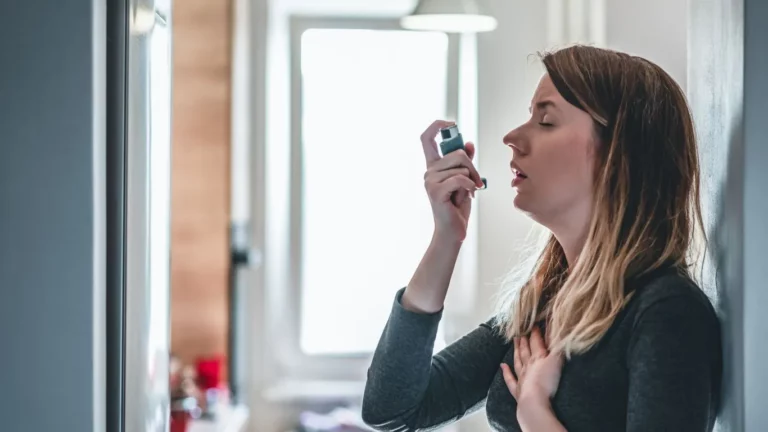
What Causes Asthma in Adults? – A Comprehensive Guide
html
Are you struggling with asthma as an adult? Wondering what could be triggering your symptoms? We’re diving into the causes of asthma in adults and what you can do about it. From environmental factors to genetics, let’s explore what might be behind your breathing issues.
Asthma in adults can be a tricky condition to manage, especially if you’re just being diagnosed or have dealt with it for years. It’s not always easy to pinpoint exactly what causes asthma in adults, as the condition can be triggered by a combination of environmental, lifestyle, and genetic factors. But understanding these causes is a crucial first step toward managing your symptoms effectively. In this guide, we’ll take a look at the common causes of adult asthma, the role of triggers, and practical tips for living with the condition.
Understanding Asthma in Adults
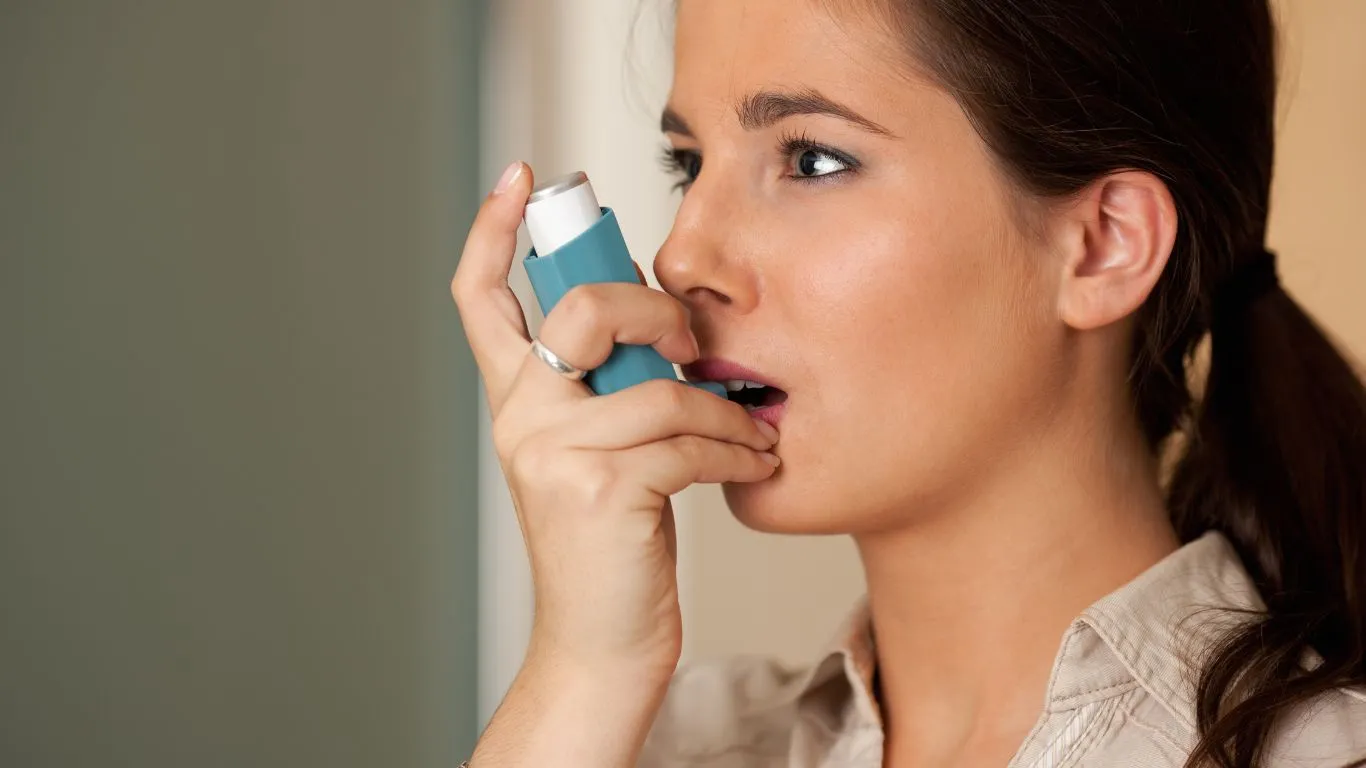
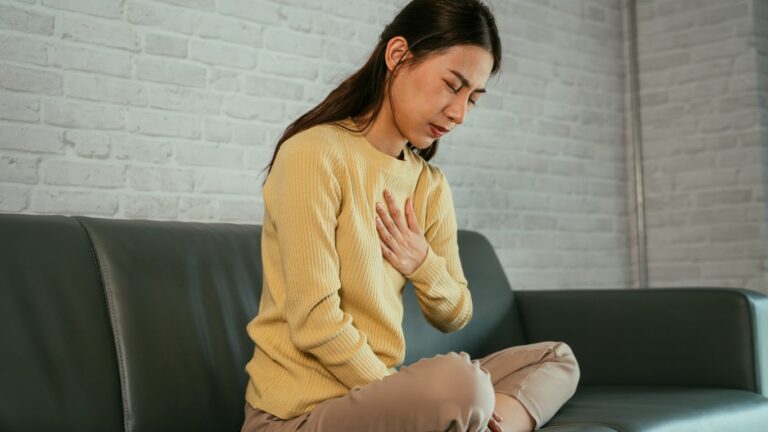
Before we jump into what causes asthma, it’s important to know exactly what asthma is. Asthma is a chronic condition that affects your airways, making it difficult to breathe. When asthma flares up, your airways become inflamed and narrowed, which can lead to coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and tightness in the chest. These symptoms can range from mild to severe, and in some cases, an asthma attack can be life-threatening. Asthma can start at any age, but it often develops in childhood. However, many adults are diagnosed with asthma later in life, which can be particularly challenging to cope with. The good news is, with the right treatment plan, adults with asthma can live a healthy, active life. 
What Causes Asthma in Adults?
The exact cause of asthma in adults isn’t always clear, and it can vary from person to person. However, researchers have identified several factors that contribute to the development of asthma or trigger asthma attacks in adults. Let’s break them down:
