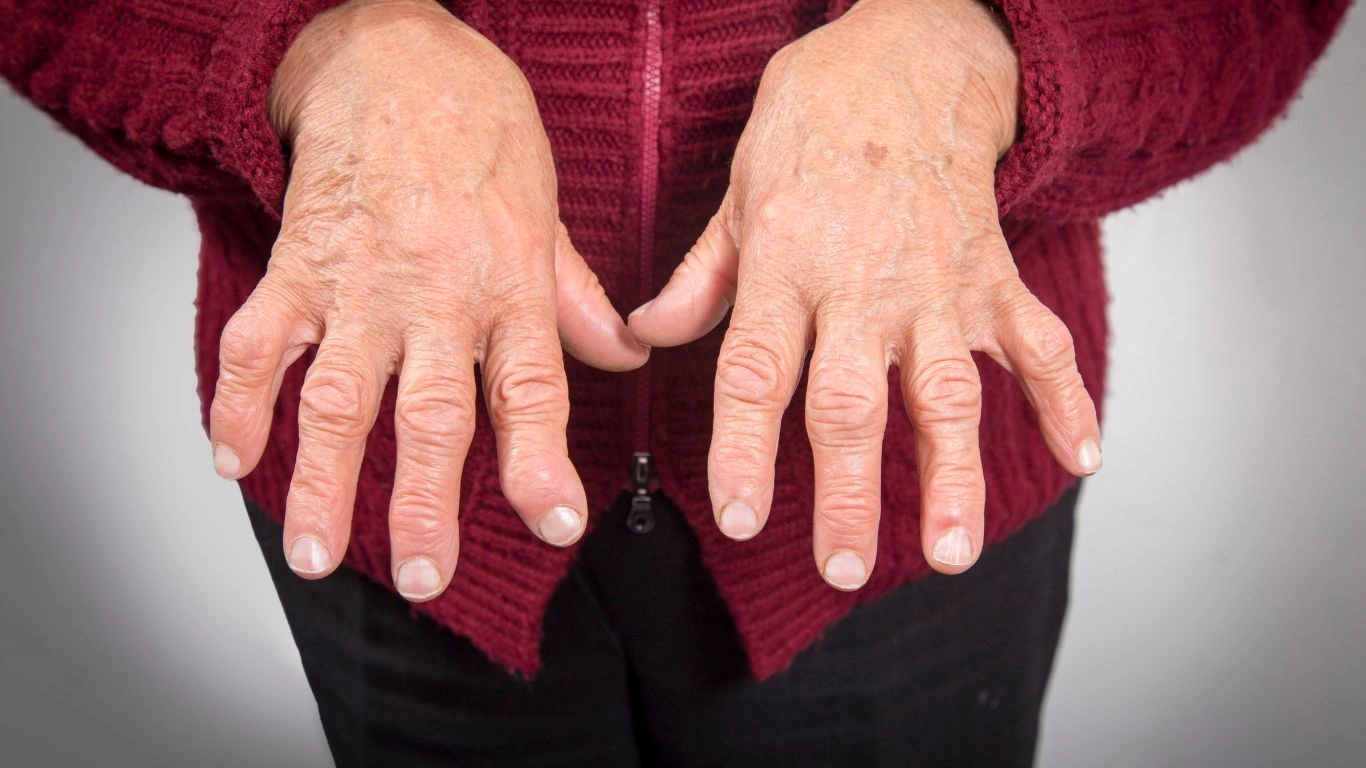
Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Management Techniques – A Complete Guide
Are you struggling to manage the constant pain of rheumatoid arthritis (RA)? Don’t worry, you’re not alone! In this guide, we’ll explore the best pain management techniques to help ease the discomfort and improve your quality of life.
Living with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) can be an ongoing battle, especially when it comes to managing the pain. RA is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes inflammation in the joints, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness. But the good news? There are plenty of techniques and treatments that can help reduce the pain and make day-to-day life a little bit easier.
In this article, we’ll dive into the most effective pain management techniques for rheumatoid arthritis, from medication to lifestyle changes and natural remedies.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain
Before we dive into pain management techniques, it’s important to understand what’s happening in your body. RA causes the immune system to mistakenly attack the synovial membrane—the lining of the joints—leading to inflammation. This inflammation is what causes the pain and stiffness that many people with RA experience.
