Acid Reflux and Chest Pain: Understanding the Link and Relief Strategies
If you’ve ever experienced chest pain and wondered whether acid reflux was to blame, you’re not alone. I still remember thinking, “This can’t be heartburn—it hurts too much.” But surprisingly, chest discomfort is one of the most common and confusing symptoms of acid reflux. And while it’s not usually dangerous, it definitely feels alarming. In this article, we’ll look at how acid reflux can cause chest pain, what it actually feels like, and what you can do to feel better fast.
How Acid Reflux Leads to Chest Pain

The Science Behind the Burn
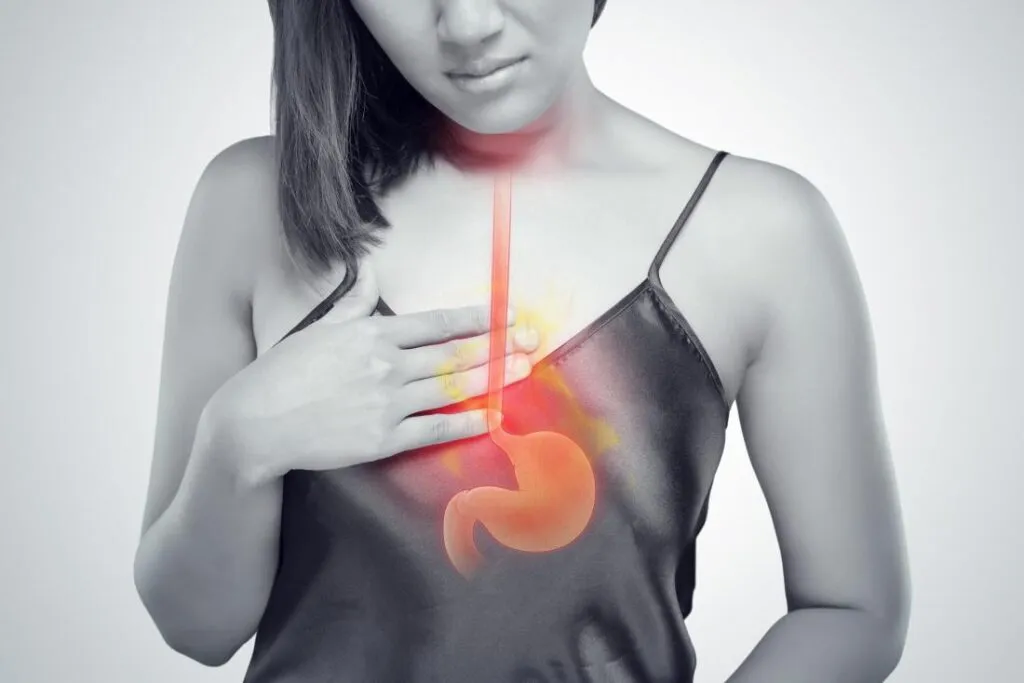
Acid reflux occurs when stomach acid escapes upward into your esophagus, irritating its lining. Unlike your stomach, the esophagus isn’t equipped to handle this acid. The resulting irritation can feel like burning, tightness, or pressure in the chest—often behind the breastbone.
Chest Pain and the LES
The lower esophageal sphincter (LES) is a ring of muscle that acts like a valve between your stomach and esophagus. When it weakens or relaxes at the wrong time, acid slips through, leading to reflux. Repeated exposure to acid is what causes the painful sensation in the chest.
Reflux Pain vs. Cardiac Pain
- Acid reflux pain often worsens after eating or lying down.
- It may improve with antacids or upright posture.
- It usually doesn’t radiate to the arms or jaw like heart pain might.
Still, any new or intense chest pain should always be checked by a healthcare provider to rule out heart-related causes first.
What Chest Pain from Reflux Feels Like
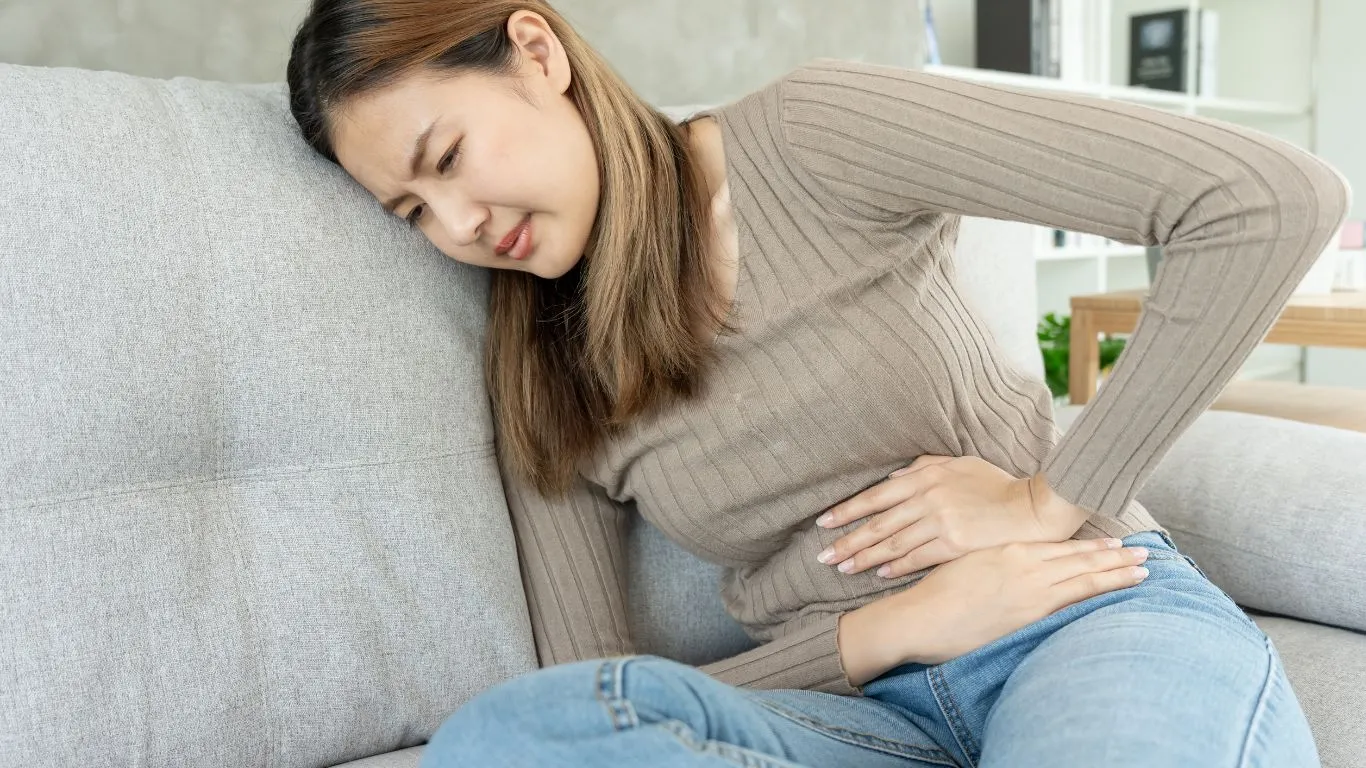

