Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms and Treatment
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms and Treatment
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder that affects millions worldwide. The symptoms can range from mild joint pain to severe inflammation and deformities. If you’re dealing with RA, it’s important to know what to look for and how to manage it effectively.

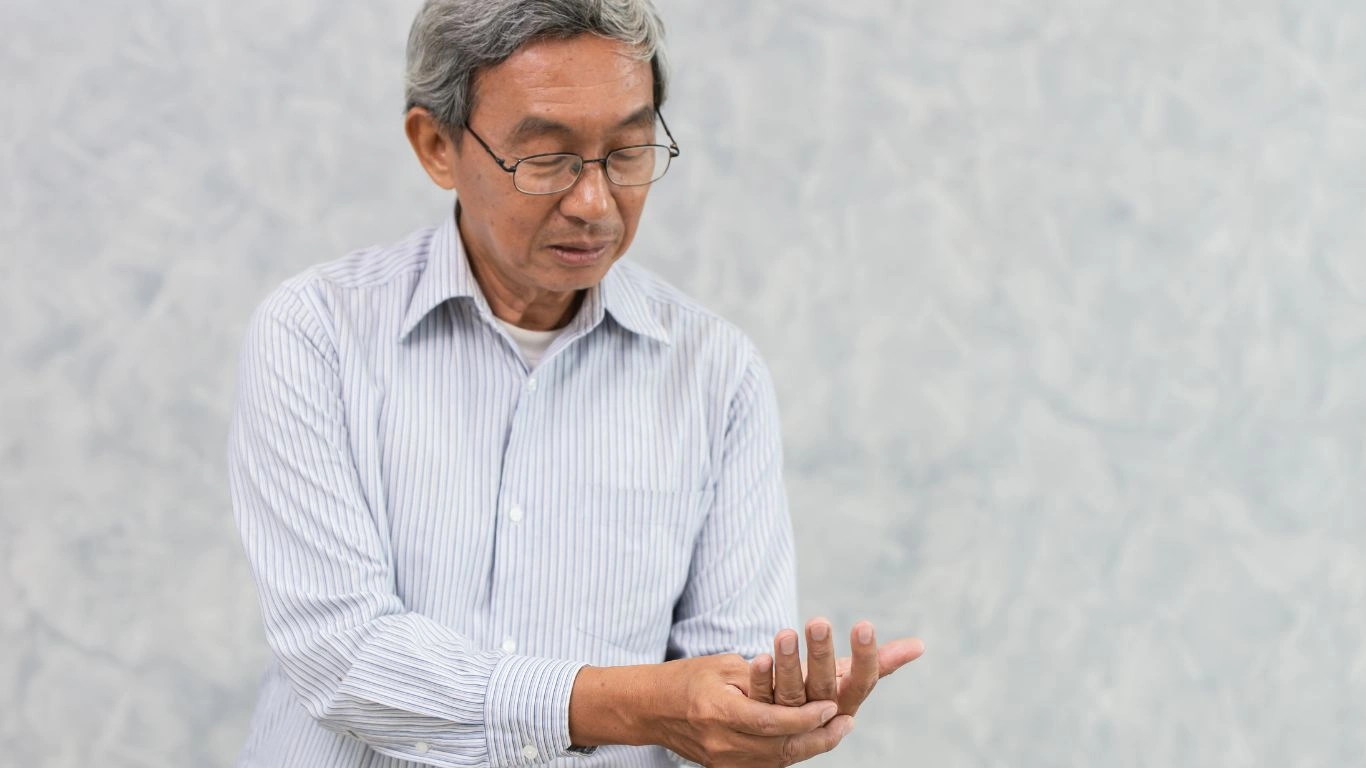
One of the early signs of rheumatoid arthritis is joint stiffness. This can often be worse in the mornings, and it may lead to trouble with everyday tasks, like opening a jar or even getting dressed.

