Omega-3 and Cholesterol: Heart-Healthy Insights and Benefits
Introduction to Omega-3 and Cholesterol
Cholesterol, a waxy substance found in your body’s cells, serves as a vital component for various physiological functions. However, when cholesterol levels become imbalanced, particularly elevated LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, it can contribute to atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by plaque buildup in arteries. Omega-3 fatty acids, a group of essential polyunsaturated fats, have gained substantial attention for their potential role in promoting cardiovascular health. In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore the intricate interplay between omega-3 and cholesterol, shedding light on their effects and benefits.
Understanding Cholesterol and Its Types
Cholesterol isn’t a singular villain; it comes in two primary forms—LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol and HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol. LDL cholesterol is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol because excess amounts can lead to the accumulation of plaque in arterial walls, impairing blood flow and increasing the risk of heart disease. On the other hand, HDL cholesterol is considered “good” cholesterol as it helps transport excess cholesterol away from arteries, reducing the risk of plaque formation.
Exploring Omega-3 Fatty Acids
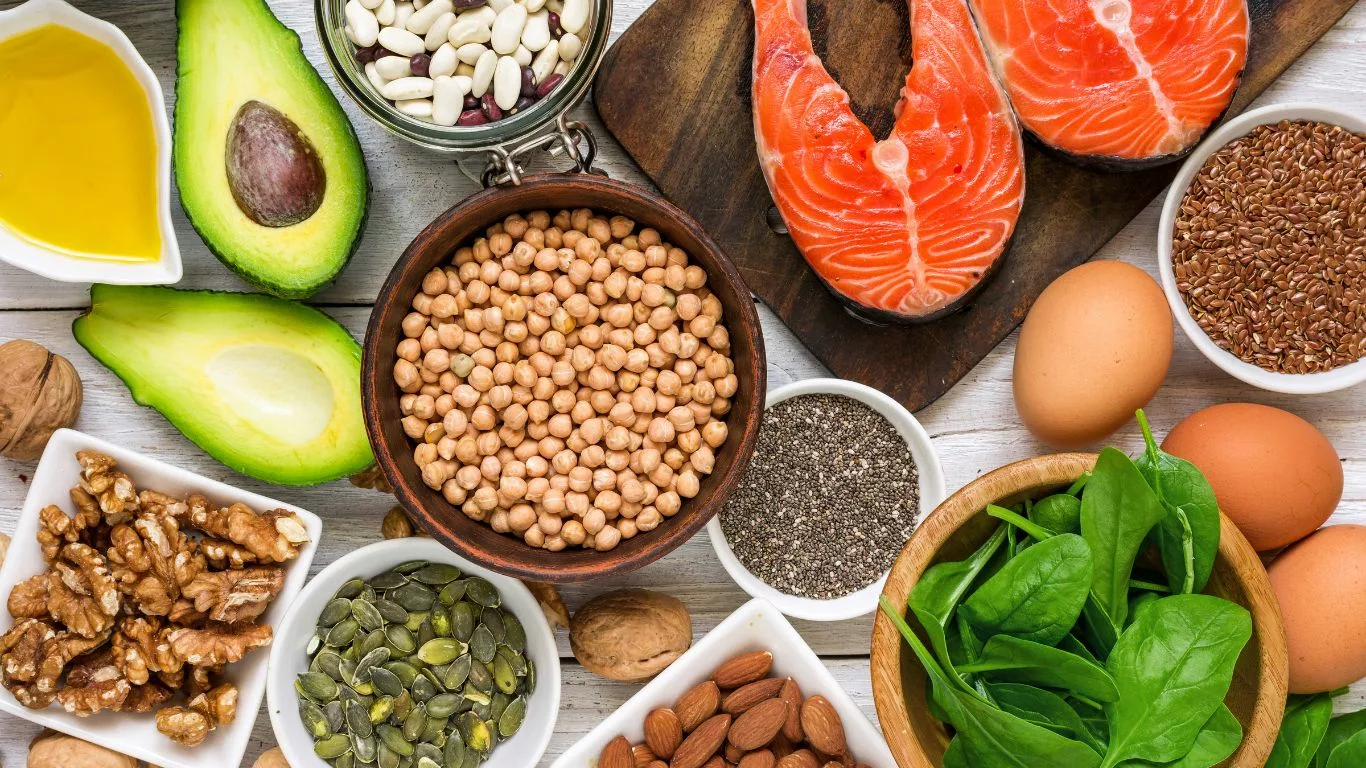
Omega-3 fatty acids are a diverse group of polyunsaturated fats that play a crucial role in maintaining optimal health. Three main types of omega-3s are EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), and ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). EPA and DHA are predominantly found in fatty fish, while ALA is present in plant-based sources. Research suggests that EPA and DHA have more potent cardiovascular benefits, but ALA, found in foods like flaxseeds and walnuts, also contributes to heart health.