RA pain can vary from person to person. For some, it’s mild and comes and goes. For others, it can be chronic and debilitating. The good news is that no matter where you are on the pain spectrum, there are several strategies that can help you feel better.

Top Pain Management Techniques for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Let’s explore some of the most effective rheumatoid arthritis pain management techniques that you can incorporate into your routine:
1. Medications: The First Line of Defense
Medications are often the go-to solution for managing RA pain. Your doctor may prescribe various types of medications, each targeting different aspects of the condition.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): DMARDs help slow down the progression of RA by targeting the immune system’s attack on your joints. These drugs can reduce inflammation, making them an effective way to manage pain over time.
Biologic DMARDs: If conventional DMARDs aren’t effective, your doctor might recommend biologics. These are a newer class of drugs that work by targeting specific parts of the immune system, helping to reduce inflammation and pain.
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation. They’re a great option for flare-ups and temporary relief, but they should be used cautiously to avoid side effects like stomach issues.
Corticosteroids: Steroid medications are often used in more severe cases to quickly reduce inflammation and pain. They can be effective for short-term relief, but long-term use should be monitored closely.

2. Physical Therapy and Exercise
While medications can help manage pain, physical therapy and exercise play a key role in improving joint function and reducing discomfort over time.
Physical Therapy: Working with a physical therapist can help you learn the proper exercises to improve your mobility and strengthen the muscles around your joints. Strengthening these muscles can provide better support for the affected joints, reducing strain and pain.
Low-Impact Exercises: Activities like swimming, walking, and cycling are great for people with RA because they’re easy on the joints. Regular exercise helps to maintain joint flexibility and muscle strength, which can alleviate pain and prevent further damage.

3. Heat and Cold Therapy
Sometimes, all you need is a little heat or cold to relieve joint pain. These are simple, non-invasive methods that can be used at home.
Cold Therapy: Applying an ice pack or cold compress to an inflamed joint can reduce swelling and numb the pain. This is particularly effective during a flare-up.
Heat Therapy: Heat pads, warm baths, or heating pads can help relax stiff muscles and improve blood circulation. Heat is often best used when you’re experiencing stiffness rather than active inflammation.
4. Diet and Supplements
What you eat can significantly impact your RA symptoms. While there’s no one-size-fits-all diet for rheumatoid arthritis, certain foods and supplements may help manage inflammation and reduce pain.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Focus on a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like omega-3 fatty acids (found in fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds), leafy greens, berries, and whole grains. These foods can help to reduce overall inflammation in the body.
Supplements: Some people with RA find relief from joint pain by taking supplements like turmeric (curcumin), ginger, and omega-3 fatty acids. These supplements may have natural anti-inflammatory properties, but always consult with your doctor before adding any new supplement to your routine.
5. Mind-Body Techniques: Stress Reduction
Chronic pain can take a mental toll, and stress can make RA pain worse. Incorporating stress-reducing techniques into your daily routine can be beneficial for both your physical and emotional well-being.
Meditation and Mindfulness: Mindfulness practices, including deep breathing and guided meditation, can help reduce stress and improve your tolerance to pain. Even just a few minutes a day can make a difference.
Yoga and Tai Chi: These mind-body practices combine gentle movements, breathing techniques, and meditation to promote relaxation and reduce pain. Many people with RA find them helpful in managing their symptoms.
6. Alternative Therapies
In addition to conventional treatments, many people with RA turn to alternative therapies for relief. These can be effective for some people, though results can vary.
Acupuncture: Acupuncture involves inserting fine needles into specific points on the body. Some people with RA find that acupuncture can help reduce pain and improve joint function.
Massage Therapy: Gentle massage can help improve circulation, reduce muscle tension, and alleviate pain in affected joints. Be sure to work with a trained massage therapist who is familiar with arthritis.
