Blood Pressure Monitoring for Beginners: A Complete Guide
Taking control of your health starts with understanding your blood pressure. If you’re a beginner, don’t worry—we’ve got you covered with this easy guide to monitoring your blood pressure!
Monitoring your blood pressure is an essential part of maintaining your overall health, especially if you’re at risk for hypertension or just want to keep track of your cardiovascular health. Whether you’re looking to take preventive measures or simply want to stay informed, learning how to monitor your blood pressure correctly is the first step.
In this article, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know as a beginner, from understanding what blood pressure is to tips for taking accurate readings. You’ll feel more confident in monitoring your health and ensuring you’re on the right track!
What Is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps it around your body. It’s measured in two numbers: systolic pressure (the top number) and diastolic pressure (the bottom number).
Systolic Pressure: This measures the force when your heart beats.
Diastolic Pressure: This measures the force when your heart is at rest between beats.
A normal blood pressure reading is usually around 120/80 mm Hg, though this can vary based on age, health, and other factors. It’s crucial to monitor these numbers regularly, as high or low blood pressure can indicate underlying health issues.
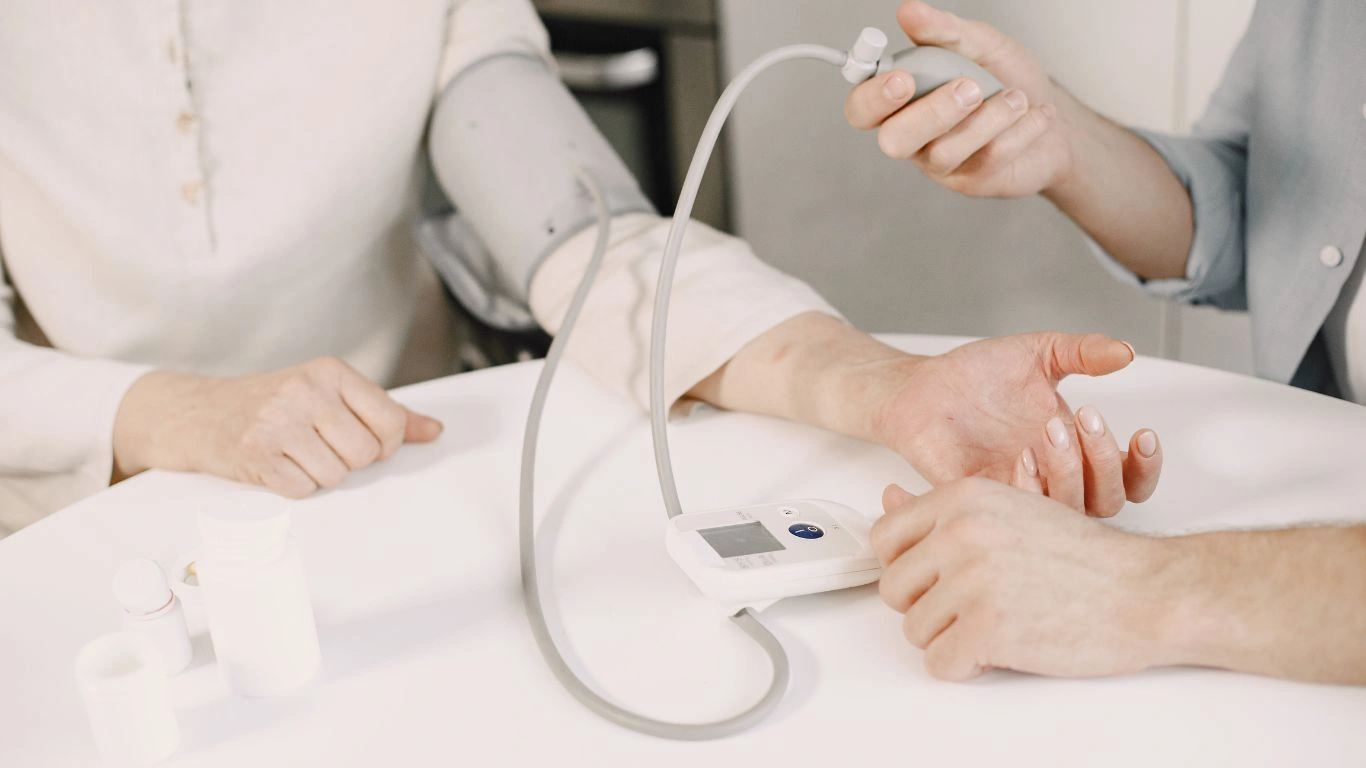
How to Measure Blood Pressure at Home
If you’re new to blood pressure monitoring, the good news is that it’s relatively easy to measure at home using a digital blood pressure cuff. Here’s how to do it:
- Choose the Right Equipment: You’ll need an automatic blood pressure cuff, which can be easily found at drugstores or online. These devices are easy to use, and many models even store your readings for later use.