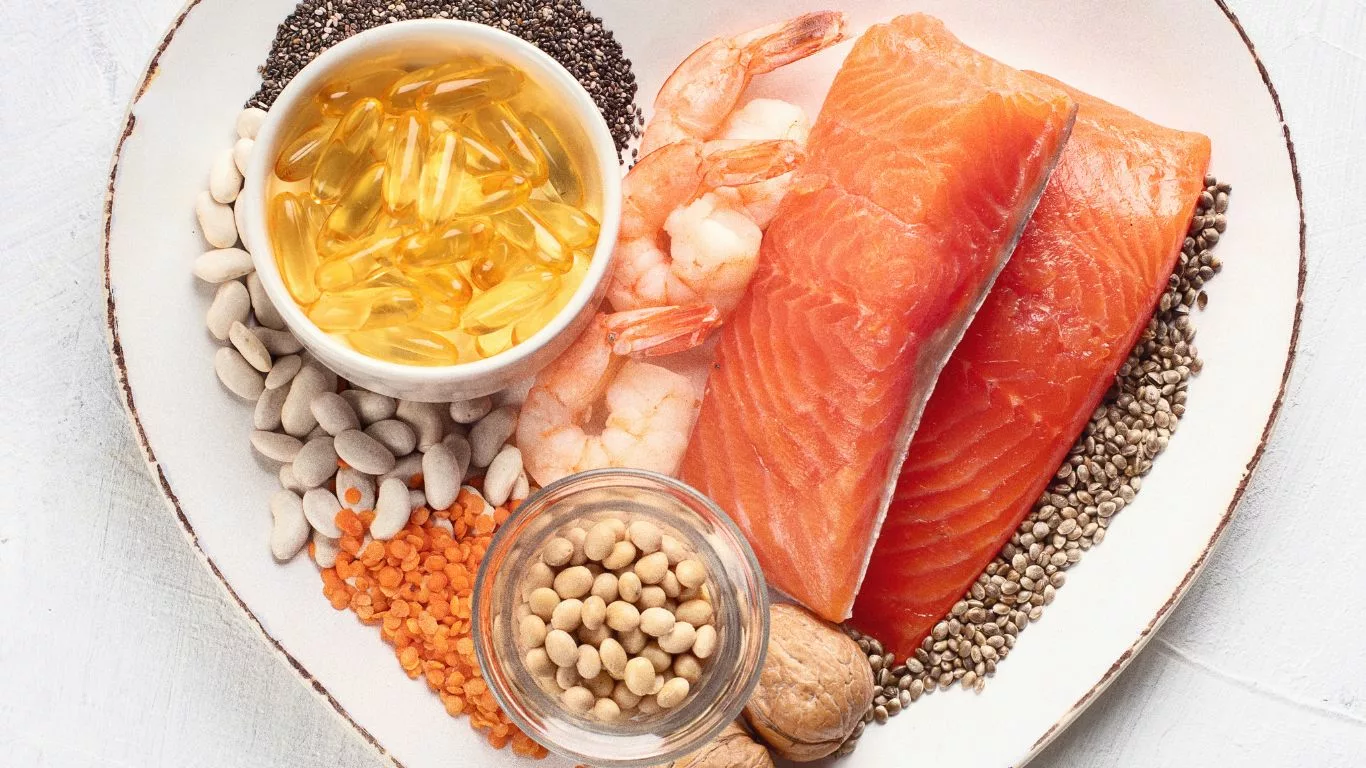

Omega-3’s Impact on Cholesterol Levels
The effects of omega-3 fatty acids on cholesterol levels are multifaceted and impressive. These healthy fats have been shown to tackle cholesterol from various angles, contributing to a more favorable lipid profile.