The disease typically affects the smaller joints first, such as those in your hands and feet. It’s not just the pain that can be debilitating—RA can cause long-term damage to the joints if left untreated.
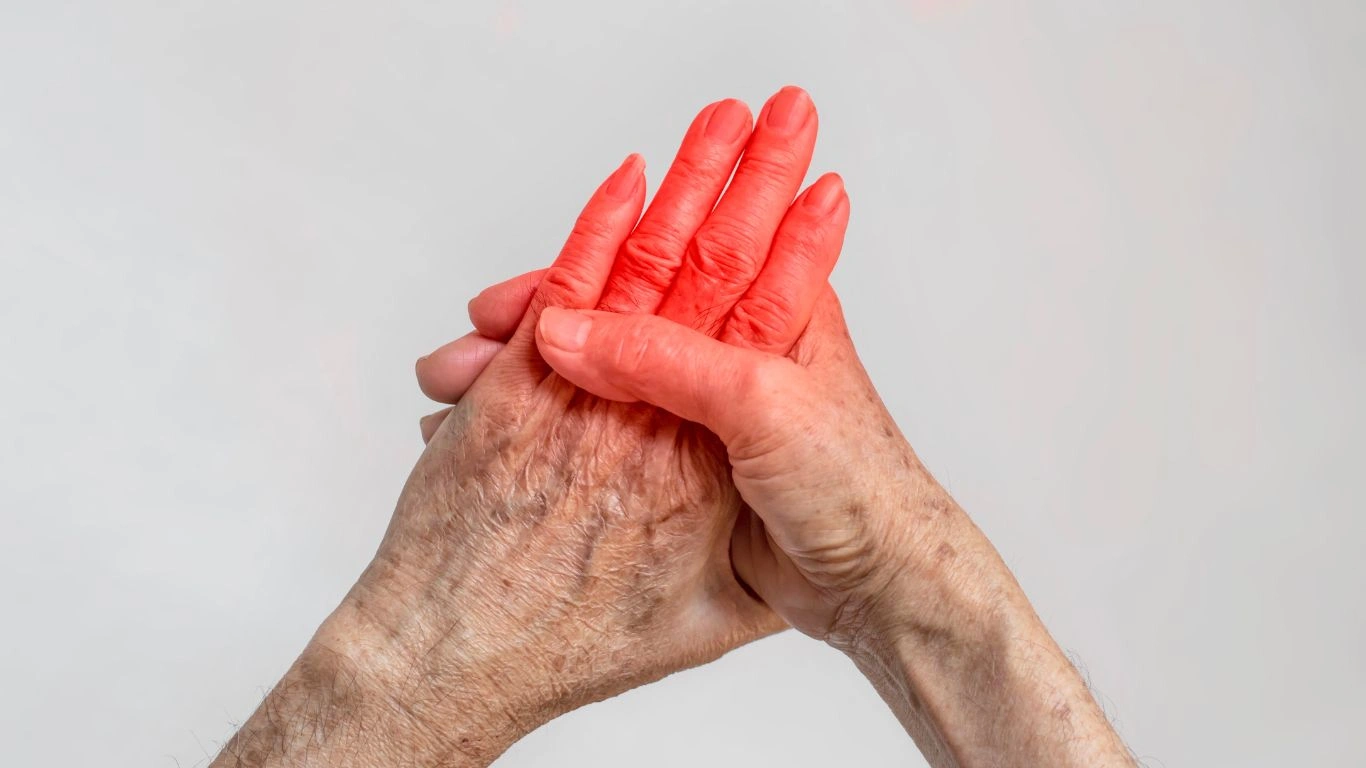
Managing RA often involves a combination of medication and lifestyle changes. Exercise, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgery can help improve quality of life for people living with the condition.

Remember, if you suspect you have RA or are experiencing symptoms, it’s important to get a diagnosis from your doctor. Early intervention can help prevent joint damage and improve long-term outcomes.
References
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. “Rheumatoid Arthritis.” https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/rheumatoid-arthritis
- American College of Rheumatology. “What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?” https://www.rheumatology.org/What-is-Rheumatoid-Arthritis
FAQs
What are the first signs of rheumatoid arthritis?
The first signs often include joint stiffness, pain, and swelling, especially in the hands and feet. Symptoms may be worse in the morning.
Can rheumatoid arthritis be cured?
Currently, there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, but early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent joint damage.
Is physical therapy helpful for RA?
Yes, physical therapy can help improve joint function, reduce pain, and maintain mobility in people with RA.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment options tailored to your specific needs.

Tarra Nugroho is a dedicated Nurse Practitioner with a strong foundation in family and preventive care. She brings both compassion and clinical expertise to her practice, focusing on patient-centered care and health education. As a contributor to Healthusias.com, Tarra translates medical knowledge into clear, empowering articles on topics like women’s health, chronic disease management, and lifestyle medicine. Her mission is simple: help people feel seen, heard, and informed—both in the clinic and through the content she creates. When she’s not caring for patients, Tarra enjoys weekend hikes, plant-based cooking, and curling up with a good health podcast.