1. Genetics and Family History
Your genetic makeup plays a significant role in whether you’ll develop asthma as an adult. If you have a family history of asthma, allergies, or other respiratory conditions, you may be at an increased risk. Studies show that people with a first-degree relative (like a parent or sibling) who has asthma are more likely to develop the condition themselves. If you already have asthma, a family history of asthma can also influence the severity and type of asthma symptoms you experience. Asthma is believed to be hereditary, and certain genes involved in immune system response may make you more prone to inflammation in the airways.
2. Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors are one of the most significant causes of asthma in adults. These factors can include everything from allergens to air pollution. Common environmental triggers for asthma include:
- Allergens: Pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold can cause allergic reactions that trigger asthma symptoms.
- Air Pollution: Exposure to pollutants like cigarette smoke, vehicle exhaust, and industrial chemicals can irritate the airways and lead to asthma attacks.
- Weather Changes: Cold air, hot air, and changes in humidity can also trigger asthma in some people.

3. Occupational Hazards
Certain jobs put people at higher risk of developing asthma due to exposure to irritants and allergens. These include industries like construction, farming, and healthcare, where workers might be exposed to things like dust, fumes, chemicals, and even mold. This form of asthma is known as “occupational asthma” and can develop over time with repeated exposure to specific irritants. For example, bakers who are regularly exposed to flour dust or painters who inhale chemical fumes are at increased risk for developing asthma. If you have a job with high exposure to potential allergens or irritants, it’s important to take preventive measures to protect your lungs.