Mechanisms Behind Omega-3 and Cholesterol Interaction
Omega-3 fatty acids exert their influence by enhancing the breakdown and clearance of triglycerides, a type of fat found in your blood. This reduction in triglycerides not only contributes to heart health but also positively impacts overall lipid balance. Additionally, omega-3s promote the transformation of large, dense LDL particles into smaller, less harmful ones, thus mitigating the risk of plaque buildup. Furthermore, these remarkable fats stimulate the production of HDL cholesterol, which helps remove excess cholesterol from arteries, maintaining their flexibility and functionality.
Scientific Evidence of Omega-3’s Cholesterol Benefits
Numerous clinical trials have investigated the impact of omega-3 supplementation on cholesterol levels. These studies consistently demonstrate that omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, can lead to a reduction in triglycerides and LDL cholesterol. For instance, a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology reported that omega-3 supplementation resulted in a significant decrease in triglycerides and a modest reduction in LDL cholesterol levels. Moreover, observational studies across diverse populations have shown that individuals with higher omega-3 intake tend to exhibit healthier cholesterol profiles and a reduced risk of heart disease.
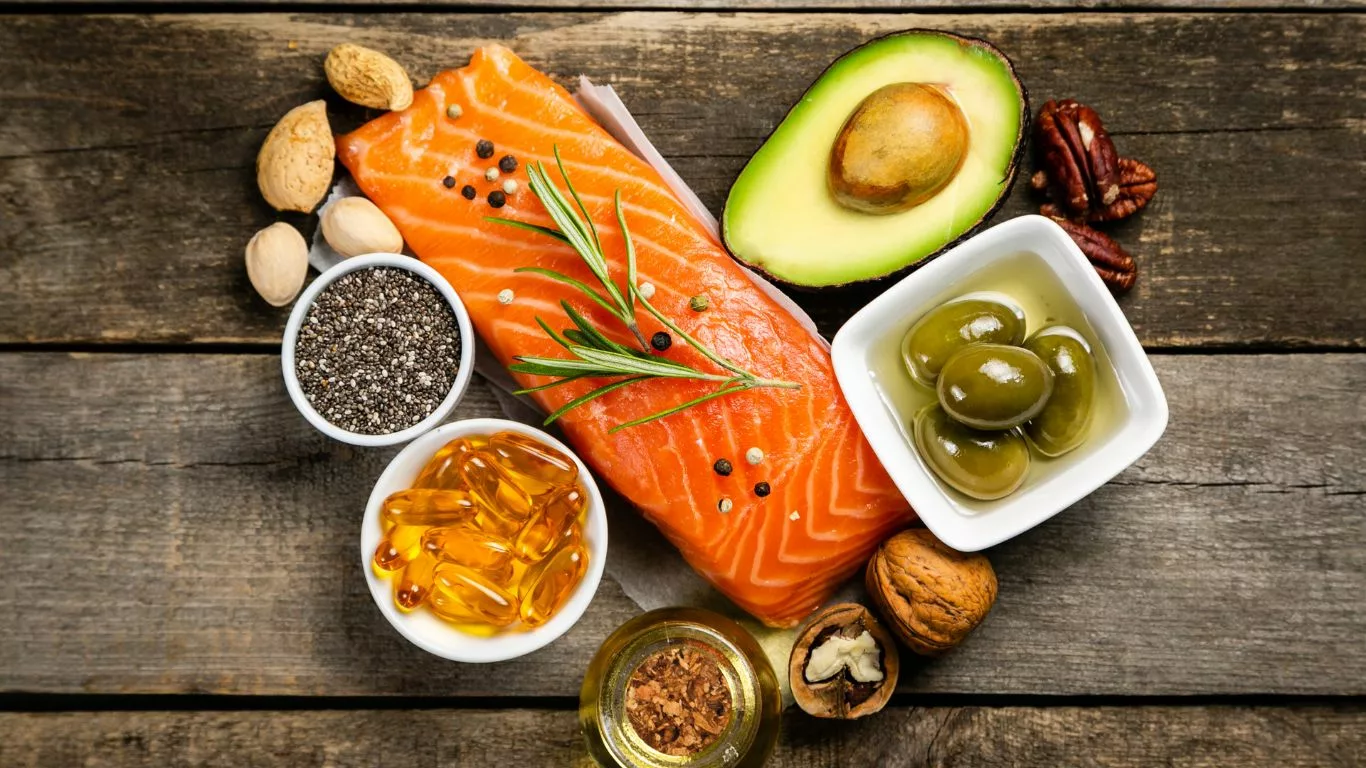

Optimal Sources of Omega-3 for Cholesterol Management
Incorporating omega-3-rich foods into your diet is a strategic approach to managing cholesterol levels effectively. Both fatty fish and plant-based sources offer distinct advantages.
Fatty Fish Rich in Omega-3
Fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, stand as nutritional powerhouses brimming with EPA and DHA. These omega-3s not only contribute to cholesterol management but also exert anti-inflammatory effects, supporting overall cardiovascular health. A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition revealed that consuming fatty fish twice a week led to significant reductions in triglycerides and LDL cholesterol.
Plant-Based Omega-3 Alternatives
Plant-based sources of omega-3, including flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, offer an excellent way for vegetarians and vegans to reap the benefits of these essential fatty acids. While ALA, the omega-3 found in these foods, is less potent than EPA and DHA, the body can convert it to EPA and DHA to some extent. Research published in the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition highlighted that incorporating flaxseed into the diet resulted in improved lipid profiles, including decreased LDL cholesterol levels.

