Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints. It causes inflammation, pain, and stiffness in the joints, and can lead to severe damage and disability if left untreated. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available for managing RA.
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic disease that causes the body’s immune system to mistakenly attack healthy joint tissues. This leads to inflammation and, over time, can result in joint damage and deformity.
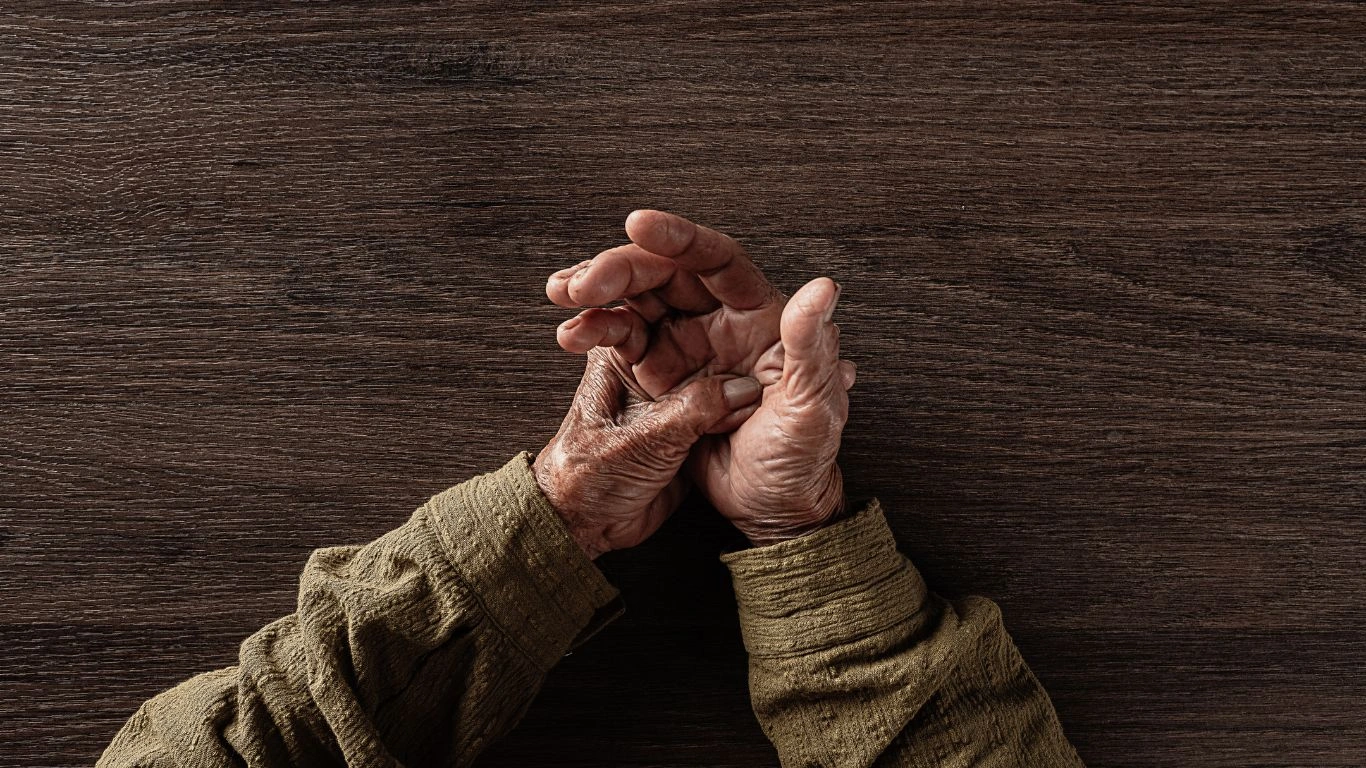

Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The exact cause of RA is unknown, but it is believed to be triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Genetics may play a role, as certain genes have been linked to an increased risk of developing the disease. Environmental factors like smoking and infections may also trigger RA in people who are genetically predisposed.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
RA symptoms can vary in severity, but common symptoms include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and fatigue. The symptoms often affect both sides of the body, such as the hands, wrists, and knees. In addition to joint symptoms, RA can also cause fever, weight loss, and a general feeling of being unwell.
Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Although there is no cure for RA, treatments are available to help manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and slow the progression of the disease. Treatment options include medications, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgery. Early intervention is key to managing RA effectively and preventing long-term damage.
Medications
Common medications used in the treatment of RA include disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologics, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). DMARDs help slow the progression of the disease, while biologics target specific components of the immune system.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is essential in maintaining joint mobility and preventing stiffness. A physical therapist will create an individualized plan to help improve joint function and alleviate pain.
Conclusion
Rheumatoid arthritis is a serious condition that requires ongoing management. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help individuals with RA lead a fulfilling life, despite the challenges posed by the disease.
Appendix
References
- American College of Rheumatology. (2022). Rheumatoid Arthritis. Retrieved from https://www.rheumatology.org
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). Rheumatoid Arthritis. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org
FAQ
1. What are the first signs of rheumatoid arthritis?
Early signs of RA include joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, particularly in the hands and feet. Fatigue and a feeling of overall unwellness can also occur.
2. Can rheumatoid arthritis be cured?
Currently, there is no cure for RA. However, treatments are available to manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
3. How long does rheumatoid arthritis last?
RA is a lifelong condition. With proper management, symptoms can be controlled, but the disease itself does not go away.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment options tailored to your individual needs.

Tarra Nugroho is a dedicated Nurse Practitioner with a strong foundation in family and preventive care. She brings both compassion and clinical expertise to her practice, focusing on patient-centered care and health education. As a contributor to Healthusias.com, Tarra translates medical knowledge into clear, empowering articles on topics like women’s health, chronic disease management, and lifestyle medicine. Her mission is simple: help people feel seen, heard, and informed—both in the clinic and through the content she creates. When she’s not caring for patients, Tarra enjoys weekend hikes, plant-based cooking, and curling up with a good health podcast.