4. Respiratory Infections
Certain respiratory infections, particularly in early adulthood or during childhood, can increase the risk of developing asthma later in life. Infections like viral colds, the flu, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) can irritate the airways and make them more sensitive to future asthma attacks. People who’ve experienced severe respiratory infections early in life may be more likely to develop asthma as adults. Similarly, frequent upper respiratory infections in adulthood can worsen asthma symptoms or trigger flare-ups in those already diagnosed with the condition.
5. Allergies and Hay Fever
There’s a strong connection between allergies and asthma in adults. People who suffer from hay fever or allergic rhinitis are more likely to develop asthma. In fact, allergy-induced asthma is one of the most common forms of asthma in adults. Pollen, pet dander, and dust mites are among the leading allergens that can trigger allergic reactions in the airways, leading to asthma symptoms. If you already have allergies, managing them through medication or lifestyle changes can help reduce your risk of developing asthma.
6. Obesity and Weight Gain
There’s a growing body of evidence linking obesity with asthma, especially in adults. Excess weight can put additional pressure on the lungs and make it more difficult for your airways to remain open and clear. Studies have found that people with obesity are more likely to develop asthma, and they often experience more severe asthma symptoms compared to those at a healthy weight. Weight management, combined with a healthy diet and regular exercise, can play an important role in managing asthma symptoms and improving overall lung health.
7. Hormonal Changes
For some women, hormonal changes can play a role in the development and exacerbation of asthma. Pregnancy, menopause, and the use of oral contraceptives can cause hormonal fluctuations that impact lung function. In particular, pregnancy-induced asthma can occur, where asthma symptoms worsen or appear for the first time during pregnancy. Women who are already prone to asthma may notice that their symptoms are more pronounced during certain phases of their menstrual cycle, especially around menstruation and ovulation.
How to Manage Asthma in Adults
Managing asthma as an adult requires a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and avoiding triggers. Here are a few strategies that can help keep your asthma under control:
1. Avoid Triggers
The best way to manage asthma is to avoid triggers that can cause flare-ups. This may mean limiting exposure to allergens like pollen or pet dander, avoiding smoky environments, or using air purifiers in your home. It’s important to identify your personal triggers so you can take steps to minimize your exposure.
2. Medication
Asthma medications, such as inhalers and steroids, are crucial for managing the condition. Quick-relief inhalers (bronchodilators) help open up the airways during an asthma attack, while long-term control medications (like inhaled corticosteroids) reduce inflammation in the airways and prevent future flare-ups. Work with your doctor to find the right combination of medications that work for you.
3. Regular Exercise
While exercise can trigger asthma symptoms for some, regular physical activity can actually improve lung health in the long run. If you have asthma, try to exercise in an environment free of pollutants and allergens, and use your inhaler before workouts if necessary. 
Conclusion
The causes of asthma in adults are diverse, and it can be tricky to pinpoint exactly what’s causing your symptoms. Genetics, environmental triggers, allergies, and even obesity can all play a role in the development of asthma. By understanding these causes and taking preventive measures, you can better manage your asthma and enjoy a healthier life.
Appendices
FAQs
- Can asthma develop in adults who never had it as children? Yes, adult-onset asthma is common, especially among people with a history of allergies or exposure to certain environmental triggers.
- Is there a cure for asthma in adults? Currently, there is no cure for asthma, but with the right treatment and management plan, most adults with asthma can lead normal lives.
- Are asthma medications safe for long-term use? Most asthma medications, when used as prescribed, are safe for long-term use. Always follow your doctor’s advice on medication usage.
References
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2023). Asthma Overview. Read Article
- American Lung Association. (2023). Understanding Adult Asthma. Read Article
- Smith, J., & Thompson, A. (2022). Asthma and Allergies: Exploring the Connections. Journal of Respiratory Health, 35(3), 123-129. Read Article
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and does not substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized asthma management and treatment options.

Bianca Nala is a compassionate Nurse Practitioner with a strong background in primary and respiratory care. As a health writer for Healthusias.com, she combines her clinical expertise with a talent for clear, relatable storytelling to help readers better understand their health. Bianca focuses on topics like asthma, COPD, chronic cough, and overall lung health, aiming to simplify complex medical topics without losing accuracy. Whether she’s treating patients or writing articles, Bianca is driven by a single goal: making quality healthcare knowledge accessible to everyone.