical therapist can design a tailored treatment plan to address your specific needs and improve mobility, strength, and posture. Stretching exercises targeting the chest, shoulders, and back can help relieve tension and improve flexibility, reducing the likelihood of muscle strain and discomfort. Massage therapy can promote relaxation and alleviate muscle tightness, while manual techniques such as joint mobilization and soft tissue manipulation can improve spinal alignment and reduce pressure on the affected area.
Additionally, posture correction exercises can help you maintain proper spinal alignment and reduce the risk of aggravating back pain during daily activities. Regular sessions with a physical therapist can complement other GERD treatments and contribute to long-term pain relief and improved quality of life.
Surgical Intervention
For individuals with severe GERD symptoms that do not respond adequately to conservative treatments, surgical intervention may be necessary to provide lasting relief from back pain and other associated symptoms. Fundoplication is a common surgical procedure used to treat GERD by reinforcing the lower esophageal sphincter, the muscle that prevents stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus. During the procedure, the upper part of the stomach is wrapped around the lower esophagus to create a tighter valve, reducing the occurrence of acid reflux.
While fundoplication is generally effective in relieving GERD symptoms, it is considered a last resort option due to the risks and potential complications associated with surgery. It’s important to discuss the potential benefits and risks of surgery with your healthcare provider to make an informed decision about the most appropriate treatment approach for your condition.

Expert Advice and Considerations
Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals is essential for effectively managing GERD-related back pain:
Consult with a Gastroenterologist
A gastroenterologist can evaluate your symptoms, perform diagnostic tests, and recommend appropriate treatment options tailored to your condition. They can also provide valuable insights into managing GERD and minimizing back pain.
Collaborate with a Physical Therapist
A physical therapist specializing in musculoskeletal disorders can assess your back pain and develop a personalized rehabilitation plan to improve mobility, strength, and posture. Regular sessions with a physical therapist can complement other GERD treatments and enhance overall comfort.
Follow Up Regularly
Schedule regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare providers to monitor your progress, adjust treatment plans as needed, and address any concerns or new symptoms that arise.

Conclusion
Managing GERD-related back pain requires a comprehensive approach that combines lifestyle modifications, treatment options, and expert guidance. By making proactive changes to your diet, sleep habits, stress management, and seeking appropriate medical care, you can find relief from GERD symptoms and improve your overall quality of life.
Remember, finding the right combination of strategies may take time, so be patient and persistent in your efforts to alleviate GERD-related back pain. With dedication and support from healthcare professionals, you can regain control of your symptoms and enjoy a more comfortable and fulfilling life.
Appendices
References
For further exploration of managing GERD-related back pain, consider reviewing the following references:
- El-Serag, H. B., Sweet, S., Winchester, C. C., & Dent, J. (2014). Update on the epidemiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Gut, 63(6), 871-880. Read Article
- Katz, P. O., Gerson, L. B., & Vela, M. F. (2013). Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. American Journal of Gastroenterology, 108(3), 308-328. Read Article
- Fundoplication for the Treatment of GERD. (2016). Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES). Read Article
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about managing GERD-related back pain:
- Can GERD cause back pain? Yes, GERD can cause back pain due to irritation of the esophagus, which is located close to the spine. Back pain associated with GERD can range from mild discomfort to severe, impacting daily activities.
- How can I alleviate GERD-related back pain? Lifestyle adjustments such as dietary changes, elevating your sleeping position, and stress management can help alleviate GERD-related back pain. Additionally, medications, physical therapy, and surgical intervention may be recommended depending on the severity of symptoms.
- When should I see a doctor for GERD-related back pain? If you experience persistent or severe back pain along with symptoms of GERD such as heartburn, difficulty swallowing, or chest pain, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for evaluation and appropriate management.
Related Table
Here’s a summary table of key information regarding managing GERD-related back pain:
| Aspect | Information |
|---|---|
| Lifestyle Adjustments | Dietary changes, elevated sleeping position, stress management |
| Treatment Options | Medications, physical therapy, surgical intervention |
| Expert Advice | Consultation with gastroenterologist, collaboration with physical therapist, regular follow-up |
Note: Individual treatment plans may vary, and it’s important to seek personalized advice from healthcare professionals.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article. Reliance on any information provided in this article is solely at your own risk.

Camellia Wulansari is a dedicated Medical Assistant at a local clinic and a passionate health writer at Healthusias.com. With years of hands-on experience in patient care and a deep interest in preventive medicine, she bridges the gap between clinical knowledge and accessible health information. Camellia specializes in writing about digestive health, chronic conditions like GERD and hypertension, respiratory issues, and autoimmune diseases, aiming to empower readers with practical, easy-to-understand insights. When she’s not assisting patients or writing, you’ll find her enjoying quiet mornings with coffee and a medical journal in hand—or jamming to her favorite metal band, Lamb of God.