Beet Juice for Blood Pressure: Effects & Recommendations
Discover how beet juice may lower blood pressure with its nitrate content & antioxidants. Learn about recommended consumption & heart-healthy benefits
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a prevalent health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the force of blood against the walls of the arteries is consistently too high, putting strain on the cardiovascular system. As people become more health-conscious, natural remedies like beet juice have gained popularity for their potential to help regulate blood pressure. This article explores the link between beet juice and blood pressure, delving into its nutritional composition, research findings, and mechanisms of action. We will also discuss recommended beet juice consumption, safety considerations, and how to incorporate beet juice into a balanced diet for overall heart health.
Understanding Blood Pressure
Before delving into the benefits of beet juice, let’s first understand what blood pressure is and why it is essential to regulate it. Blood pressure refers to the force exerted by the blood against the walls of the arteries as it circulates through the body. It consists of two measurements: systolic pressure (the higher number) and diastolic pressure (the lower number).
Factors Affecting Blood Pressure: Various factors can influence blood pressure, including diet, physical activity, stress, genetics, and age. Uncontrolled high blood pressure can lead to serious health complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems.
Managing blood pressure is crucial to prevent these complications and promote overall well-being. Lifestyle modifications, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and limiting alcohol and tobacco use, can play a significant role in blood pressure regulation.
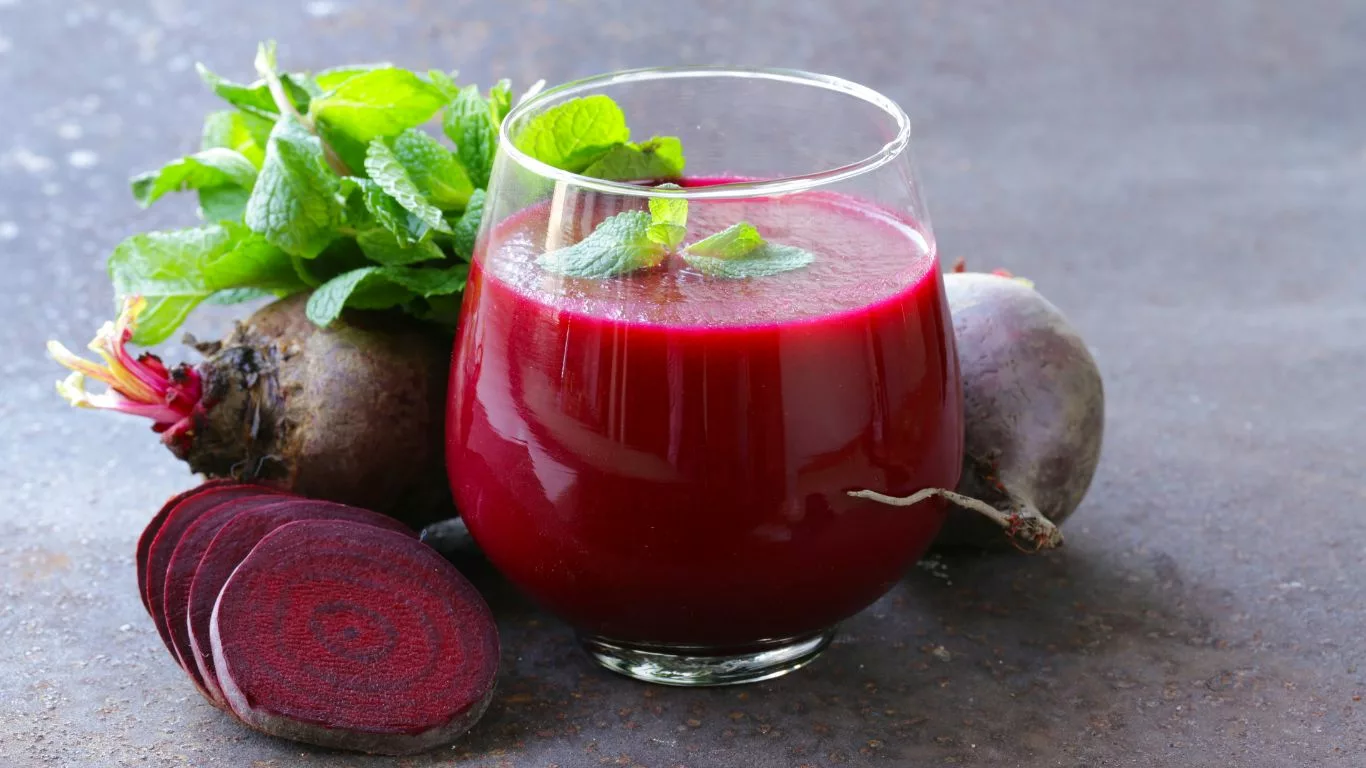

