Signs of Severe Acid Reflux – A Comprehensive Guide
Learn about the signs of severe acid reflux in this comprehensive guide. Understand its causes, symptoms, triggers, and potential complications. Discover effective treatment options, preventive measures, and when to seek medical attention.
Introduction
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is a common digestive disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. While mild cases of acid reflux can often be managed with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter medications, severe acid reflux requires prompt attention and comprehensive treatment. In this extensive article, we will delve deep into the signs and symptoms of severe acid reflux, its potential causes, how to recognize triggers, possible complications, diagnosis methods, treatment options, preventive measures, and when to seek medical attention.
What is Acid Reflux?
Acid reflux occurs when the stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and inflammation. This backflow is a natural process that happens occasionally in most people, but when it becomes frequent and severe, it can lead to GERD. Understanding the mechanics of acid reflux is crucial to comprehend the factors contributing to its severity.
Understanding Severe Acid Reflux
Severe acid reflux refers to persistent and intense symptoms that significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Unlike mild cases, severe acid reflux may require more aggressive treatment options and lifestyle adjustments. Recognizing the gravity of the condition allows patients to seek timely medical intervention and improve their overall well-being.

Causes of Severe Acid Reflux
Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle choices can contribute to the development of severe acid reflux. Lifestyle factors such as obesity, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and lying down after meals can exacerbate the symptoms and increase the risk of complications. Understanding the role of lifestyle in acid reflux allows individuals to make informed changes to improve their condition.
Diet and Eating Habits
The relationship between diet and acid reflux is well-established. Certain foods and eating habits can trigger or worsen severe acid reflux. Foods such as spicy, fatty, and acidic options, as well as consuming large meals and eating late at night, are common culprits. Delving into the impact of diet and eating habits on acid reflux enables patients to make dietary modifications to manage their symptoms better.
Medical Conditions and Medications
Various medical conditions can increase the risk of severe acid reflux. Conditions like hiatal hernia, pregnancy, and connective tissue disorders can contribute to the severity of GERD symptoms. Additionally, certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and specific antidepressants, may also exacerbate acid reflux symptoms. Identifying the medical conditions and medications associated with severe acid reflux helps healthcare providers tailor treatment plans to individual needs.

Recognizing the Symptoms
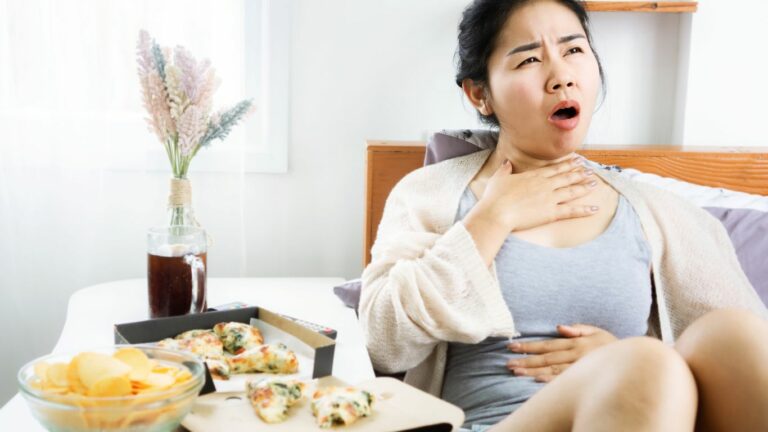
Heartburn and Chest Pain
Heartburn is a hallmark symptom of acid reflux, characterized by a burning sensation in the chest. This discomfort is often accompanied by a sour taste in the mouth. In severe cases, heartburn can cause chest pain, which may be mistaken for a heart attack. Understanding the nature of heartburn and its association with severe acid reflux is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Regurgitation and Sour Taste
Regurgitation refers to the feeling of stomach acid or partially digested food coming back into the throat or mouth. This experience can leave a sour or bitter taste in the mouth, which is another common symptom of severe acid reflux. Recognizing the connection between regurgitation and acid reflux helps patients differentiate it from other digestive issues.
Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia)
Severe acid reflux can lead to difficulty swallowing, a condition known as dysphagia. This symptom can be distressing and may feel like food is getting stuck in the throat or chest. Understanding the implications of dysphagia and its association with acid reflux is crucial in developing appropriate treatment strategies.
Chronic Cough and Hoarseness
A persistent dry cough and hoarseness are potential signs of severe acid reflux, especially if they worsen at night or after meals. These symptoms often result from the irritation of the esophagus caused by stomach acid. Identifying the link between chronic cough, hoarseness, and acid reflux can guide healthcare providers in determining the most effective treatment plan.
Asthma or Asthma-like Symptoms
Acid reflux can trigger asthma symptoms or worsen existing asthma in some individuals. This is known as reflux-induced asthma or acid-induced asthma. Understanding the association between acid reflux and asthma allows patients to manage both conditions simultaneously, improving overall respiratory health.
Dental Erosion and Bad Breath
The repeated exposure of teeth to stomach acid can lead to dental erosion, causing tooth decay and other dental problems. Additionally, persistent acid reflux may cause bad breath. Understanding the impact of acid reflux on dental and oral health helps patients take preventive measures to protect their teeth and maintain oral hygiene.
Identifying Triggers
Trigger Foods and Beverages
Certain foods and beverages can trigger severe acid reflux in susceptible individuals. Items like citrus fruits, tomatoes, chocolate, coffee, and carbonated drinks are common triggers. Identifying and avoiding these trigger foods and beverages can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of acid reflux episodes.
Trigger Activities and Postures
In addition to diet, specific activities and postures can exacerbate acid reflux symptoms. Bending over, lying down immediately after eating, and heavy lifting can contribute to the occurrence of acid reflux. Recognizing trigger activities and postures empowers individuals to modify their daily routines to minimize symptom flare-ups.
Stress and Emotional Triggers
Stress and strong emotions can lead to an increase in stomach acid production, worsening acid reflux symptoms. Understanding the impact of stress and emotions on acid reflux enables patients to explore stress management techniques and relaxation strategies to alleviate symptoms.