Incorporating Omega-3 into Your Diet for Cholesterol Control
When it comes to integrating omega-3 fatty acids into your diet, understanding recommended intakes and supplementation options is key.
Recommended Daily Omega-3 Intake
The recommended intake of omega-3 fatty acids varies based on individual health considerations. Generally, consuming around 250-500 milligrams of combined EPA and DHA daily is associated with cardiovascular benefits. However, individuals with specific health conditions may require higher doses. Consultation with a healthcare professional can help determine the optimal omega-3 intake for your needs.
Leveraging Omega-3 Supplements
Omega-3 supplements, available in the form of fish oil capsules or algal oil capsules for plant-based consumers, provide a convenient way to ensure adequate omega-3 intake. These supplements often undergo rigorous quality testing and can be a valuable addition to a heart-healthy lifestyle. A meta-analysis published in the Journal of Clinical Lipidology found that omega-3 supplementation led to a significant reduction in triglycerides and LDL cholesterol levels.
Striking the Omega-3 and Omega-6 Balance
While omega-3s offer numerous benefits, it’s important to strike a balance between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Both types of fatty acids play essential roles in the body, but modern diets tend to be higher in omega-6s due to the prevalence of vegetable oils. A balanced ratio of omega-3 to omega-6, ideally around 1:1 to 1:4, supports optimal cardiovascular health. To achieve this balance, consider reducing the consumption of processed and fried foods rich in omega-6 oils.

Omega-3 and Cholesterol: Role of Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices have a profound impact on cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health. Incorporating regular physical activity and making mindful dietary decisions are vital components of cholesterol management.
Exercise as a Cholesterol-Modulating Factor
Engaging in regular physical activity has been shown to have a positive impact on cholesterol levels. Exercise not only raises HDL cholesterol, promoting its beneficial effects, but also assists in weight management, another crucial factor in maintaining healthy lipid profiles. A study published in the Journal of Applied Physiology demonstrated that aerobic exercise led to significant improvements in HDL cholesterol levels and reduced LDL cholesterol.