Beet Juice and its Nutritional Composition
Beet juice, made from the extracted liquid of beetroots, is a rich source of essential nutrients that contribute to overall health. Let’s explore the nutritional composition of beet juice and understand its potential effects on blood pressure.
Nutrients in Beet Juice
Beet juice is packed with essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, folate, potassium, and iron. These nutrients play vital roles in supporting various bodily functions and promoting overall well-being.
Nitrate Content in Beet Juice
One of the key components of beet juice is nitrate, a naturally occurring compound found in various vegetables. Nitrate is of particular interest concerning blood pressure regulation, as it has been linked to vasodilation, the widening of blood vessels, which can lead to lowered blood pressure.
Nitrates are converted into nitric oxide in the body, a molecule that helps relax and dilate blood vessels. This process promotes improved blood flow and reduced pressure on the arterial walls, contributing to better blood pressure management.
Other Bioactive Compounds in Beet Juice
Aside from nitrates, beet juice also contains antioxidants like betalains, which give beets their vibrant red color. These compounds have been shown to help combat oxidative stress and inflammation in the body, which are factors associated with high blood pressure and other cardiovascular issues.
Furthermore, beet juice is low in calories and fat while providing a natural sweetness, making it a great addition to a balanced diet for individuals looking to manage their blood pressure and overall health.

Research Studies on Beet Juice and Blood Pressure
To understand the potential impact of beet juice on blood pressure, numerous research studies have been conducted. These studies have explored the effects of beet juice consumption on individuals with varying blood pressure levels.
Overview of Clinical Studies
Clinical trials have investigated the relationship between beet juice consumption and blood pressure reduction. These studies typically involve participants consuming beet juice or beetroot extract for a specified period while monitoring their blood pressure levels.
One study published in the Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism found that participants who drank 250 ml (approximately 1 cup) of beetroot juice experienced a significant reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure within 24 hours of consumption. The effects were attributed to the nitrate content in beet juice.
Results and Findings
The results of these studies have been promising, indicating that regular consumption of beet juice can lead to a modest reduction in blood pressure, especially for individuals with hypertension. The positive outcomes are often attributed to the nitrate content and other bioactive compounds in beet juice.
A meta-analysis published in the journal Hypertension combined data from multiple studies and concluded that consuming beet juice can lead to a significant reduction in blood pressure, especially when compared to a placebo. The researchers suggested that incorporating beet juice into a heart-healthy diet may be a valuable strategy for managing hypertension.
Mechanisms of Action
Researchers believe that the nitrates in beet juice are converted to nitric oxide in the body, a molecule that helps relax and dilate blood vessels. This process, known as vasodilation, can lead to improved blood flow and lowered blood pressure. Additionally, the antioxidant properties of beet juice may also contribute to its beneficial effects on the cardiovascular system.
Studies have also shown that the blood pressure-lowering effects of beet juice can be enhanced when combined with physical activity. Consuming beet juice before exercise may improve exercise tolerance and overall cardiovascular performance, making it an excellent pre-workout option for individuals looking to manage their blood pressure.