Complications of Severe Acid Reflux
Esophagitis and Ulcers
Chronic acid reflux can cause inflammation of the esophagus (esophagitis) and lead to the formation of ulcers. These ulcers may result in bleeding or narrowing of the esophagus, affecting swallowing and causing discomfort.
Barrett’s Esophagus
In some cases, long-term acid reflux can cause changes in the esophageal lining, leading to a condition called Barrett’s esophagus. This condition is associated with an increased risk of esophageal cancer. Recognizing the potential complications of severe acid reflux emphasizes the importance of timely diagnosis and treatment.
Respiratory Problems
Aspiration of stomach acid into the lungs can lead to respiratory issues, such as chronic cough, pneumonia, or bronchitis. These respiratory problems can be severe and may necessitate immediate medical attention.
Dental and Oral Health Complications
The repeated exposure of tooth enamel to stomach acid can lead to tooth decay, gum problems, and other oral health issues. Managing acid reflux effectively is crucial for preserving dental health and preventing further complications.

Diagnosing Severe Acid Reflux
Medical History and Physical Examination
Doctors will review the patient’s medical history, ask about symptoms, and conduct a physical examination to evaluate signs of severe acid reflux. A comprehensive medical history helps healthcare providers identify potential triggers and risk factors for GERD.
Endoscopy and Biopsy
Endoscopy is a common procedure used to visualize the esophagus and take tissue samples for biopsy. This allows doctors to check for inflammation or cellular changes in the esophageal lining, aiding in the diagnosis of severe acid reflux and related complications.
Esophageal pH Monitoring
Esophageal pH monitoring is a diagnostic test that measures the level of acidity in the esophagus over a 24-hour period. This test helps determine the frequency and duration of acid reflux episodes, providing valuable information for treatment planning.
Barium Swallow Test
The barium swallow test is an X-ray procedure that involves swallowing a barium solution. This test highlights the esophagus and stomach, allowing doctors to detect abnormalities and assess the function of these organs.
Other Diagnostic Tests
Additional tests like esophageal manometry, impedance testing, and motility studies may be used to assess esophageal function and rule out other conditions that can mimic severe acid reflux symptoms.
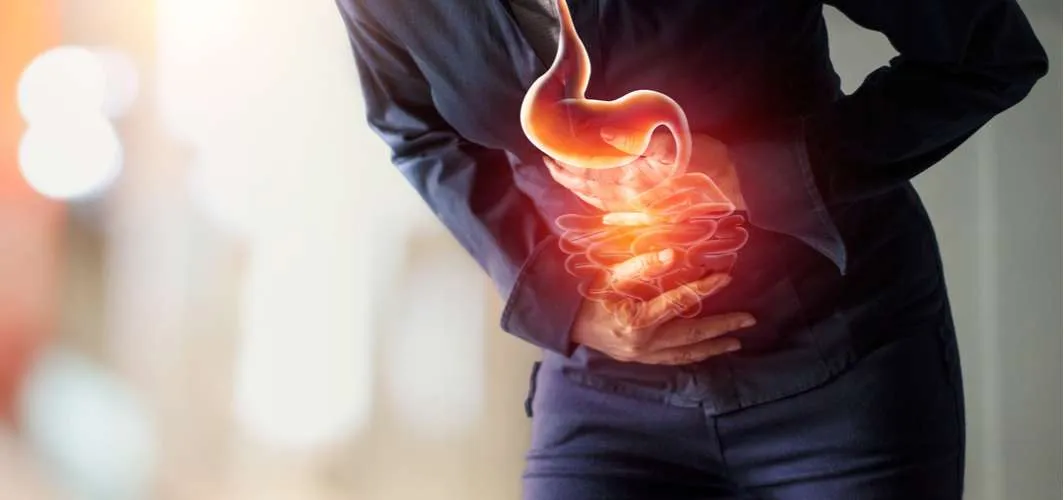