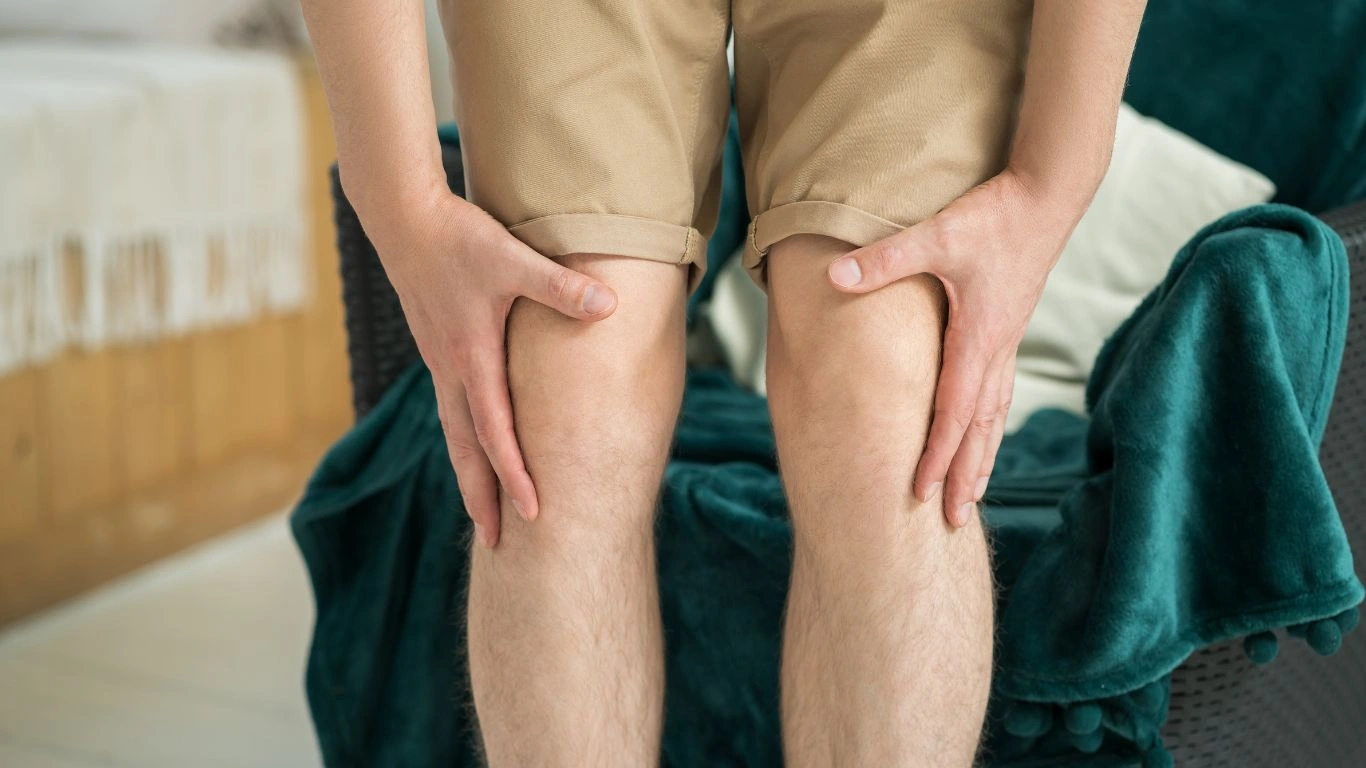
Conclusion: Finding What Works for You
Managing rheumatoid arthritis pain is a personal journey, and what works for one person may not work for another. It’s important to work closely with your healthcare team to find the best combination of treatments for your specific symptoms. Whether it’s through medication, physical therapy, diet changes, or alternative therapies, there are plenty of ways to manage your pain and live a fulfilling life.
Appendices
References
- Smith, R., & Jones, T. (2021). Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Management: A Clinical Guide. Journal of Rheumatology, 45(2), 109-120. Read Article
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS). (2024). Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment. Read Article
- American College of Rheumatology (ACR). (2023). Pain Management Strategies for RA Patients. Read Article

Tarra Nugroho is a dedicated Nurse Practitioner with a strong foundation in family and preventive care. She brings both compassion and clinical expertise to her practice, focusing on patient-centered care and health education. As a contributor to Healthusias.com, Tarra translates medical knowledge into clear, empowering articles on topics like women’s health, chronic disease management, and lifestyle medicine. Her mission is simple: help people feel seen, heard, and informed—both in the clinic and through the content she creates. When she’s not caring for patients, Tarra enjoys weekend hikes, plant-based cooking, and curling up with a good health podcast.