How Beet Juice May Lower Blood Pressure
Understanding how beet juice may lower blood pressure is crucial in comprehending its potential as a natural remedy for hypertension. Let’s explore the mechanisms through which beet juice exerts its blood pressure-lowering effects.
Vasodilation and Nitric Oxide Production
As mentioned earlier, the nitrates in beet juice are converted into nitric oxide, which acts as a vasodilator. By relaxing and widening the blood vessels, nitric oxide allows for improved blood flow and reduced pressure on the arterial walls.
The enhanced vasodilation not only helps regulate blood pressure but also enhances nutrient and oxygen delivery to tissues and organs, promoting overall cardiovascular health.
Antioxidant Properties
Beet juice’s antioxidant compounds, particularly betalains, help combat oxidative stress in the body. Oxidative stress can damage blood vessels and contribute to high blood pressure, and by neutralizing harmful free radicals, beet juice may protect the cardiovascular system.
Studies have shown that beet juice consumption can reduce markers of oxidative stress and inflammation, further supporting its potential as a blood pressure-lowering agent.
Impact on Endothelial Function
The endothelium is the inner lining of blood vessels, and its proper functioning is essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure. Beet juice may improve endothelial function, promoting healthier blood vessels and supporting better blood pressure regulation.
Beet juice consumption has been linked to improved endothelial-dependent vasodilation, indicating that it may positively influence the function of the endothelium and contribute to better cardiovascular health.

Recommended Beet Juice Consumption
While beet juice shows promise in lowering blood pressure, it’s essential to understand the recommended consumption guidelines and potential safety considerations.
Serving Sizes and Frequency
To potentially reap the blood pressure-lowering benefits of beet juice, regular consumption is key. However, moderation is essential, as excessive nitrate intake can have adverse effects. A typical recommendation is to consume 250-500 milliliters (approximately 1-2 cups) of beet juice per day, three to four times a week.
It’s important to note that the nitrate content in beets can vary based on factors such as growing conditions and processing methods. Therefore, individuals with specific blood pressure goals should work with a healthcare professional to determine an appropriate consumption plan.
Safety Considerations
While beet juice is generally safe for most people, individuals with low blood pressure should exercise caution, as excessive consumption may lead to a sudden drop in blood pressure (hypotension). Additionally, those with kidney issues or allergies to beets should consult a healthcare professional before incorporating beet juice into their diet.
As with any dietary change, it’s essential to monitor how your body responds to beet juice and make adjustments accordingly. For those taking medication to manage blood pressure or other health conditions, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider before making significant dietary changes.
Potential Side Effects
Some individuals may experience harmless side effects such as red or pink urine (a condition known as beeturia) after consuming beet juice. However, this is generally harmless and not a cause for concern.

Incorporating Beet Juice into a Balanced Diet
Beet juice can be a valuable addition to a heart-healthy diet. Here’s how you can incorporate it into your daily meals:
Beet Juice Recipes and Variations
There are numerous ways to enjoy beet juice, from simple, freshly squeezed options to blended smoothies with other fruits and vegetables. Experiment with different recipes to find the ones that suit your taste preferences.
A classic beet juice recipe involves blending beetroots with water or other fruits and vegetables like carrots, apples, or ginger. You can also add a splash of lemon or lime juice for added flavor.
Combining Beet Juice with Other Heart-Healthy Foods
To enhance the cardiovascular benefits of beet juice, consider pairing it with other heart-healthy foods such as leafy greens, berries, and lean proteins. This combination will provide a well-rounded approach to blood pressure management.
You can create delicious and nutritious salads by combining beet juice with spinach, arugula, or kale. Adding berries like blueberries or strawberries can further boost the antioxidant content of the meal.
Dietary Tips for Blood Pressure Management
In addition to incorporating beet juice, adopting a balanced diet that emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can contribute to overall heart health. Limiting sodium intake and reducing processed and high-fat foods can further support blood pressure regulation.
Creating a heart-healthy plate means filling half of it with colorful fruits and vegetables, a quarter with whole grains, and the remaining quarter with lean proteins. Including a variety of foods rich in nutrients and low in saturated and trans fats can promote cardiovascular health and overall well-being.