Treatment Options
Lifestyle and Dietary Changes
Lifestyle modifications play a significant role in managing severe acid reflux. Adopting healthy habits, such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding trigger foods, and elevating the head of the bed, can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the frequency of acid reflux episodes.
Over-the-Counter Medications
For mild to moderate acid reflux, over-the-counter antacids and H2 blockers can provide temporary relief by neutralizing stomach acid or reducing its production.
Prescription Medications
In more severe cases, healthcare providers may prescribe proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and other medications that decrease stomach acid production. These medications are often more potent than over-the-counter options and can help control acid reflux symptoms effectively.
Surgical Interventions
In cases where medications and lifestyle changes are ineffective, surgical procedures like fundoplication may be recommended to strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter and prevent acid reflux.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Some individuals find relief from acid reflux symptoms through alternative and complementary therapies, such as acupuncture, herbal remedies, or relaxation techniques. These therapies can be used in conjunction with traditional treatments under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
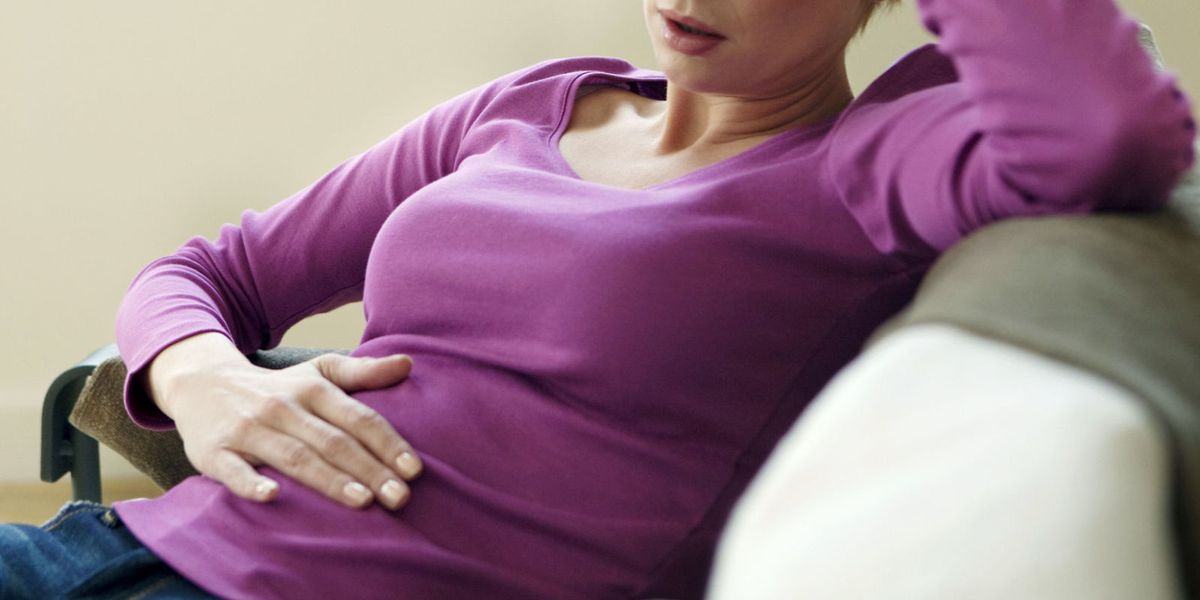

