Fish Oil’s Impact on Blood Pressure: Mechanisms and Benefits
Explore how fish oil’s omega-3s impact blood pressure. Learn mechanisms, scientific evidence, benefits, dosages, and lifestyle strategies for heart health.
Introduction to Fish Oil and Blood Pressure
The quest for optimal cardiovascular health has led researchers to explore various dietary interventions, and one compound that has captured considerable attention is fish oil. Derived from fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, fish oil is rich in omega-3 fatty acids – a group of polyunsaturated fats with a wide array of potential health benefits. In recent years, the focus has intensified on fish oil’s potential to impact blood pressure, a key determinant of cardiovascular well-being. In this comprehensive article, we embark on a journey to unravel the complexities of the fish oil-blood pressure nexus, delving into the mechanisms, evidence, and practical considerations.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: The Heart-Healthy Nutrients
To comprehend the fish oil-blood pressure relationship, it’s essential to grasp the foundational role of omega-3 fatty acids in cardiovascular health.
Exploring the Role of Omega-3s
Omega-3 fatty acids are bioactive compounds that exhibit a remarkable range of physiological effects. Beyond their structural role in cell membranes, they serve as precursors to potent lipid mediators known as eicosanoids. These molecules regulate inflammation, blood clotting, and vascular tone, all of which are intricately tied to blood pressure regulation. Notably, omega-3s promote the production of vasodilators like prostacyclin and nitric oxide, contributing to relaxed blood vessels and improved blood flow.
Types of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids come in three main forms: eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). While ALA is primarily found in plant sources like flaxseeds and walnuts, EPA and DHA are abundant in fatty fish. EPA and DHA, due to their more direct impact on blood pressure-related mechanisms, are the primary focus in the context of cardiovascular health.

Fish Oil’s Impact on Blood Pressure
The mechanisms through which fish oil influences blood pressure are intricate and multifaceted, underscoring the potential significance of its incorporation into cardiovascular care.
Mechanisms Behind Blood Pressure Regulation
Fish oil’s influence on blood pressure operates through a constellation of interconnected mechanisms. The most prominent of these is the enhancement of nitric oxide (NO) production. Nitric oxide acts as a vasodilator, relaxing the smooth muscles of blood vessels and thereby reducing resistance to blood flow. Additionally, omega-3s exert anti-inflammatory effects by modulating immune responses and reducing cytokine production, which can contribute to endothelial dysfunction and high blood pressure.
Does Fish Oil Lower Blood Pressure?
The culmination of research findings suggests that fish oil has the potential to modestly lower blood pressure. Numerous clinical trials and observational studies have investigated this phenomenon, often observing decreases in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure following fish oil supplementation. Notably, a meta-analysis of multiple studies reported significant reductions in blood pressure, particularly among individuals with elevated levels.

Scientific Evidence and Studies
The scientific exploration of fish oil’s impact on blood pressure has traversed a trajectory from curiosity to established knowledge.
Reviewing Clinical Research
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs), considered the gold standard in scientific research, have been instrumental in elucidating fish oil’s effects on blood pressure. These trials, conducted across diverse populations and varying dosages, collectively affirm the potential of fish oil to contribute to blood pressure management.
Examining Blood Pressure Outcomes
Meta-analyses, which aggregate data from multiple studies, provide a panoramic view of fish oil’s impact on blood pressure. A meta-analysis published in the American Journal of Hypertension concluded that omega-3 supplementation significantly reduced both systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Notably, the magnitude of reduction was more pronounced among individuals with hypertension.

Benefits of Fish Oil for Hypertension
The benefits of fish oil extend beyond its effects on blood pressure numbers, encompassing a spectrum of cardiovascular advantages.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of many cardiovascular conditions, including hypertension. Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, exhibit potent anti-inflammatory actions by influencing immune responses, cellular signaling pathways, and gene expression. This anti-inflammatory milieu contributes to improved endothelial function and reduced oxidative stress, ultimately promoting healthy blood pressure levels.
Promoting Arterial Health
Arterial stiffness, a common consequence of aging and hypertension, contributes to elevated blood pressure. Fish oil’s ability to enhance arterial elasticity and reduce stiffness is a pivotal mechanism in its blood pressure-lowering effects. By supporting optimal arterial function, fish oil contributes to efficient blood circulation and pressure regulation.

Optimal Dosage and Usage
Determining the optimal dosage of fish oil for blood pressure benefits involves a nuanced understanding of various factors.
Recommended Fish Oil Intake
Health organizations, including the American Heart Association, generally recommend a daily intake of 250-500 milligrams of combined EPA and DHA for cardiovascular support. However, evidence suggests that higher doses in the range of 1000-3000 milligrams per day may be more effective in producing noticeable blood pressure reductions.
Incorporating Fish Oil into Your Routine
Before embarking on a fish oil regimen, it is prudent to seek guidance from a qualified healthcare professional. Factors such as individual health status, current medications, and specific cardiovascular goals play a crucial role in determining the appropriate dosage and formulation.