Real Symptoms, Real Frustration
From my own experience, reflux-related chest pain felt like a dull, nagging pressure that would sometimes flare into sharp burning. It was always worse at night or after eating something greasy. For others, the pain can range from mild discomfort to a sensation that feels like it’s squeezing your chest.
Other Symptoms That May Tag Along
In many cases, chest pain from acid reflux comes with other digestive symptoms:
- Regurgitation (a sour or bitter taste in your mouth)
- Burping or bloating
- A dry cough or hoarseness
- Feeling of food stuck in the throat
All of these are signals that your upper digestive system is under stress.
What Makes Reflux-Related Chest Pain Worse

Common Triggers You Might Overlook
Even small daily habits can make reflux—and the chest pain it causes—worse. These include:
- Overeating or eating too fast
- High-fat meals, spicy food, citrus, or caffeine
- Lying down right after meals
- Wearing tight clothing around your waist
For me, switching from three large meals to five small ones significantly reduced both reflux and chest tightness. I also made it a rule to stay upright for at least 2–3 hours after eating—and that helped a ton.
Effective Ways to Manage Chest Pain from Reflux

Natural Approaches That Work
- Elevate your upper body during sleep: Use a wedge pillow to keep acid down.
- Stay hydrated: Sip water slowly to flush acid back down.
- Chew sugar-free gum: It stimulates saliva and helps neutralize acid.
Medical Options That Help
If symptoms persist, you might need medications. These include:
- Antacids for fast, temporary relief
- H2 blockers like ranitidine (if available) or famotidine
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) like omeprazole for longer-term control
Talk to your doctor about the right option for you—especially if you’re using meds more than occasionally.
Understanding the Bigger Picture

When to Seek Further Help
If your chest pain happens more than twice a week, or it’s interfering with your sleep, appetite, or peace of mind, it’s time to get professional help. Long-term reflux can damage the esophagus and increase your risk of complications.
To better understand the root causes and long-term management of reflux-induced chest discomfort, explore our in-depth GERD chest pain article here.
Knowledge = Power (and Comfort)
Acid reflux may seem like a nuisance, but when it hits your chest, it can be incredibly disruptive and even frightening. The more you understand how reflux works, the more confident you’ll feel taking control of it. And trust me—once you learn your personal triggers and solutions, life gets a lot more comfortable.

Camellia Wulansari is a dedicated Medical Assistant at a local clinic and a passionate health writer at Healthusias.com. With years of hands-on experience in patient care and a deep interest in preventive medicine, she bridges the gap between clinical knowledge and accessible health information. Camellia specializes in writing about digestive health, chronic conditions like GERD and hypertension, respiratory issues, and autoimmune diseases, aiming to empower readers with practical, easy-to-understand insights. When she’s not assisting patients or writing, you’ll find her enjoying quiet mornings with coffee and a medical journal in hand—or jamming to her favorite metal band, Lamb of God.