Managing Severe Acid Reflux During Pregnancy
Pregnant women with severe acid reflux should work closely with their healthcare providers to manage symptoms safely. Pregnancy-specific considerations and treatment options are essential to safeguard both the mother and the developing fetus.
Tips for Preventing Severe Acid Reflux
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce pressure on the stomach and lower the risk of acid reflux. A comprehensive approach to weight management, including diet and exercise, is vital for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
Eat Smaller, More Frequent Meals
Eating smaller meals more frequently can prevent excessive stomach distention and reduce the likelihood of acid reflux. Mindful eating and portion control are valuable strategies for managing acid reflux symptoms.
Avoid Trigger Foods and Beverages
Identifying and avoiding trigger foods and beverages can minimize acid reflux episodes. Keeping a food diary and tracking symptoms can aid in recognizing individual triggers.
Elevate the Head of Your Bed
Raising the head of the bed by about 6-8 inches can help prevent stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus during sleep. Elevating the head of the bed is a simple yet effective strategy to reduce nighttime reflux.
Manage Stress and Anxiety
Stress and anxiety can exacerbate acid reflux symptoms. Practicing stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can help manage acid reflux triggered by stress.
Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol Intake
Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can exacerbate acid reflux symptoms, so reducing or quitting these habits is beneficial for overall health and symptom management.
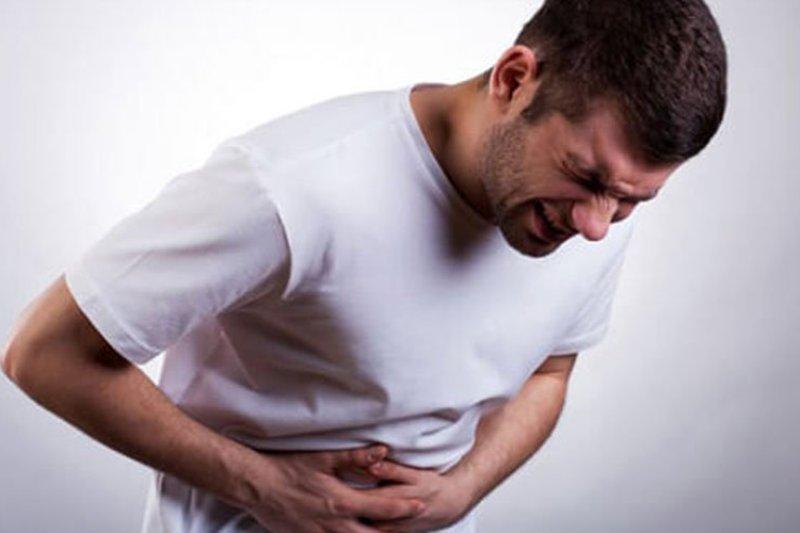

When to Seek Medical Attention
Individuals experiencing severe or persistent acid reflux symptoms, or those with complications like difficulty swallowing, should seek medical attention promptly. Timely intervention is crucial to prevent further complications and improve the quality of life for individuals with severe acid reflux.
Conclusion
Severe acid reflux is a chronic condition that requires attention and appropriate management to prevent complications. Understanding the signs, symptoms, triggers, and potential complications associated with severe acid reflux empowers individuals to take proactive steps in their treatment journey. By adopting lifestyle modifications, following medical advice, and seeking timely medical attention, individuals with severe acid reflux can find relief and improve their overall well-being. Remember, each person’s experience with severe acid reflux is unique, so personalized treatment plans are essential for successful management. Consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment options based on individual needs.
Appendices
References:
- El-Serag, H. B., & Sweet, S. (2014). Update on the epidemiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Gut, 63(6), 871-880.
- Shaheen, N. J., & Hansen, R. A. (2013). The epidemiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Gut, 62(2), 281-289.
- Katz, P. O., Gerson, L. B., & Vela, M. F. (2013). Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. American Journal of Gastroenterology, 108(3), 308-328.
- Kahrilas, P. J., & Shaheen, N. J. (2008). Review article: gastro-oesophageal reflux disease—pathophysiology and treatment. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 27(12), 12-25.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). (2021). Gastroesophageal Reflux (GER) and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD). Retrieved from https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/acid-reflux-ger-gerd-adults#:~:text=Print%20All%20Sections-,Definition%20%26%20Facts,leads%20to%20complications%20over%20time.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider regarding any medical concerns or conditions. The author and publisher of this article are not liable for any adverse effects or consequences resulting from the use or misuse of the information presented herein.

Camellia Wulansari is a dedicated Medical Assistant at a local clinic and a passionate health writer at Healthusias.com. With years of hands-on experience in patient care and a deep interest in preventive medicine, she bridges the gap between clinical knowledge and accessible health information. Camellia specializes in writing about digestive health, chronic conditions like GERD and hypertension, respiratory issues, and autoimmune diseases, aiming to empower readers with practical, easy-to-understand insights. When she’s not assisting patients or writing, you’ll find her enjoying quiet mornings with coffee and a medical journal in hand—or jamming to her favorite metal band, Lamb of God.