Consulting Your Healthcare Professional
The integration of fish oil into a blood pressure management strategy should be under the supervision of a healthcare provider.
Seeking Expert Advice
Given the personalized nature of healthcare, consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is essential. A healthcare provider can assess your medical history, existing conditions, and potential interactions to provide tailored recommendations.
Personalized Recommendations
A healthcare professional’s expertise enables the formulation of a personalized approach to fish oil supplementation. This includes selecting the appropriate dosage, considering potential interactions, and monitoring for any adverse effects.

Potential Considerations and Interactions
While fish oil offers an array of benefits, it’s prudent to be mindful of potential considerations and interactions.
Addressing Concerns and Risks
Fish oil is generally considered safe when taken within recommended dosages. However, excessive consumption can lead to gastrointestinal discomfort, increased bleeding tendencies, and impaired immune function. Adhering to recommended dosages and seeking guidance from a healthcare professional is crucial.
Interactions with Medications
Fish oil’s anticoagulant properties, while beneficial for cardiovascular health, can interact with certain medications. Individuals taking blood-thinning medications, such as aspirin or warfarin, should coordinate with their healthcare provider to minimize the risk of excessive bleeding.

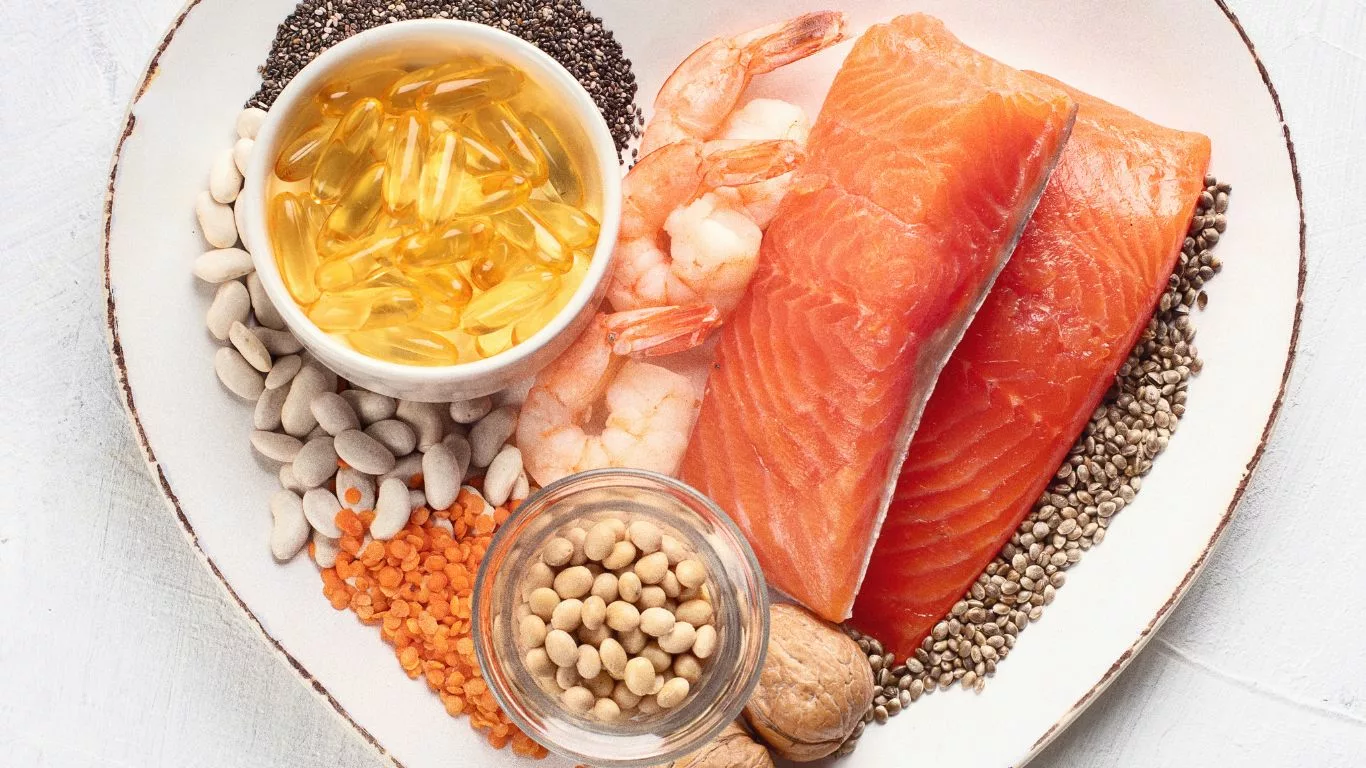
Choosing the Right Fish Oil Supplements
The selection of high-quality fish oil supplements is pivotal for achieving desired outcomes.
Selecting Quality Products
The supplement market is diverse, and product quality can vary significantly. Opt for fish oil supplements that have undergone third-party testing for purity, potency, and absence of contaminants such as heavy metals and pollutants.
Reading Labels Effectively
Careful scrutiny of supplement labels is essential. Look for products that specify the EPA and DHA content per serving, as well as the ratio of EPA to DHA. Additionally, ensure that the supplement is sourced from reputable and sustainable fisheries.