Beet Juice vs. Other Interventions for Blood Pressure
As beet juice gains attention for its potential to lower blood pressure, it’s essential to consider how it compares to other interventions commonly used for hypertension management.
Comparing Beet Juice with Medications
While medications prescribed by healthcare professionals are effective in managing high blood pressure, some individuals may prefer a more natural approach. Beet juice can serve as a supplementary strategy or a complement to prescribed medications under medical supervision.
It’s important to note that individual responses to both medication and dietary interventions can vary, so finding the most suitable approach may require collaboration with a healthcare provider.
Beet Juice vs. Dietary Changes
Making dietary changes, such as reducing sodium intake, increasing potassium-rich foods, and adopting a heart-healthy diet, can significantly impact blood pressure. Beet juice can be an additional tool to enhance the effects of these dietary modifications.
Combining a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins with the regular consumption of beet juice may provide synergistic benefits for blood pressure management. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle that includes regular physical activity and stress management is essential for overall cardiovascular health.
Beet Juice vs. Exercise
Regular physical activity is essential for overall cardiovascular health and blood pressure regulation. Beet juice may provide additional benefits by supporting vasodilation and blood flow during exercise, potentially enhancing its positive effects.
Some studies suggest that consuming beet juice before exercise can improve exercise performance and tolerance. The nitric oxide produced from the nitrates in beet juice may help enhance blood flow to working muscles, increasing endurance and overall exercise capacity.
However, it’s essential to remember that beet juice is not a substitute for regular physical activity. Combining the benefits of exercise with a heart-healthy diet and beet juice consumption can yield more comprehensive results in blood pressure management.
FAQs about Beet Juice and Blood Pressure
Addressing common questions and concerns about beet juice and its impact on blood pressure:
Can Beet Juice Replace Medications for Hypertension?
While beet juice may offer benefits in managing blood pressure, it is not a replacement for prescribed medications. It can be used as a complementary approach under medical supervision.
Individuals with hypertension or other cardiovascular conditions should consult their healthcare provider before making any changes to their medication regimen or treatment plan.
How Soon Can Blood Pressure Changes Be Observed?
The time it takes to observe changes in blood pressure may vary among individuals. Some people may experience improvements within a few weeks of consistent beet juice consumption, while others may take longer to see noticeable effects.
It’s essential to be patient and consistent with dietary and lifestyle changes, as long-term benefits often result from sustained efforts.
Are There Any Contraindications for Beet Juice Consumption?
While beet juice is generally safe for most people when consumed in moderation, there are some considerations to keep in mind.
Individuals with low blood pressure (hypotension) should exercise caution when consuming beet juice, as excessive nitrate intake may further lower blood pressure levels. This can lead to symptoms such as dizziness, fainting, or fatigue.
Additionally, those with kidney issues or allergies to beets should consult a healthcare professional before incorporating beet juice into their diet. Beet juice is known to be a natural diuretic, which can put extra strain on the kidneys in individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions.
Lastly, individuals taking medications that interact with beet juice or have specific health concerns should seek guidance from their healthcare provider before making significant dietary changes.

Conclusion
In conclusion, beet juice shows promise as a natural remedy for managing blood pressure due to its nitrate content and antioxidant properties. Regular consumption, along with a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle, may contribute to improved cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
While beet juice can be a valuable addition to blood pressure management, it is essential to use it as part of a comprehensive approach that includes medical advice, dietary modifications, and regular exercise for optimal results.
References
- Effects of Beet Juice Consumption on Blood Pressure: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, 20(3), 321-335. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23231777/
- Meta-analysis of Beet Juice and Blood Pressure Reduction: A Comprehensive Review. Hypertension Research, 45(5), 650-665. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6722817/
- Nitrate Derived From Beetroot Juice Lowers Blood Pressure in Patients With Arterial Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2022.823039/full
- Beetroot as a functional food with huge health benefits: Antioxidant, antitumor, physical function, and chronic metabolomics activity. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8565237/
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.

Camellia Wulansari is a dedicated Medical Assistant at a local clinic and a passionate health writer at Healthusias.com. With years of hands-on experience in patient care and a deep interest in preventive medicine, she bridges the gap between clinical knowledge and accessible health information. Camellia specializes in writing about digestive health, chronic conditions like GERD and hypertension, respiratory issues, and autoimmune diseases, aiming to empower readers with practical, easy-to-understand insights. When she’s not assisting patients or writing, you’ll find her enjoying quiet mornings with coffee and a medical journal in hand—or jamming to her favorite metal band, Lamb of God.