- Find a Quiet Spot: Before measuring, make sure you’re in a calm, quiet space. Stress and movement can affect your readings, so take a few minutes to relax before starting.
- Sit Properly: Sit down with your back straight and your feet flat on the floor. Keep your arm supported on a flat surface, with the cuff positioned at the level of your heart.
- Follow Instructions: Turn on the device and follow the instructions for inflating the cuff. The cuff will automatically inflate and deflate, taking your reading in the process.
- Record Your Results: After the reading is taken, record the systolic and diastolic numbers. A typical reading will show something like “120/80.” Take several readings (at least 2-3) and average them to get the most accurate result.

What Do Your Blood Pressure Numbers Mean?
Understanding your blood pressure numbers is crucial for interpreting your health. Here’s a breakdown of the ranges you should know:
- Normal: Less than 120/80 mm Hg
- Elevated: 120-129 systolic and less than 80 diastolic
- Hypertension Stage 1: 130-139 systolic or 80-89 diastolic
- Hypertension Stage 2: 140 or higher systolic or 90 or higher diastolic
- Hypertensive Crisis: 180 or higher systolic and/or 120 or higher diastolic
If your readings are consistently outside the normal range, it might be a sign to consult with your healthcare provider. High blood pressure can lead to serious health issues, so keeping track is important.
Tips for Accurate Blood Pressure Readings
To get the most accurate blood pressure reading, here are a few tips to keep in mind:
- Take Multiple Readings: Take at least two or three readings, a minute or two apart, and average the results for the most accurate picture.
- Check at the Same Time Daily: Blood pressure can vary throughout the day, so try to check at the same time each day to get consistent readings.
- Avoid Caffeine and Smoking: Caffeine and smoking can temporarily raise your blood pressure, so it’s best to avoid them before taking a reading.
- Stay Relaxed: Stress can skew your results, so take a few deep breaths before measuring and try to stay calm.
How Often Should You Monitor Your Blood Pressure?
If you’re just starting out, it’s a good idea to monitor your blood pressure regularly, especially if you have any risk factors for hypertension, such as a family history of heart disease, being overweight, or leading a sedentary lifestyle.
For those who are healthy, checking once a month can be sufficient. However, if your doctor has recommended more frequent monitoring (for instance, daily or weekly), be sure to follow their advice to stay on top of your health.
Conclusion
Blood pressure monitoring doesn’t have to be complicated, and with the right equipment and techniques, it’s easy to do at home. By learning how to take accurate readings and understanding what your numbers mean, you can better manage your health and prevent complications down the road.
Whether you’re just starting out or looking to improve your blood pressure habits, this guide should give you a solid foundation. Keep your numbers in check, and don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional if you have concerns!
Appendices
FAQs
- How often should I check my blood pressure at home? It’s best to follow your healthcare provider’s advice. For most people, checking once or twice a week is a good starting point.
- Can my blood pressure vary throughout the day? Yes, it can. Factors like stress, exercise, and even time of day can affect your reading, so it’s important to check at consistent times.
- What should I do if my blood pressure is high? If your readings are consistently high, it’s essential to consult with a doctor. Lifestyle changes, medication, and dietary adjustments may be needed.
- Is it necessary to use a blood pressure cuff with a digital readout? While it’s not mandatory, digital cuffs are easier to use and give you accurate readings. Manual cuffs require more skill and practice.
- Does exercise affect my blood pressure readings? Yes, exercise can temporarily raise your blood pressure. Make sure to measure your blood pressure when you’re at rest.
References
- American Heart Association (2023). Understanding Blood Pressure Readings. Read Article
- National Institutes of Health (2024). Hypertension Management. Read Article
- Mayo Clinic (2024). How to Monitor Your Blood Pressure at Home. Read Article
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for general educational purposes only and is not a substitute for medical advice. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance on monitoring and managing your blood pressure.

Dr. Gwenna Aazee is a board-certified Internal Medicine Physician with a special focus on hypertension management, chronic disease prevention, and patient education. With years of experience in both clinical practice and medical writing, she’s passionate about turning evidence-based medicine into accessible, actionable advice. Through her work at Healthusias.com, Dr. Aazee empowers readers to take charge of their health with confidence and clarity. Off the clock, she enjoys deep dives into nutrition research, long walks with her rescue pup, and simplifying medical jargon one article at a time.