Lifestyle Modifications for Blood Pressure Management
Fish oil supplementation can be further complemented by a holistic lifestyle approach to blood pressure management.
Complementary Dietary Changes
A heart-healthy diet characterized by abundant fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats synergizes with fish oil’s benefits. Reduced sodium intake, often achieved through mindful food choices, further contributes to blood pressure control.
Exercise and Stress Reduction
Physical activity is a cornerstone of cardiovascular health. Engaging in regular aerobic and resistance exercises enhances heart function, reduces blood pressure, and promotes overall well-being. Stress reduction techniques, such as mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing, can further contribute to blood pressure management.

Incorporating Fish Oil into a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
Sustaining the benefits of fish oil requires integration into a broader heart-healthy lifestyle.
Cooking with Omega-3-Rich Foods
In addition to supplements, whole food sources of omega-3s can play a pivotal role. Fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and herring, are not only delicious but also offer a natural source of EPA and DHA.
Long-Term Strategies for Blood Pressure
Achieving lasting blood pressure benefits necessitates a long-term commitment to cardiovascular health. Consistency in fish oil supplementation, dietary choices, exercise routines, stress management practices, and regular medical check-ups collectively contribute to a comprehensive blood pressure management strategy.
Conclusion: Fish Oil and Blood Pressure
The marriage of science and nature is evident in the evolving understanding of fish oil’s influence on blood pressure. From its fundamental role in enhancing nitric oxide production to its multifaceted interactions with inflammation and arterial function, fish oil emerges as a multifunctional ally in the quest for cardiovascular well-being.
While the pursuit of definitive answers continues, the current body of evidence suggests that fish oil, particularly its omega-3 fatty acids, holds promise as an adjunctive strategy for blood pressure management. As you navigate the realm of cardiovascular health, armed with insights from scientific research and guided by healthcare professionals, consider fish oil an empowering tool in your journey toward optimal blood pressure and overall vitality.

Appendices
References
- Mozaffarian D, Wu JHY. (2011). Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease: Effects on Risk Factors, Molecular Pathways, and Clinical Events. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 58(20), 2047-2067. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22051327/
- Miller PE, Van Elswyk M, Alexander DD. (2014). Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid and Blood Pressure: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. American Journal of Hypertension, 27(7), 885-896. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24610882/
- Calder PC. (2015). Marine omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: Effects, mechanisms and clinical relevance. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids, 1851(4), 469-484. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1388198114001656
FAQs
Q1: What are omega-3 fatty acids? A: Omega-3s are essential fats that support cardiovascular health by influencing inflammation and blood vessel function.
Q2: How does fish oil impact blood pressure? A: Fish oil’s omega-3s promote vasodilation and reduced inflammation, contributing to improved blood pressure levels.
Q3: Can fish oil replace blood pressure medication? A: Fish oil may complement blood pressure management, but consultation with a healthcare provider is crucial.
Q4: What’s the recommended fish oil dosage? A: Health organizations advise 250-500mg EPA and DHA daily, but higher doses may be effective for blood pressure benefits.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical advice and should not replace professional consultation. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before making dietary or supplementation changes, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications. The authors and publisher are not responsible for any consequences that arise from the use of the information in this article.

Camellia Wulansari is a dedicated Medical Assistant at a local clinic and a passionate health writer at Healthusias.com. With years of hands-on experience in patient care and a deep interest in preventive medicine, she bridges the gap between clinical knowledge and accessible health information. Camellia specializes in writing about digestive health, chronic conditions like GERD and hypertension, respiratory issues, and autoimmune diseases, aiming to empower readers with practical, easy-to-understand insights. When she’s not assisting patients or writing, you’ll find her enjoying quiet mornings with coffee and a medical journal in hand—or jamming to her favorite metal band, Lamb of God.