Crafting a Cholesterol-Friendly Diet Plan
A diet rich in fiber, antioxidants, and heart-healthy fats can effectively manage cholesterol levels. Foods high in soluble fiber, such as oats, legumes, and fruits, contribute to reduced LDL cholesterol by binding to cholesterol molecules and facilitating their excretion. Furthermore, limiting saturated and trans fats—commonly found in fried foods and baked goods—is essential for preventing LDL cholesterol buildup. Research published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition indicated that diets high in soluble fiber and low in saturated fats resulted in significant improvements in LDL cholesterol.

Collaborating with Healthcare Professionals
Before making significant dietary or lifestyle changes, it’s imperative to collaborate with healthcare professionals who can provide personalized guidance.
Consulting Your Doctor about Omega-3 and Cholesterol
Physicians possess the expertise to assess your individual health status and offer tailored recommendations. They can help you understand how omega-3 fatty acids specifically impact your cholesterol profile and address any potential interactions with other medications or health conditions.
Monitoring Cholesterol Levels and Progress
Regular monitoring of cholesterol levels is essential to gauge the effectiveness of your efforts. Scheduled check-ups with your healthcare provider allow you to track changes in your lipid profile over time and make informed decisions regarding your cholesterol management plan.
Tailoring Omega-3 Approach to Individual Health Needs
Individual factors, such as genetics, age, and overall health, play a significant role in how your body responds to omega-3 fatty acids. Working closely with your healthcare provider ensures that your omega-3 strategy aligns with your unique health requirements, optimizing your chances of achieving desired outcomes.

Conclusion: Embracing Omega-3 for Healthy Cholesterol Levels
In conclusion, the synergy between omega-3 fatty acids and cholesterol management is undeniable. Omega-3s, through their multifaceted mechanisms, offer a compelling approach to achieving and maintaining healthy cholesterol levels. By incorporating fatty fish or plant-based omega-3 sources, considering supplements under professional guidance, and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, you can embark on a journey toward optimal cardiovascular well-being. Remember, small changes today can yield significant benefits for your heart’s health tomorrow.
Appendices
References
- Mozaffarian D, Wu JH. (2011). Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease. J Am Coll Cardiol, 58(20), 2047-2067. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22051327/
- Calder PC. (2013). Omega-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: new developments and applications. Prog Lipid Res, 52(4), 510-517. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24200766/
- Harris WS, Dayspring TD, Moran TJ. (2013). Omega-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: new developments and applications. Mayo Clin Proc, 88(10), 1222-1231. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15075702/
FAQs
Q1: What are omega-3 fatty acids?
A1: Omega-3 fatty acids are essential polyunsaturated fats found in fatty fish and plant-based sources. They offer numerous health benefits, including cardiovascular support.
Q2: How do omega-3s impact cholesterol levels?
A2: Omega-3s reduce triglycerides, regulate LDL cholesterol, and increase HDL cholesterol, contributing to a healthier lipid profile and reduced heart disease risk.
Q3: Can I get enough omega-3s from plant-based sources?
A3: Yes, foods like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts provide ALA, a type of omega-3 that can be converted into beneficial forms in the body.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical advice and should not replace consultation with qualified healthcare professionals. Always consult a healthcare provider before making changes to your diet, exercise routine, or medical treatment.

Camellia Wulansari is a dedicated Medical Assistant at a local clinic and a passionate health writer at Healthusias.com. With years of hands-on experience in patient care and a deep interest in preventive medicine, she bridges the gap between clinical knowledge and accessible health information. Camellia specializes in writing about digestive health, chronic conditions like GERD and hypertension, respiratory issues, and autoimmune diseases, aiming to empower readers with practical, easy-to-understand insights. When she’s not assisting patients or writing, you’ll find her enjoying quiet mornings with coffee and a medical journal in hand—or jamming to her favorite metal band, Lamb of God.